Table of Contents
How effectively does your company monitor and manage its IT assets?” This is an essential question because companies now depend significantly on technology to function effectively. This underlines the importance of effective IT asset management (ITAM) practices in maintaining cost control, compliance, and security.
“Organizations that fail to implement effective IT asset management strategies risk losing up to 30% of their IT budget due to inefficiencies and hidden costs.”- According to Gartner
What is IT Asset Management?
IT asset management (ITAM) is the process of monitoring, managing, and optimizing IT assets of an organization throughout their life cycle. ITAM helps ensure that businesses realize maximum value from their IT investments while ensuring compliance and security. ITAM extends to hardware, software, networks, and cloud services, assisting organizations in managing costs, minimizing risks, and enhancing operational effectiveness.
ITAM is a mix of policies, procedures, and technologies used to track and control IT assets. An organized ITAM framework assists companies in making asset procurement, usage, maintenance, and disposal decisions. Through a centralized catalog of all IT assets, organizations can avoid unnecessary expenses, implement cybersecurity controls, and comply with industry regulations. ITAM also assists in planning future IT requirements, maximizing software license utilization, and maintaining business continuity by reducing downtime and interruptions. In many cases, procurement process management software is also used to help manage asset purchases and vendor coordination more effectively.
What is an IT Asset?
An IT asset is any technology resource owned by the company that holds value and must be managed. Such assets can be divided into:
- Hardware: Servers, computers, networking equipment, storage equipment, and mobile devices.
- Software: Licensed software, operating systems, and cloud applications.
- Cloud Resources: Cloud storage, virtual machines, and cloud applications.
- Network Infrastructure: Routers, switches, firewalls, and access points.
- Peripheral Devices: Printers, scanners, and other peripherals.
Overview of the IT Asset Management (ITAM) Process
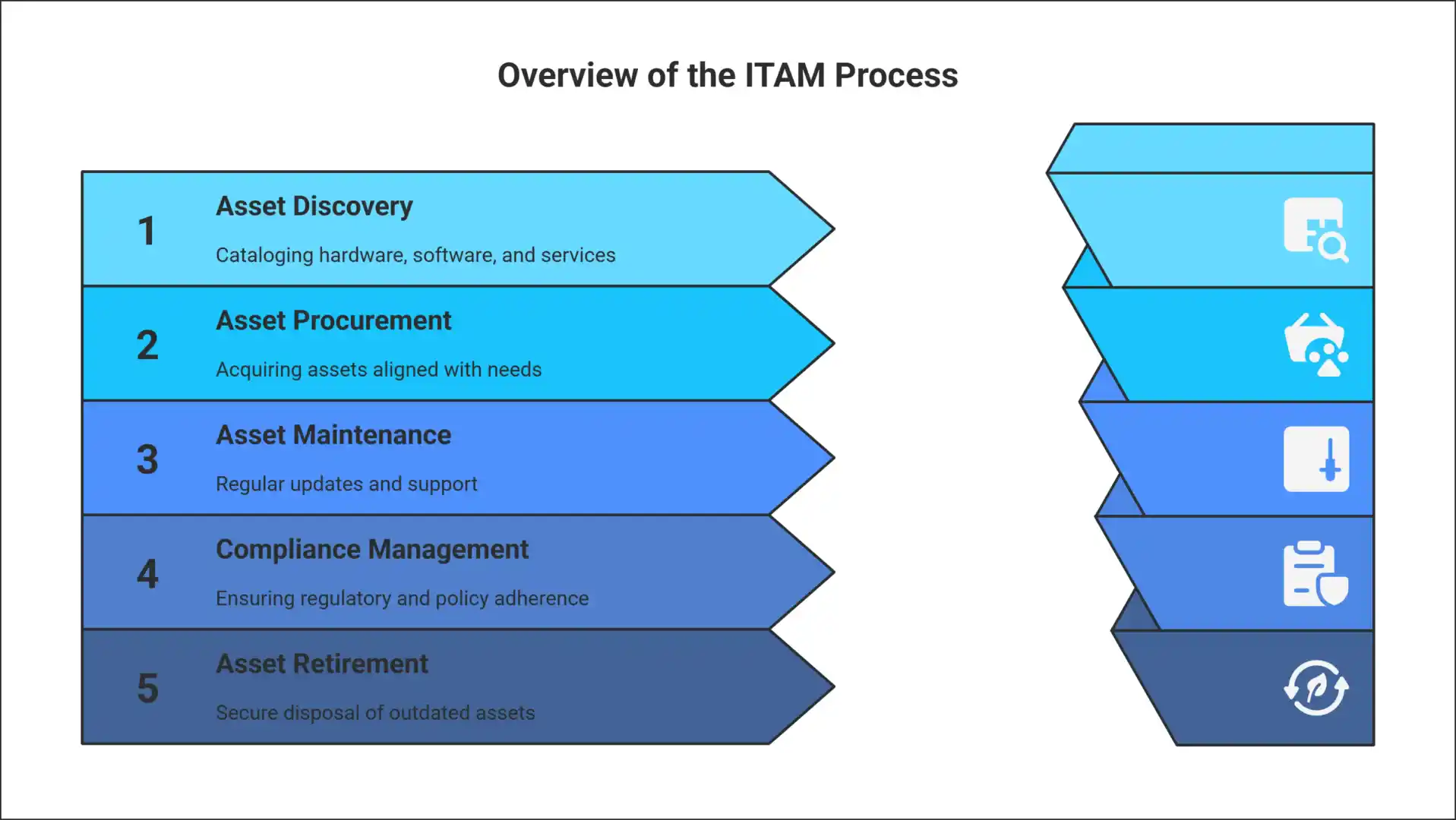
The IT Asset Management (ITAM) process is a methodical process to monitor, maintain, and maximize IT assets through their lifecycle. It provides cost-effectiveness, security, and regulatory compliance along with maximizing IT investment value. The following are the main building blocks of ITAM and how they help to manage IT assets effectively.
1. Asset Discovery and Inventory Management
- Discovers and inventories all IT assets (hardware, software, cloud services, and virtual machines).
- Utilizes automated asset discovery solutions to monitor newly installed or retired assets.
- Has a centralized inventory with real-time visibility of asset locations, utilization, and ownership.
Example: A business using an ITAM tool automatically scans its network and identifies all devices connected to it, thereby guaranteeing correct asset tracking.
2. Asset Procurement and Deployment
- Ensures that IT assets are procured according to the company’s needs and financial constraints.
- Reviews vendor contracts, warranties, and service agreements for efficient procurement.
- Deploys assets by installing required software, setting up security parameters, and allocating them to users.
Example: An expanding company buys new workstations and cloud services in accordance with manpower growth plans while being cost-effective and in line with vendor contracts.
3. Asset Maintenance and Support
- Regularly checks hardware performance, software upgrades, and security updates.
- Schedules preventative maintenance to minimize failures and increase asset lifespan.
- Offers technical support and troubleshooting to reduce downtime and enhance productivity.
Example: An IT department employs an ITAM system to monitor warranty end dates and schedule automatic software updates, eliminating security vulnerabilities.
4. Compliance and Risk Management
- Enforces all assets in accordance with the software license agreements, industry regulations, and security policies.
- Regularly runs audits to confirm license utilization, software compliance, and asset security.
- Determines possible security threats, unauthorized software installations, and policy infractions.
Example: A financial company enforces PCI-DSS compliance by auditing IT assets processing payment information regularly to protect against penalties and security vulnerabilities.
5. Asset Retirement and Disposal
- Retires aging, broken, or redundant assets to eliminate security threats.
- Employs secure data sanitization practices like data wiping, degaussing, or physical destruction.
- Disposes of assets by resale, recycling, or donation in compliance with environmental and regulatory requirements.
Example: A medical practitioner safely deletes patient information from outdated storage devices prior to shipping them in for recycling in order to meet HIPAA standards.
Stages of the IT Asset Lifecycle
IT assets need to be managed effectively in order to optimize utilization, reduce costs, and maintain security. The five most important phases of the IT asset lifecycle are:
1. Planning
- Concerned with the evaluation of business needs and projection of future IT demands.
- Sets budget limits and maps IT procurements to long-term business objectives.
- Sets policy on asset purchase, utilization, and lifecycle management.
Example: An organization that is looking to increase the number of its employees considers the number of new hires and calculates the number of laptops, software licenses, and network infrastructure improvements needed before ordering.
2. Procurement
- Includes buying or leasing IT assets, including hardware (laptops, servers, network equipment) and software licenses.
- Ensures adherence to financial and regulatory guidelines by selecting vendors offering the most favorable pricing, warranties, and support.
- Manages vendor contracts and keeps history for future audit and renewals.
Example: An IT organization chooses bulk software licenses with multi-year support in order to cut costs and satisfy vendor agreements.
3. Deployment
- Consists of installing, setting up, and integrating IT assets into the organization’s infrastructure.
- Ensures assets are adequately tagged, logged in the IT asset management (ITAM) system, and allocated to users.
- Enforces security controls, including encryption, endpoint protection, and access controls, to protect corporate information.
Example: When a new employee is added, the IT department installs authorized applications, sets security options, and grants access to corporate infrastructure before handing over the laptop.
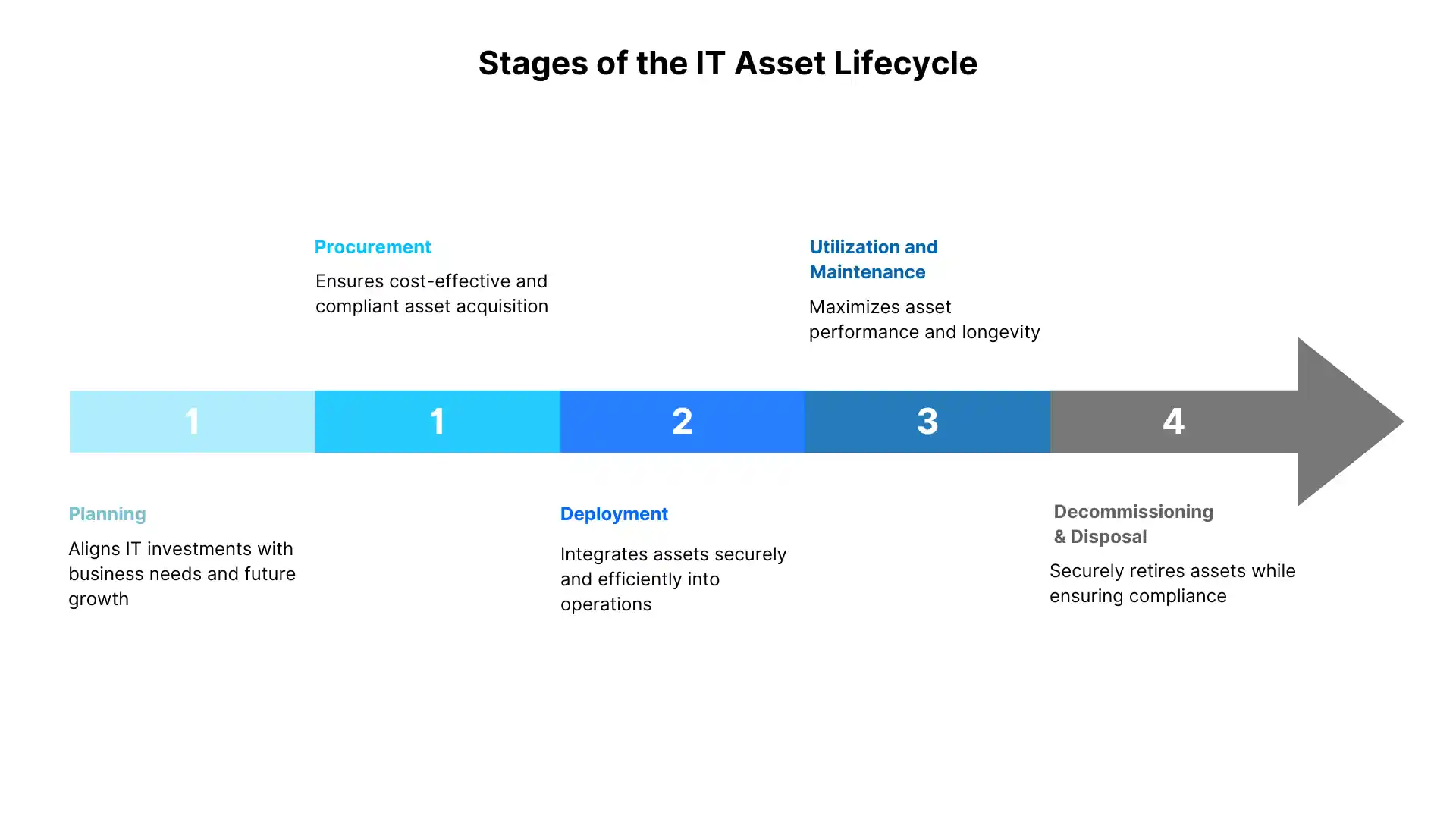
4. Utilization and Maintenance
- Emphasizes effective asset management, performance monitoring, and maintenance to maximize longevity and productivity.
- Comprises patch management solutions, software updates, warranty tracking, and repairs to avoid downtime.
- Assists organizations in monitoring asset utilization and maximizing resource utilization.
Example: An organization employs automated ITAM software to track hardware performance, identify underutilized assets, and automate preventive maintenance scheduling.
5. Decommissioning and Disposal
- Refers to retiring old or non-functional assets while maintaining data security and regulatory compliance.
- Assets are redeployed, resold, recycled, or disposed of securely to reduce environmental footprint.
- Data sanitization processes, including data wiping, degaussing, or physical destruction, are applied to avoid unauthorized access.
Example: A financial institution securely wipes data from retired storage servers prior to recycling them to meet GDPR and data protection regulations.
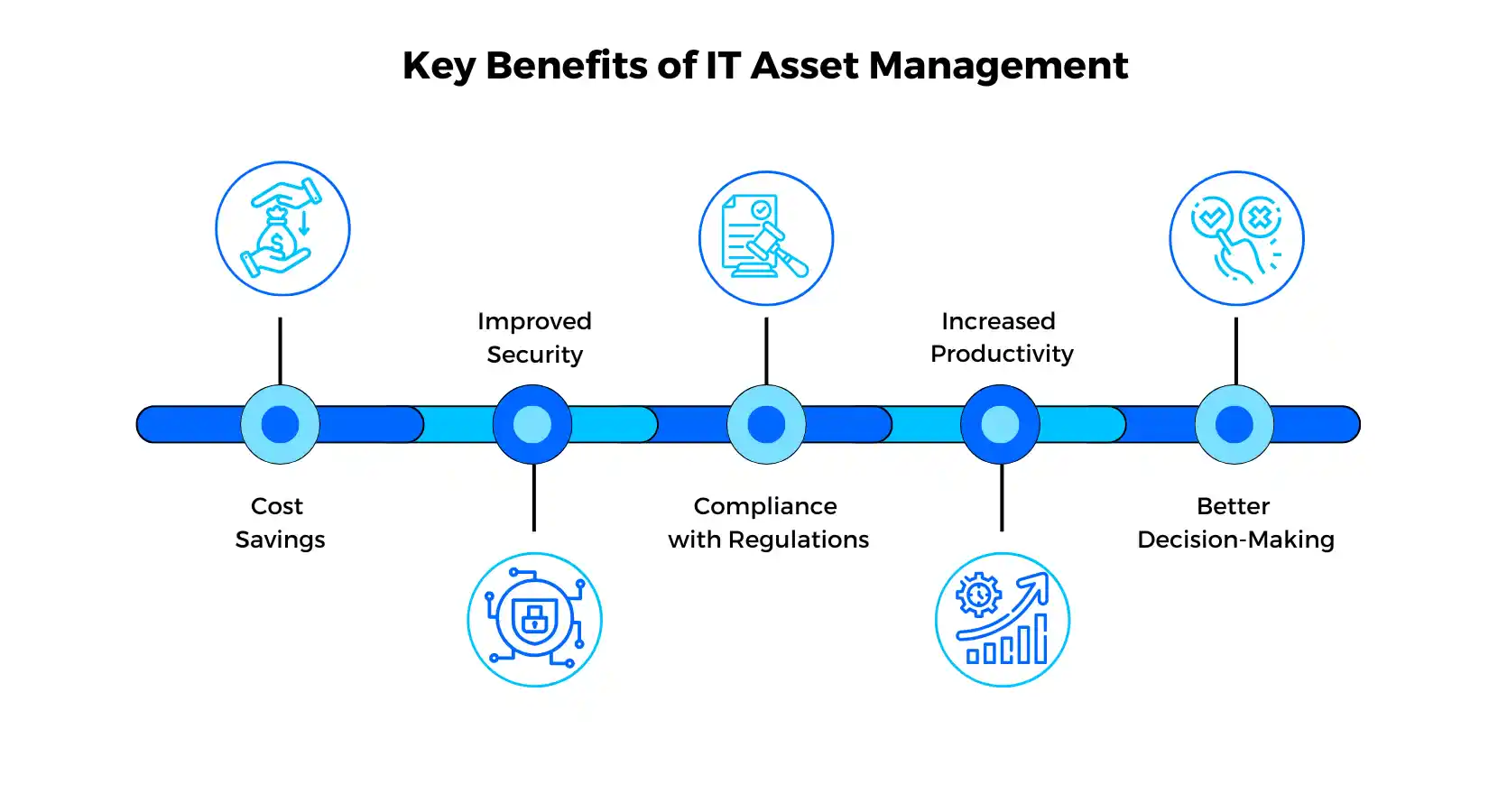
Key Benefits of IT Asset Management (ITAM)
Implementing an IT Asset Management (ITAM) strategy helps businesses optimize their IT resources, reduce costs, and enhance overall efficiency. Below is a detailed breakdown of its advantages:
1. Cost Savings
- Avoids duplicate purchases by offering visibility into current IT assets.
- Maximizes asset utilization, making sure IT resources are utilized effectively.
- Maximizes asset life through ongoing maintenance tracking.
- Saves on licensing and compliance expenses by preventing software non-compliance penalties and maximizing license assignment.
Example: An organization employing ITAM can monitor software licenses and redistribute unused ones rather than buying new ones, saving thousands of dollars.
2. Improved Security
- Traces all IT assets, so no unauthorized device is able to connect to the network.
- Discovers vulnerabilities by identifying software that is out of date, systems that are not patched, and unknown devices.
- Implements security policies to guarantee adherence to corporate security policies.
- Reduces insider threats by monitoring who can access what assets, and lowers the risk of internal data breaches.
Example: When an employee departs the company, ITAM traces their allocated laptop, which gets returned and data wiped securely.
3. Compliance with Regulations
- Software license management guarantees compliance with software vendor contracts (e.g., Microsoft, Adobe, Oracle).
- Data protection compliance brings IT asset management into compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, SOX, ISO 27001, and PCI-DSS.
- Audit preparation is enhanced with a record of IT asset history, so that reports are simpler to produce at audit times.
Example: Medical software and storage systems containing patient data at a healthcare company covered by ITAM ensure adherence to HIPAA laws, with legal sanctions evaded.
4. Increased Productivity
- Reduces downtime with ability for preventive maintenance and asset location.
- Prevents employees from performing their tasks due to insufficient hardware, software, or licensing.
- Streamlines IT workflows, lowering the amount of manual labor involved in IT operations through the automation of asset tracking, maintenance planning, and reporting.
Example: An organization can utilize ITAM to track the performance of laptops and servers and replace them prior to failure to avoid business downtime.
5. Better Decision-Making
- Delivers data-driven insights that enable companies to make calculated IT investment choices.
- Enhances IT budgeting through the monitoring of asset depreciation and replacement cycles.
- Improves vendor management by having records of service agreements, vendor contracts, and warranties so businesses can negotiate advantageous deals
Example: A bank can measure which IT assets are performing sub optimally and determine whether they should upgrade, replace, or repurpose them for cost saving.
IT Asset Management (ITAM) Software Overview
IT Asset Management (ITAM) software is fundamental in assisting organizations in monitoring, managing, and maximizing their IT assets from their onset to disposal. The software offers real-time visibility, compliance management, and financial management of hardware and software assets. Following is a description of some widely used ITAM software solutions and their features.
1. ServiceNow IT Asset Management
An ITAM cloud-based solution that is integrated with IT Service Management (ITSM).
- Integration with ITSM & CMDB: Facilitates effortless tracking of IT assets within an organization’s current IT environment.
- Lifecycle Management: Tracks assets from purchase to disposal.
- Automated Workflows: Eliminates the need for manual labor in tracking and reporting assets.
- Software License Management: Assists companies in evading software compliance issues.
Best For: Organizations requiring a centralized ITAM and ITSM solution with automated features.
2. Ivanti IT Asset Management
A robust ITAM tool with automated asset tracking and compliance management.
- Real-time Asset Visibility: Discovers and monitors IT assets throughout the organization.
- Software Compliance & Cost Optimization: Verifies licensing and removes unnecessary software expenditure.
- Security & Risk Management: Identifies unauthorized software and security risks.
- Cloud and On-Premise Deployment: Offers flexible deployment choices.
Best For: Cost optimization and compliance enforcement-oriented organizations.
3. ManageEngine AssetExplorer
A user-friendly ITAM solution that offers asset discovery, monitoring, and management.
- Automatic Asset Discovery: Scans and inventories IT assets on a network.
- Hardware & Software Tracking: Tracks usage and compliance status.
- IT Purchase & Contract Management: Handles procurement, contracts, and software licenses.
- Integration with Help Desk Software: Optimizes IT support efficiency.
Best For: Mid-sized companies looking for an affordable yet feature-rich ITAM tool.
4. Lansweeper
A powerful IT asset discovery tool for hardware and software tracking.
- Network Scanning & Asset Inventory: Automatically identifies all connected IT assets.
- Custom Reporting & Dashboards: Offers visibility into IT asset health and usage.
- Software License Auditing: Assists organizations to stay in compliance.
- Integration with ITSM & Security Tools: Improves overall IT operations.
Best For: Organizations that need thorough IT asset discovery and network-wide tracking.
5. InvGate Asset Management
InvGate Asset Management is a no-code solution for inventory and IT asset lifecycle management.
- Automated asset discovery with multiple data inputs (Discovery, agent, manual, CSV) and database normalization.
- IT Asset Lifecycle Management: Manage, automate, and report on your IT inventory from asset acquisition to disposal.
- Integrations with leading Service Management solutions, such as InvGate Service Management, ServiceNow and Jira, to unify all IT operations in one place.
- Software metering and deployment.
- Dynamic tags to automate asset tagging and trigger alerts to streamline daily operations.
- Report customization with option to schedule and share reports with users both in the platform and via email.
Best for companies of every size and industry – though organizations with 1000 to 5000 employees will benefit the most out of it.
Business Opportunity for IT Services
Companies are putting more emphasis on IT Asset Management (ITAM) and IT Inventory Management to minimize costs, enhance efficiency, and stay compliant with regulatory requirements in their industry. This trend opens up several business opportunities for IT service providers. These are ways that companies can benefit from this trend:
1. Consulting Services
- Most companies don’t have the knowledge to carry out an effective ITAM plan.
- IT service providers can provide consulting and advisory services to enable companies to:
- Formulate IT asset lifecycle management plans.
- Maximize asset usage and eliminate unnecessary spending.
- Establish best practices in tracking and maintaining IT assets.
2. Software Development
- The need for custom ITAM software is on the rise, particularly for companies that require customized asset management solutions.
- There are opportunities in creating software that:
- Tracks and reports assets automatically.
- Connects to existing IT environments (ERP, ITSM, CMDB).
- Utilizes AI and predictive analytics to forecast asset lifecycles.
3. Managed IT Services
- ItAM and inventory management are outsourced by many organizations because of the complexity of maintaining assets in several locations.
- IT service providers may provide managed ITAM services, such as:
- Remote IT asset monitoring.
- Periodic maintenance and upgrades.
- IT asset security and risk management.
4. Compliance Auditing
- Organizations are required to abide by several IT regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, SOX).
- IT service providers may provide audit and compliance services to verify:
- IT assets are documented and secured appropriately.
- Companies comply with licensing needs and do not incur fines.
- ITAM audits are regularly performed to conform to industry standards.
Conclusion
Good IT Asset Management is essential for organizations to maximize their IT assets, save costs, and maintain security compliance. By adopting ITAM best practices and software tools, organizations can streamline operations and stay ahead of the competition. Additionally, the increasing need for ITAM services creates profitable opportunities for IT service providers to assist businesses in managing their IT investments.
Aside from this, since technology continues to change, ITAM will be required to move in the same direction as cutting-edge trends that include AI-backed asset management, IoT tracking for assets, and cloud ITAM. Such advancements will help them invest better into managing their assets with optimal utilization and remaining top players in today’s ever-developing digital life.
For enterprises seeking to augment their ITAM strategy, putting money into effective IT asset monitoring, routine audit, and tying into ITSM processes will become the norm. As companies go on to ramp up their IT infrastructure, ITAM will still be the mainstay of economic and environmentally viable IT operations.
FAQs
What is IT Asset Management (ITAM) and why is it important?
ITAM is the process of tracking, managing, and optimizing IT assets throughout their lifecycle. It helps organizations reduce costs, improve security, ensure compliance, and maximize the value of IT investments.
How does ITAM help with software license management?
ITAM tracks software usage, prevents over-licensing, ensures compliance with vendor agreements, and helps reallocate unused licenses to save costs.
What are the key components of ITAM?
ITAM includes asset discovery, procurement, deployment, maintenance, compliance management, and asset disposal, ensuring complete lifecycle management of IT assets.
How does ITAM improve security and compliance?
ITAM helps identify unauthorized assets, enforce security policies, track software vulnerabilities, and ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS.