Table of Contents
Introduction to Automated Market Makers (AMMs)
Automated Market Makers are critical players in a fast-changing decentralized finance, revolutionizing the trading of digital assets. It’s a new peer-to-peer financial system based on the blockchain and cryptocurrencies; an innovation aimed at avoiding intermediaries and centralized entities within the transaction of money and funds. DeFi lowers costs, also with a faster rate for the transaction, making direct interaction between users an exciting choice to conventional systems.
At the center of this system, Automated Market Makers enable permissionless and seamless exchanges through algorithmic mechanisms rather than traditional buyer-seller interactions. Through the use of liquidity pools, Automated Market Makers make trading much easier by giving traders the necessary liquidity to conduct their trades efficiently. Assets are contributed to these pools, where constant mathematical formulas are used to determine the prices of tokens, hence driving liquidity and market stability.
It’s the market wherein swapping cryptocurrencies occurs instantly; one doesn’t have to wait for a match above is exactly what Automated Market Makers give. On the other hand, however, comes with challenges: DeFi is still in its infancy and is rather fragile. Such rapid development in this area has easily left it prone to hacking and theft, which occurred primarily due to poor testing and programming mistakes.
In that regard, users need to face these risks in pursuing the many opportunities available from Automated Market Makers. Using the might of algorithms and community power, Automated Market Makers are doing more than revolutionizing the way we trade cryptocurrencies are opening up the possibility of a decentralized financial future.
How Do Automated Market Makers Work?
AMMs work on the idea of liquidity pools that are smart contracts holding a pair of assets, for example, ETH and DAI in a certain ratio. Users deposit equal values of both tokens into the pools, which are also called liquidity providers or LPs.
When a trader seeks to swap tokens, they engage directly with the liquidity pool instead of depending on particular buyers or sellers. The algorithm of the Automated Market Makers (AMMs) establishes the exchange rate based on the existing asset ratios within the pool. Following a trade, the reserves of the pool are adjusted, thereby affecting the prices for subsequent transactions.
This mechanism ensures liquidity is always available and enables trading in a wide variety of assets, including less well-known cryptocurrencies. Automated Market Makers reduce the entry barriers and make a more accessible marketplace by directly executing algorithmic trades. Therefore, they become one of the core components of the DeFi ecosystem.
Key Features of Automated Market Makers
Impermanent loss occurs in the decentralized finance space due to the algorithms of Automated Market Makers (AMM) causing divergence between an asset’s price within a liquidity pool and its actual market price. This usually leaves liquidity providers with temporary losses, especially in periods when dramatic market changes occur.
Slippage is essentially the difference between an asset’s calculated price and the actual price at which a trade is executed. Therefore, it is the amount paid for immediate trades in liquid markets. Although slippage in cryptocurrency trading is common, it also occurs in mainstream financial markets.
Impermanent loss and slippage are two primary considerations for traders and liquidity providers in the DeFi space. Both affect trading plans and outcomes.
Challenges and Risks of AMMs
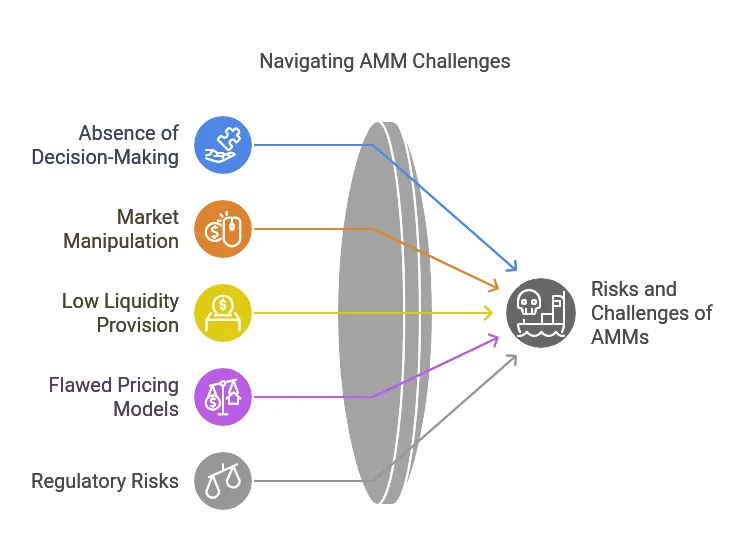
Absence of Prudent Decision-Making
Automated Market Makers operates via preset algorithms and lacks the flexibility that a human market maker possesses. Thus, the rigid rules mean that during unexpected or extreme turbulence events, Automated Market Makers could misprice some assets, which could lead to users making trades at unfavorable prices.
Susceptibility to Market Manipulation
Market makers suffer from market manipulation by traders with ulterior motives who are smart enough to manipulate their algorithmic nature. Big traders can also set up trades in certain transactions to try to influence their price, causing other market players dependent on AMM pricing to incur losses.
Provision of Liquidity is Low
While Automated Market Makers were meant to provide liquidity, they can find trouble during turbulent market times or for an exceptionally illiquid cryptocurrency. As a result, precautionary increases could bristle due to lack of liquidity, resulting in wider bid ask-spreads and increased slippage, increasing costs to users during a trade, especially those in high-volume.
Flawed Pricing Models
Automated Market Makers rely on mathematical models to put a price on assets – unfortunately, these are not infallible in any way. For instance, under certain conditions the constant product equation that determines the price can lead to some pricing inaccuracies, creating arbitrage opportunities that drain liquidity and may destabilize the market.
Regulatory and Compliance Risks
The decentralized nature of the operation of Automated Market Makers makes it complicated to honor some of the regulatory standards such as Know Your Customer or Anti-Money Laundering. Such lack of oversight opens up operators and users to legal risks as some transactions may very easily escape the attention of authorities-the absence of a sufficiently public watchdog renders it impossible to trace transactions involving fraudulent activities and disputes.
The Future of AMMs
Bright prospects lie ahead for Automated Market Makers (AMMs) in the crypto ecosystem, as they are constantly molded by some key trends.
- Broader Access: AMMs will make trading much simpler for users lacking technical know-how in DeFi.
- Layer 2 Integration: Layer 2 solutions will allow AMMs to become more efficient by offering high-speed and low-cost transactions.
- Creation of New Financial Products: Synthetic assets and derivatives would further improve investment opportunities.
- Cross-Chain Functionality: Cross-chain AMMs seamlessly allow trading on different blockchain networks with increased liquidity and better market efficiency.
- Tokenization of Real-World Assets: AMMs will have a major role in tokenizing real-world assets which would facilitate fractional ownership and widen up investment access.
- Algorithms and AI: The introduction of sophisticated algorithms and AI will aid in boosting liquidity management and improving trading strategies, unattractively enhancing the user experience.
- Community-Driven Improvements: A better set of protocols and features will arise from the efforts of the very active developer community, with each new AMM adding to the diversifying financial innovation in DeFi and AMMs.
- Greater Educated Base: With more awareness of the benefits and risks of AMMs at play, the navigation of DeFi by its users will continue.
These defining trends that could be a game-changer for AMMs would bring the evolution of trading experiences in the DeFi environment to an entirely new level and would reestablish inclusivity in the financial ecosystem.
Ready to Leverage the Future of AMMs?
Join HyScaler today to unlock innovative trading solutions and stay ahead in the rapidly changing DeFi space. Discover how our platform can help you navigate the world of Automated Market Makers effectively. Contact us now!