Table of Contents
Currently, AI systems have a major contribution to enhancing business processes, customer experience, and assessment. Nevertheless, not every AI system is equal. Various types of AI exist, with each characterized by its ability, autonomy, and functionality. Businesses need to understand the types of AI in order to leverage its potential.
This overview examines the various kinds of AI and how they play a role in innovation and effectiveness. Whether your goal is to implement AI into your company or learn more about this technology, learning the details of AI is the beginning step toward effective use.
Artificial Intelligence is an intelligent entity created by humans and can make intelligent decisions or accurate predictions through algorithms within a specifically given and defined problem domain.
Three Phases in AI
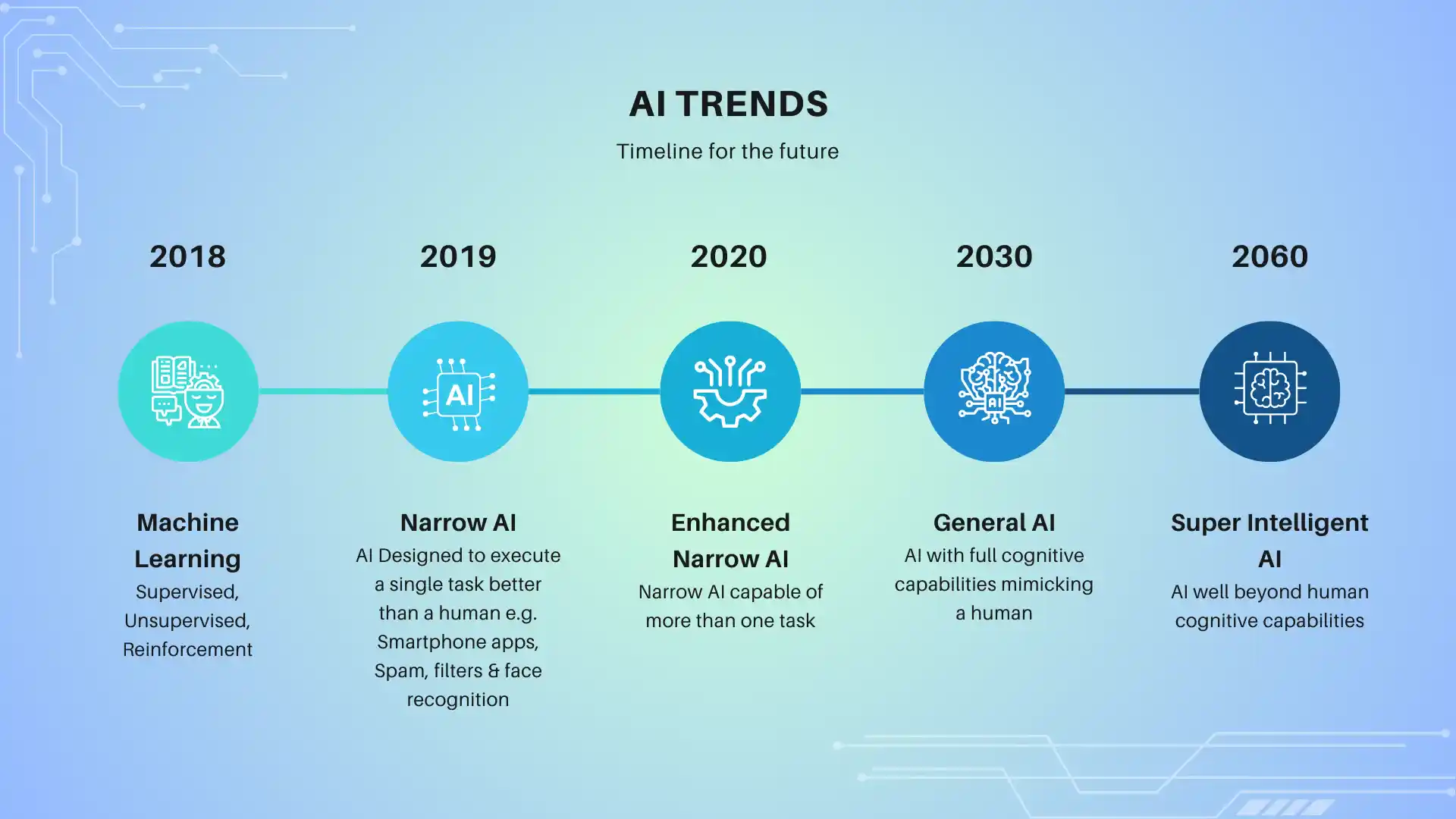
Generally, AI is divided broadly into three phases: Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI) – Narrow AI & Enhanced Narrow AI, Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), and Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI).
Presently, we are in the age of Enhanced Narrow AI. As reported in recent issues of the Superhuman AI newsletter, this current phase is characterized by specialized AI systems that excel at specific tasks but still lack general intelligence capabilities.
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI) is computer programming AI specifically trained and designed to perform a single, narrow task or a related set of tasks. This is the most widespread form of AI in use today.
Capabilities:
- Task-specific intelligence with specialized performance in a single area
- Incapable of performing tasks beyond its pre-designed purpose.
- Extremely effective at solving particular problems within its domain.
Real-Time Examples:
- Voice Assistants (Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant): These are created to accomplish specific functions like answering questions, managing smart devices, and playing music. They do not carry their functions outside of their predefined boundaries.
- Spam Filters: Email services utilize ANI in order to automatically sort and eliminate spam emails by predefined parameters.
- Image Recognition Software: Google Photos or face recognition systems in airports utilize ANI to recognize given images or individuals.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is machines that can have the capacity to know, learn, and execute intelligence across a wide variety of tasks, much like human cognitive functions. AGI can do any intellectual task that a human can.
Capabilities:
- Ability to generalize knowledge in many fields.
- Capable of learning and adapting easily without requiring retraining for various tasks.
- Reasoning, decision-making, and problem-solving capabilities are high.
Real-Time Examples: AGI remains theoretical, and we don’t yet have systems with real general intelligence. Nevertheless, there are research projects targeting the creation of AGI, and it is the future direction in AI development.
Artificial Super intelligence (ASI)
Artificial Superintelligence (ASI) is AI that is smarter than human intelligence in all domains, such as creativity, decision-making, problem-solving, and social intelligence. It is extremely high-end, futuristic AI.
Capabilities:
- Exceeds human mental capabilities in every way, both creative and emotional intelligence.
- Would be able to solve intricate world issues and develop innovations beyond human comprehension.
- May be able to lead to self-development and exponential intelligence growth.
Real-Time Examples: ASI is entirely speculative for now. It is still an idea frequently referenced when talking about AI safety and ethics but remains unachieved.
Types Of AI
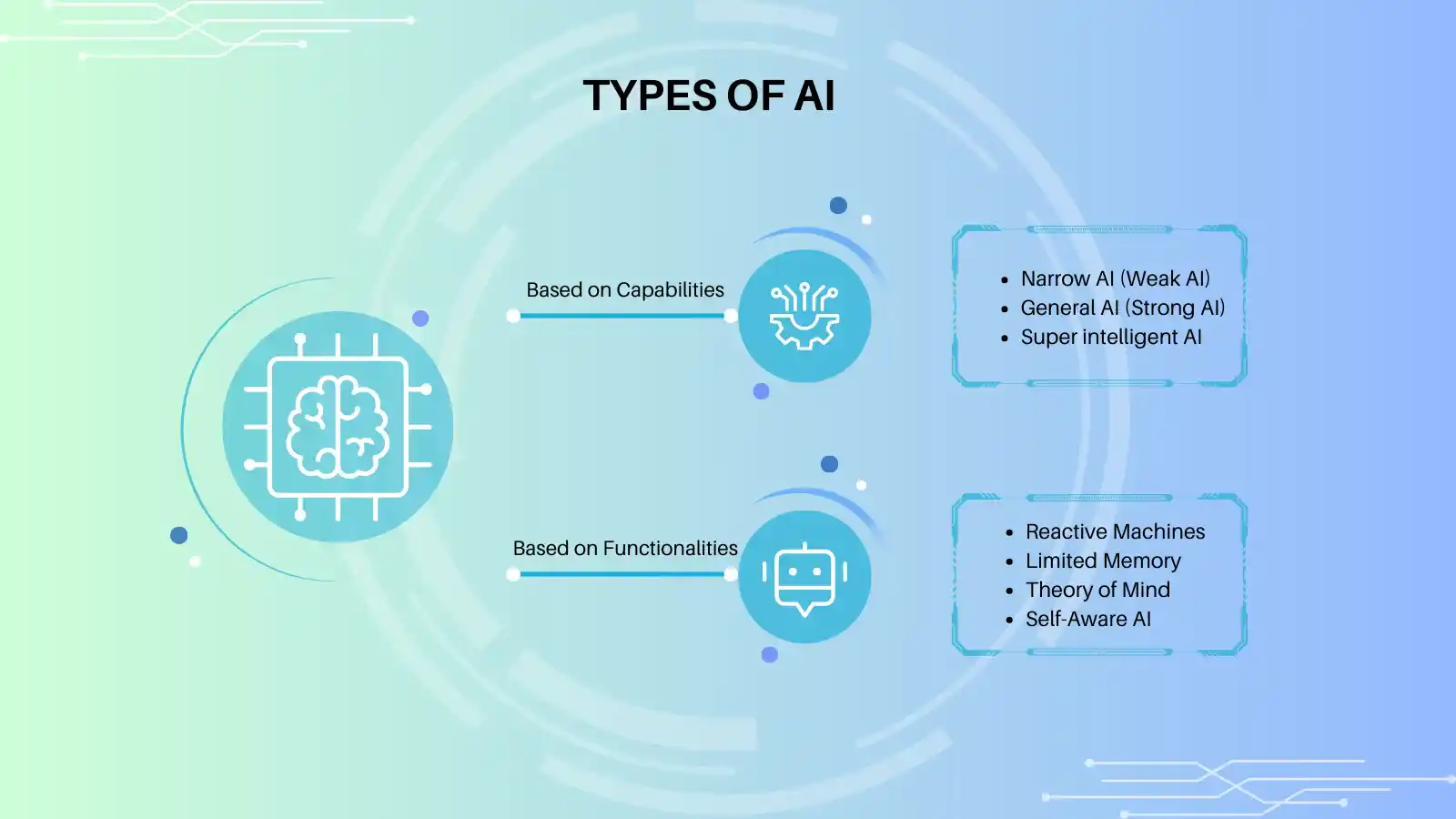
AI can be categorized into different types according to its function, ability, and application. The main types of AI are described below:
Types of AI: Based on Capabilities
This is a classification of AI systems in terms of how advanced and proficient an AI system is with respect to cognitive capacities and task performance. The principal categories are:
Narrow AI (Weak AI)
Narrow AI are specially designed and trained AI systems for performing one or a small set of tasks. Narrow AI systems are highly specialized and cannot perform tasks outside of their assigned purpose.
Capabilities:
- Task-specific capabilities (e.g., image identification, language translation, etc.)
- Cannot learn or execute tasks other than its purpose.
Real-Time Examples:
- Voice Assistants: Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant—these can execute commands in response to specific voice requests but cannot understand or execute activities outside their planned area.
- Recommendation Systems: Netflix and Amazon’s recommendation system employs narrow AI to recommend films or products as per user input.
- Self-driving Cars: Autonomous cars using AI are able to drive and obey traffic laws but cannot do tasks that are unrelated, such as playing music, without a human input.
General AI (Strong AI)
General AI involves machines that have the capacity to learn, comprehend, and exercise intelligence in a wide variety of tasks, much like human intellect. It could accomplish any mental task that an individual human could.
Capabilities:
- Can be adapted to new tasks.
- Able to learn in different fields without special training for each task.
- Reasoning, problem-solving, and abstract thinking in a variety of domains.
Real-Time Examples: General AI exists only in theory and has yet to be achieved, but it would be similar to a highly autonomous AI able to perform a variety of tasks like a human.
Superintelligent AI
Superintelligent AI would be greater than human intelligence in every area, from creativity and problem-solving to social intelligence. It may be able to surpass humans in nearly every aspect of cognitive ability.
Capabilities:
- Higher-level intelligence beyond human capacity.
- Able to think, reason, and solve problems far beyond the best human minds.
- Able to possibly solve difficult global problems or issues that humans cannot.
Real-Time Examples: Superintelligent AI is not yet developed and is still a topic of debate in the discussion of AI safety and ethics, but it is real.
Types of AI: Based on Functionalities
This categorization sorts AI by how complex it is and how well it can execute tasks through memory, interaction, and learning.
Reactive Machines
These type of AI systems are programmed to react to certain stimuli or inputs with pre-defined responses. They have no memory and cannot apply past experiences to inform future choices.
Capabilities:
- Straightforward, simple response to immediate inputs.
- Cannot learn or remember previous data.
- No decision-making based on previous interactions.
Real-Time Examples:
- IBM’s Deep Blue: The computer that played chess against Garry Kasparov. It reacted to the present board position but did not remember games or evolve strategies from experience.
- Basic AI Chatbots: Basic chatbots that have limited ability to answer particular questions with pre-programmed responses, without learning from past conversations.
Limited Memory
These types of AI can draw on past experiences or historical data to make decisions, but the memory is limited. They can apply past inputs to modify behavior in the short term but do not have long-term memories.
Capabilities:
- Can draw on past data to shape future decisions.
- Limited capacity to make adjustments or improvements over time.
Real-Time Examples:
- Self-driving Cars: These cars employ historical data (e.g., road conditions, traffic flow) to make navigation decisions in real time, but do not store long-term memories of previous journeys.
- Recommendation Systems: Web services like YouTube or Amazon employ previous interactions to suggest videos, goods, or services based on previous activity.
Theory of Mind
It is a higher level of AI that would be able to comprehend human emotions, intentions, and beliefs. It would be capable of interacting with humans in a more human-fashion by being able to grasp how others feel and think.
Capabilities:
- Able to comprehend and anticipate human emotional reactions.
- Interacts with humans on a more empathetic, intuitive level.
- Could have more natural, dynamic interactions.
Real-Time Examples: Theory of Mind AI is currently still in the process of being developed, but robotics and natural language processing developments are headed in the direction of developing machines that can actually sense human feelings and intentions, e.g., healthcare emotion-sensing robots.
Self-Aware AI
This is the most sophisticated type of AI that would have self-awareness, i.e., it would be aware of its own existence and might have subjective experiences, thoughts, and feelings.
Capabilities:
- Self-awareness and knowledge of its own state.
- Capacity to make decisions based on self-awareness and knowledge of its own capabilities.
- Ability to make complex decisions, ethical judgments, and be creative.
Real-Time Examples: AI that is self-aware exists in theory but not in practice yet, and it is something spoken about in the realm of AI ethics and future machine consciousness.
Practical Applications of different types of AI Technologies
Machine Learning
Machine Learning (ML) is one of the types of AI, which specializes in creating algorithms for computers to learn from data and make decisions accordingly. Unlike being specifically coded to do something, ML models discover patterns within data and use the patterns to predict future values or categorize data.
Real-time Examples:
- Financial Services: Banks and financial institutions use machine learning algorithms to identify real-time fraudulent activities. Firms such as Signifyd leverage AI to deliver end-to-end commerce protection.
- Email Spam Filtering: Email providers use machine learning algorithms to block spam and phishing messages.
Deep Learning
Deep Learning is a specific area of Machine Learning that utilizes artificial neural networks with many layers to represent complicated patterns in data. This method has been instrumental in making dramatic breakthroughs in fields like image and speech recognition.
Real-time Examples:
- Healthcare Diagnostics:Deep learning models scan medical images, including X-rays and MRIs, to identify abnormalities such as tumors or fractures. IBM Watson Health use deep learning models to scan medical images
- Autonomous Vehicles: Autonomous vehicles take advantage of deep learning algorithms that analyze sensor data and camera observations to make navigation and obstacle-evading decisions in real-time. Waymo and Tesla are currently leading the industry in incorporating deep learning into autonomous driving systems.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is the type of AI that is concerned with the interaction between computers and human language. It makes it possible for machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language in a meaningful and useful way. NLP integrates computational linguistics with machine learning and deep learning algorithms to process linguistic data.
Real-time Examples:
- Virtual Assistants: Virtual Assistants: Virtual assistants based on AI, like Amazon’s Alexa, Apple’s Siri and Google Assistant, use NLP to interpret and respond to commands in real-time. Virtual assistants can carry out tasks from reminders to operating smart home devices, making the user’s life more convenient.
- Language Translation: Google Translate and other applications use NLP to translate spoken or written language instantaneously, making communication between languages possible effortlessly. The real-time translation feature is a godsend for tourists and multilingual partnerships.
Computer Vision
Computer Vision is the type of AI that allows machines to analyze and process visual data from the world, replicating the sense of sight in humans. It is the process of acquiring, analyzing, and interpreting images and videos to create numerical or symbolic data.
Real-time Examples:
- Facial Recognition: Facial recognition is carried out by computer vision in security systems used in airports and other secure locations to identify people in real-time to augment security. It is also used in personal devices to authenticate users. Security systems built by companies such as SenseTime and Face++ employ computer vision to conduct facial recognition
- Retail Automation: Computer vision systems are being used by stores to track stock levels and observe customer behavior. Retailers like Amazon Go use computer vision systems to track inventory levels.
Robotics
Robotics is a type of AI which is a multidisciplinary area that combines AI to create, build, control, and use robots. Robots are capable of executing tasks autonomously or semi-autonomously, usually mimicking human movements.
Real-time Examples:
Autonomous Drones: Technology companies such as DJI Innovations produce drones with AI capacity utilized in farming to observe plant health and logistics to make parcel deliveries. Such drones have the ability to maneuver and conduct their activities autonomously, making live decisions about the surroundings.
Industrial Automation: Large manufacturing companies like Siemens and Bosch use robots in their factories to carry out intricate assembly operations with precision and speed. AI allows these robots to learn new tasks and work together with human laborers without causing any harm, boosting productivity and efficiency.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence (AI) integrates several techniques—like Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Natural Language Processing, Computer Vision, and Robotics—that have drastically impacted many industries. These technologies allow systems to learn from information, analyze intricate patterns, and execute tasks conventionally demanding human intelligence. Their combination has resulted in improvements such as real-time fraud detection, virtual assistants, and automatic quality control.
As AI continues to advance, solving issues such as data privacy and ethics is still paramount. Continued collaboration between academia, industry, and policymakers is needed to unlock the potential of AI responsibly and fairly.