Table of Contents
The mobile development landscape in 2025 demands a framework that balances technical excellence with business efficiency. React Native has emerged as the definitive answer to this challenge, transforming app development from a costly, platform-fragmented endeavor into a streamlined, unified process that delivers native-quality applications at unprecedented speed and scale.
For technical teams and business decision-makers alike, understanding React Native’s architectural innovations, performance characteristics, and ecosystem maturity is crucial for making informed technology choices. This comprehensive analysis explores why React Native has become the framework of choice for companies ranging from Meta and Microsoft to thousands of startups building the next generation of mobile experiences.
Whether you’re architecting a new mobile platform, migrating from native development, or evaluating cross-platform frameworks, this deep dive into React Native’s technical foundation and business value will provide the insights needed to make strategic app development decisions.
The Technical Revolution: React Native’s New Architecture
Understanding the Architectural Transformation
React Native’s evolution from its original architecture to the New Architecture represents a fundamental reimagining of how JavaScript-based frameworks interact with native platforms. This transformation addresses the core limitations that previously constrained cross-platform development.
The Legacy Bridge Architecture
The original React Native architecture relied on an asynchronous bridge for JavaScript-native communication. This bridge serialized data between JavaScript and native code (Java/Objective-C), processing messages in a fundamentally asynchronous manner. While revolutionary for its time, this approach introduced performance bottlenecks in scenarios requiring high-frequency updates or real-time interactions.
The New Architecture: JSI, TurboModules, and Fabric
The React Native team began redesigning the core architecture in 2018, with the New Architecture reaching production readiness in 2024 and seeing widespread adoption throughout 2025.
The New Architecture comprises three foundational pillars:
1. JavaScript Interface (JSI)
JSI eliminates the asynchronous bridge bottleneck by enabling direct synchronous communication between JavaScript and native code. TurboModules leverage the JavaScript Interface (JSI) to improve how JavaScript communicates with native modules, addressing the inefficiencies of the old architecture and offering better performance, modularity, and ease of use.
This architectural shift enables:
- Zero-copy data transfer between JavaScript and native layers
- Synchronous native method invocation when required
- Direct access to native memory without serialization overhead
- Multi-threaded JavaScript execution for compute-intensive operations
2. TurboModules
TurboModules represent the reimagined native module system, leveraging JSI to enable direct, synchronous communication between JavaScript and native code without the serialization overhead of the legacy bridge.
Key technical advantages include:
- Lazy loading: Modules load only when needed, reducing startup time
- Type safety: Automatic type checking between JavaScript and native code
- Platform code sharing: C++ implementations can be shared across iOS and Android
- Performance optimization: Direct invocation eliminates bridge serialization overhead
3. Fabric Renderer
Fabric is the new rendering system that replaces the legacy UI Manager. It operates directly with the host platform’s UI thread, enabling:
- Synchronous layout calculations for immediate UI updates
- Improved priority management for rendering operations
- Better handling of concurrent React features, including Suspense and Transitions
- Reduced memory footprint through more efficient component management
Performance Implications at Scale
Meta’s internal benchmarking showed startup time improvements of approximately 500ms on a TV emulator and 900ms on a Fire HD tablet when switching from the legacy architecture to the new one, with improvements particularly pronounced on lower-end devices.
For production applications, this translates to:
- Faster time-to-interactive across device tiers
- Smoother animations, maintaining 60fps consistently
- Reduced memory consumption during complex operations
- Better responsiveness under heavy user interaction
React Native aims to achieve at least 60 frames per second and provide a native look and feel, with optimizations handled automatically whenever feasible.
Why React Native Delivers Business Value for App Development
Strategic Advantages in Cross-Platform Development
React native app development fundamentally changes the economics and timeline of mobile application delivery. The strategic advantages extend far beyond simple cost reduction into competitive positioning and organizational efficiency.
Unified Development Velocity
Traditional native development requires maintaining separate iOS and Android codebases, teams, and knowledge bases. This separation creates inherent friction:
- Feature parity requires duplicated implementation effort
- Bug fixes must be diagnosed and resolved independently per platform
- Platform divergence increases over time without careful coordination
- Team scaling requires finding specialized talent for each platform
React Native eliminates this friction through its shared codebase architecture. Development teams write features once, deploy across platforms, and maintain a single source of truth for business logic. This unification accelerates every aspect of the development lifecycle.
Time-to-Market Compression
Market timing often determines success in competitive categories. React Native’s efficiency advantages compress development timelines by 30-40%, enabling:
- Faster MVP validation: Test product-market fit months earlier
- Rapid competitive response: Deploy features while competitors plan separate implementations
- Agile iteration cycles: Incorporate user feedback across platforms simultaneously
- Reduced release complexity: Coordinate single release cycles instead of platform-specific timelines
Resource Optimization Through Technical Efficiency
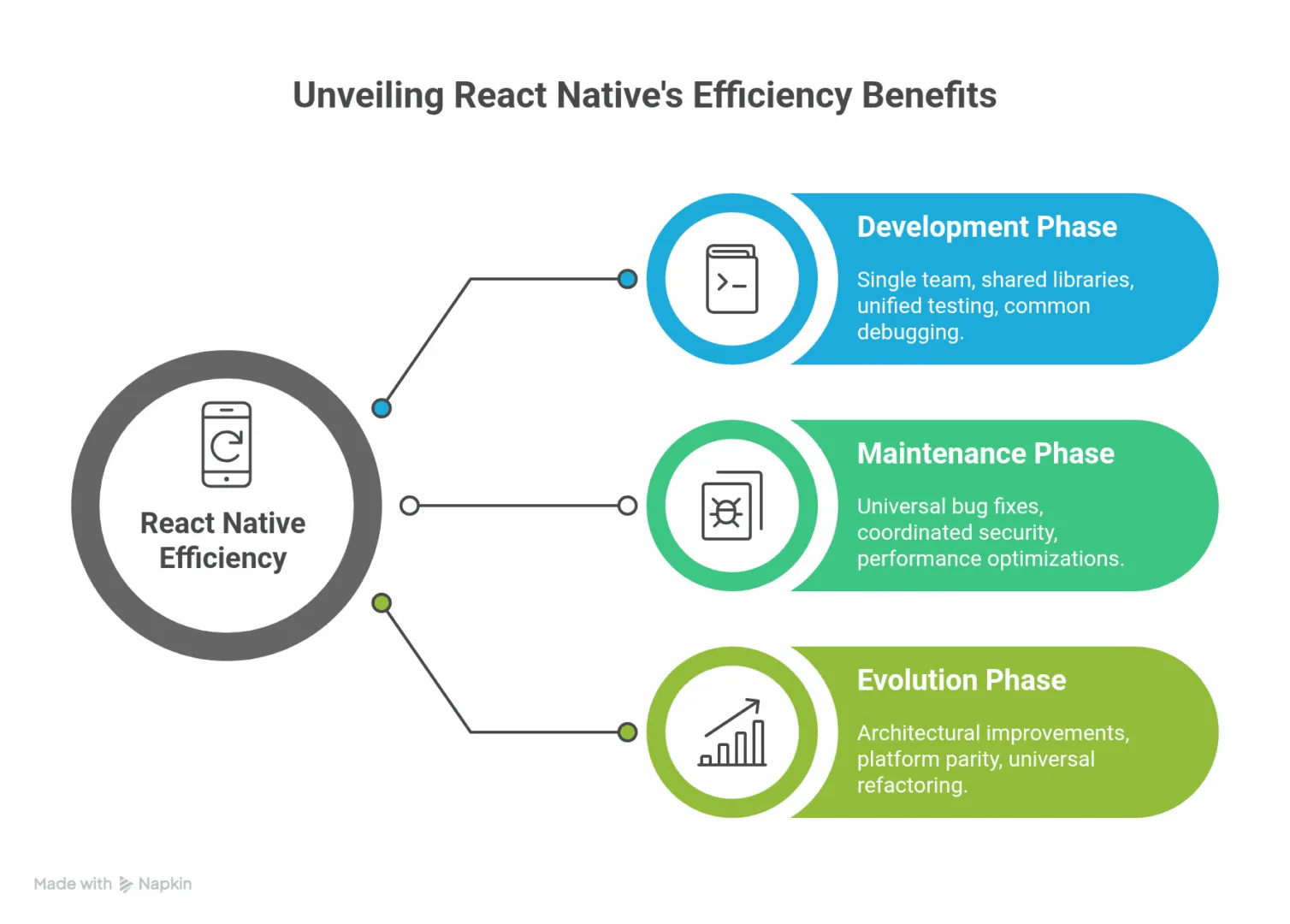
The efficiency gains in react native mobile app development compound across the application lifecycle:
Development Phase:
- Single team maintains expertise across iOS and Android
- Shared component libraries reduce redundant implementation
- The unified testing strategy covers both platforms simultaneously
- Common debugging workflows accelerate issue resolution
Maintenance Phase:
- Bug fixes deploy universally from a single implementation
- Security patches apply across platforms in coordinated releases
- Performance optimizations benefit the entire user base
- Technical debt accumulates in one codebase instead of two
Evolution Phase:
- Architectural improvements enhance both platforms
- New features launch with platform parity guaranteed
- Refactoring efforts yield universal benefits
- Technology upgrades happen once instead of twice
Technical Deep Dive: Architecture and Performance
Rendering Pipeline and Performance Characteristics
Understanding React Native’s rendering pipeline clarifies its performance profile and helps technical teams optimize applications effectively.
Component Rendering Flow
In the New Architecture, rendering flows through several optimized stages:
- JavaScript Layer: React components describe UI state
- Fabric Renderer: Translates React elements to native UI operations
- Shadow Tree: Calculates layout using Yoga layout engine
- Native UI Layer: Renders platform-native components
This pipeline maintains separation of concerns while enabling synchronous communication when performance demands it. The key innovation is that layout calculations and UI updates can happen synchronously when needed, eliminating the animation jank that plagued earlier implementations.
Memory Management
React Native’s New Architecture improves memory efficiency through:
- Smart component lifecycle management: Aggressive unmounting of off-screen components
- Optimized bridge elimination: Reduced serialization overhead
- Native resource pooling: Reuse of native components where possible
- Garbage collection optimization: Coordinated with native memory management
Thread Management
The New Architecture coordinates work across multiple threads efficiently:
- JavaScript Thread: Executes business logic and React rendering
- UI Thread: Handles native UI updates and animations
- Background Threads: Process network requests, image decoding, and heavy computations
JSI opens doors for features like multi-threaded JavaScript execution and custom native integrations, enabling parallel processing that was impossible in the legacy architecture.
State Management at Scale
Enterprise applications require sophisticated state management strategies. React Native’s ecosystem provides multiple approaches suited to different complexity levels.
Built-in State Management
React’s Context API and hooks (useState, useReducer, useMemo) handle straightforward state requirements without additional dependencies. For many business applications, these built-in mechanisms provide sufficient capability with minimal complexity.
Redux and Middleware Patterns
Redux remains prevalent in React Native applications, requiring:
- Predictable state updates through unidirectional data flow
- Time-travel debugging for complex issue diagnosis
- Middleware integration for logging, analytics, and side effects
- State persistence for offline-first applications
Modern State Solutions
Newer libraries like Zustand, Jotai, and Recoil offer alternatives with reduced boilerplate while maintaining type safety and developer experience. These solutions often integrate more naturally with React’s concurrent features.
Server State Management
React Query and SWR specialize in managing server state data fetched from APIs with built-in caching, background refetching, and optimistic updates. Separating server state from application state reduces complexity in data-intensive applications.
Navigation and Routing Architecture
Navigation represents a critical architectural decision in react native app development. The ecosystem has converged around React Navigation as the standard solution, offering:
Native Navigation Feel
Platform-specific navigation patterns (stack navigation on iOS, material navigation on Android) implemented through native components, ensuring users experience familiar navigation paradigms.
Deep Linking Support
Built-in deep linking enables external navigation into specific application screens, critical for marketing campaigns, push notifications, and inter-app communication.
State Persistence
Navigation state can persist across app restarts, maintaining user context and improving the experience in multitasking scenarios.
Performance Optimization
Lazy loading of screens, predictive preloading of likely destinations, and native transitions ensure navigation remains fluid even in complex applications.
When to Choose React Native: Use Case Analysis
Optimal Application Categories
React Native’s ecosystem provides mature libraries to support these needs while maintaining strong device security standards.
Business and Enterprise Applications:
Internal tools, CRM systems, field service applications, and workforce management platforms benefit from rapid development and maintenance efficiency. These applications prioritize functionality over cutting-edge graphics.
E-Commerce and Retail:
Shopping applications require consistent experiences, payment integration, and rapid feature testing. React Native’s ecosystem provides mature libraries for these needs.
Social and Content Platforms:
Applications focused on content consumption and social interaction leverage React Native’s efficiency for rapid iteration based on engagement data.
Productivity and Collaboration Tools:
Task management, document collaboration, and communication platforms benefit from sharing business logic while providing platform-appropriate interfaces.
On-Demand Services:
Food delivery, transportation, and marketplace applications require rapid development and frequent updates to remain competitive.
Real-World Success Stories
Major Platform Implementations
Instagram:
The photo-sharing platform integrated React Native to accelerate feature development. Adoption resulted in up to 40% faster load times, delivering an improved user experience through component-based architecture.
Microsoft Office Suite:
Microsoft’s decision to use React Native across Office, Xbox, and other products validates the framework’s enterprise-grade capabilities.
Walmart:
The retail giant achieved 95% code sharing while maintaining performance for millions of users, demonstrating React Native’s scalability.
Shopify:
The e-commerce platform serves millions of merchants worldwide through its React Native application, proving the framework’s capability in complex business applications.
Conclusion
React Native has evolved into a technically robust framework that delivers native-quality apps with unmatched efficiency. With 70–90% code reusability, faster delivery, and reduced maintenance, it transforms development economics, enabling quicker time-to-market and greater agility.
Backed by large-scale adoption and powered by innovations like JSI, TurboModules, and Fabric, React Native strikes the ideal balance between performance, cost savings, and speed, making it the pragmatic choice for modern app development.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. React Native suitable for complex enterprise applications?
Yes, major companies like Microsoft, Walmart, and Bloomberg use React Native for complex enterprise applications, demonstrating its capability at scale with demanding requirements.
Q2. How does React Native compare to Flutter?
Both frameworks offer cross-platform capabilities, but React Native uses JavaScript (broader developer pool) and true native components, while Flutter uses Dart and its own rendering engine. React Native benefits from a larger ecosystem and easier web code sharing.
Q3. Can React Native apps access all device features?
React Native provides access to most device features through core modules and community libraries. For specialized functionality, custom native modules can be created.
Q4. What’s the maintenance cost of React Native apps?
Budget approximately 20% of initial development costs annually for updates, bug fixes, and improvements, significantly less than maintaining separate native codebases.
Q5. How long does React Native app development take?
Simple apps: 2-4 months, Medium complexity: 3-6 months, Complex apps: 6-12 months. This is 30-40% faster than developing separate native applications.
Q6. Will React Native limit app performance?
For most business applications (social, e-commerce, productivity, content), React Native performance matches native apps. Only graphics-intensive applications like 3D games might benefit from pure native development.
Q7. Can we migrate existing native apps to React Native?
Yes, React Native supports gradual migration, allowing you to integrate it into existing native apps and progressively move features to the shared codebase.
Q8. What’s the talent availability for React Native developers?
React Native developers are widely available due to JavaScript’s popularity. The large talent pool helps control costs and simplifies hiring compared to platform-specific developers.