Table of Contents
In today’s digital landscape, digital biometrics is emerging as a cornerstone of innovation, seamlessly integrating advanced technologies to redefine security. From unlocking a smartphone to protecting financial transactions, digital biometrics redefined how we use technology by bridging convenience and strong security.
However, what is so revolutionary about this technology and why is it an important resource for organizations across the globe?
Let’s dive deeper into the world of digital biometrics, exploring its potential, applications, challenges, and prospects.
What Are Digital Biometrics?
Digital biometrics encompasses the identification of individuals authenticating and verifying, using unique biological and behavioral traits such as fingerprints, facial features, voice patterns, or even keyboard strokes, and so on. In contrast to what is commonly used for passwords or PINs, biometric identifiers are virtually impossible to duplicate, so for use in both individual and networked applications it is a very secure solution.
In 2022, the global biometric market equated to USD 42.9B, which is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 14.8% between the years 2023 and 2030. This rapid growth points to the growing use of digital biometrics across many applications, from individual devices to enterprise systems.

The Core Technologies Powering Digital Biometrics
Facial Recognition
Facial recognition technology employs sophisticated algorithms to capture the distinctive characteristics of a person’s face, including the distance between the eyes, the angle of the nose, and the shape of the jawline.
The power of this biometric technology comes from artificial intelligence(AI) and deep learning techniques, which improve the performance of the system in the task of face identification in different illuminations and from any side angles.
With accuracy rates exceeding 99.97%, facial recognition has become a preferred choice for applications requiring high-security standards, including mobile device authentication, airport security, and secure access to sensitive locations.
Behavioral Biometrics
Behavioral biometrics adopts a different approach, where the behavior of a user interacting with a device is captured and analyzed instead of physical attributes. This includes keystroke dynamics (such as typing speed and rhythm), mouse movement patterns, and navigation habits (like the way a user swipes on a smartphone screen).
However, by learning an individual’s private behavioral singularity with time, these systems can track behavior in real-time and identify anomalies that may alert to the possibility of fraud or account takeover. For example, if the typing pattern of a user changes dramatically, the system might flag the behavior as suspicious and require further authentication procedures.
Iris and Retina Scanning
Iris and retina scanning systems analyze the intricate and unique patterns in the human eye—particularly the iris, the colored part of the eye, and the retina, the thin layer at the back of the eyeball. These biometric identifiers are some of the most accurate and secure identifiers, facilitating identification, thanks to the complexity and individuality of eye patterns.
Iris-scanning has gained widespread use in high-security settings, including government bureaus military grounds, and airports, where access control must be very restrictive. But, with technology advancing, iris scanning has started to become more commonplace, and now has been included in consumer devices such as smartphones and computers.
Voice Recognition
Voice recognition systems, based on vocal features (e.g. pitch, tone, cadence, speech patterns), can be used for identification and authentication of users. As opposed to conventional password or PIN systems, voice recognition offers a hands-free, frictionless authentication flow.
These systems are based on the analysis of the individual physical characteristics of a person’s voice, which is relatively stable across time. Voice biometrics are increasingly being used in customer service settings, such as call centers and automated phone systems, where customers can authenticate themselves using only their voice.
Applications Across Industries
Banking and Financial Services
Digital biometrics is an important tool in improving security and preventing financial fraud. According to a 2023 survey, 67% of banks worldwide currently have biometric solutions in place for user authentication. Facial recognition is widely implemented in mobile banking apps, with fast and secure account access.
On the one hand, behavioral biometrics can identify atypical spending and fraudulent behaviors by tracking the user’s behaviors such as keystroke patterns and transaction logs. As fraud becomes more sophisticated, biometrics offers a proactive, real-time solution to protect financial transactions and customer accounts.
Healthcare
Sensitive patient information protection is increasingly crucial in healthcare. Digital biometrics provide secure measures by which electronic health records (EHRs) can be accessed and patient identity verified in telemedicine systems. The World Health Organization mentioned a 60% surge of health care cyberattacks in 2022 which highlights the shortage of security measures.
Biometric systems provide authentication for restricted access to confidential patient data by only allowing authorized persons to access such information and also improve the time required for the authentication process for healthcare providers and patients. Through strong implementation of biometric technologies, medical facilities can better safeguard against data theft and improve overall privacy and trust.
E-Commerce
Digital biometrics is changing the e-commerce industry by maximizing both security and, end-user experience. Leading platforms such as Amazon and Alibaba have introduced biometric checkout systems, allowing customers to authenticate their identity with a quick facial scan or fingerprint recognition. In this approach, fraud risk is minimized and payment processing is sped up, resulting in a better shopping experience.
With the increasing volume of e-commerce, the application of biometric technology is more and more mainstream to provide consumers with a more efficient and safe way to settle online commerce.
Travel and Immigration
In the fields of travel and immigration, the use of biometric technology not only has made it easier to identify individuals, but it also improved the effectiveness of security. Biometric passports/facial recognition systems are being widely adopted in airports, to expedite waiting time and to make the immigration procedure more effective.
As stated by the International Air Transport Association (IATA), more than 75% of airports in the world will adopt biometric solutions before the year 2025, and traveling will be more efficient and safe. Not only do these systems accelerate the process, but also reduce error, and safety at border control points.
Workplace and Enterprise Security
Biometric systems are becoming indispensable for securing physical access to restricted areas and digital access to enterprise systems. These systems control which individuals can gain access to restricted rooms and sensitive information, admitting only approved personnel.
Furthermore, behavioral biometrics provide continual monitoring of employees’ interaction with sensitive information, triggering the alarm in case of unusual behavior that may signify security threats or violation of compliance rules.
Through the use of biometrics, it is possible to better secure their security posture preventing unauthorized access to sensitive resources.
Challenges and Concerns
Although digital biometrics has significant advantages, for its ethical and practical deployment in various industries, several challenges need to be overcome.
Privacy Concerns
The collection and storage of digital biometrics data, including finger impressions, facial photographs, and iris scans, pose serious privacy issues. Biometric data is, by definition, always private, and misuse or unauthorized access to this type of intimately personal information can have serious harmful effects. As a 2020 report by the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) states, more than 1.5 billion facial recognition information was stored around the world, prompting worries about unauthorized data dissemination and monitoring.
Maintenance of compliance with privacy legislation such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States is critical to protecting individual rights and preventing breaches of digital biometrics data.
Data Security
Since digital biometrics systems store very personal information, those biometric databases are likely to be sought after by cybercriminals. If targeted, hackers could illegally access sensitive information on a large scale. A 2019 study by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) found that 18% of biometric databases in use worldwide were not adequately secured, making them vulnerable to attacks.
To prevent unauthorized access and breaches of digital biometrics, security measures need to be taken, such as robust encryption protocols, multi-factor authentication, and secure storage solutions.
Bias in Facial Recognition
Facial recognition is one of the building blocks of digital biometrics, though it has drawn criticism for its potential susceptibility to bias. Research has demonstrated that facial recognition systems are weak in correctly identifying individuals belonging to ethnic groups. A 2019 study by the MIT Media Lab revealed that commercial digital biometrics systems misidentified darker-skinned and female faces at significantly higher rates than lighter-skinned or male faces.
In certain scenarios, facial recognition algorithms were 34% more likely to be mistaken for darker-skinned women. Developers must work toward minimizing biases in digital biometrics algorithms to ensure fairness, equity, and effective use in critical sectors like law enforcement and hiring practices.
Cost of Implementation
Although digital biometrics offers significant security, the initial cost of setting up may be prohibitive, particularly for small and medium enterprises (SMEs). A 2020 Biometrics Institute survey found that 60% of small business respondents reported the cost of digital biometrics as a significant obstacle in deploying such a technology. Costs go beyond the hardware (scanner and camera), to the software, the training, and the ongoing maintenance.
Nevertheless, with the development and increased widespread acceptance of digital biometrics technology, the cost is anticipated to lower and therefore more affordable to smaller organizations in the future.
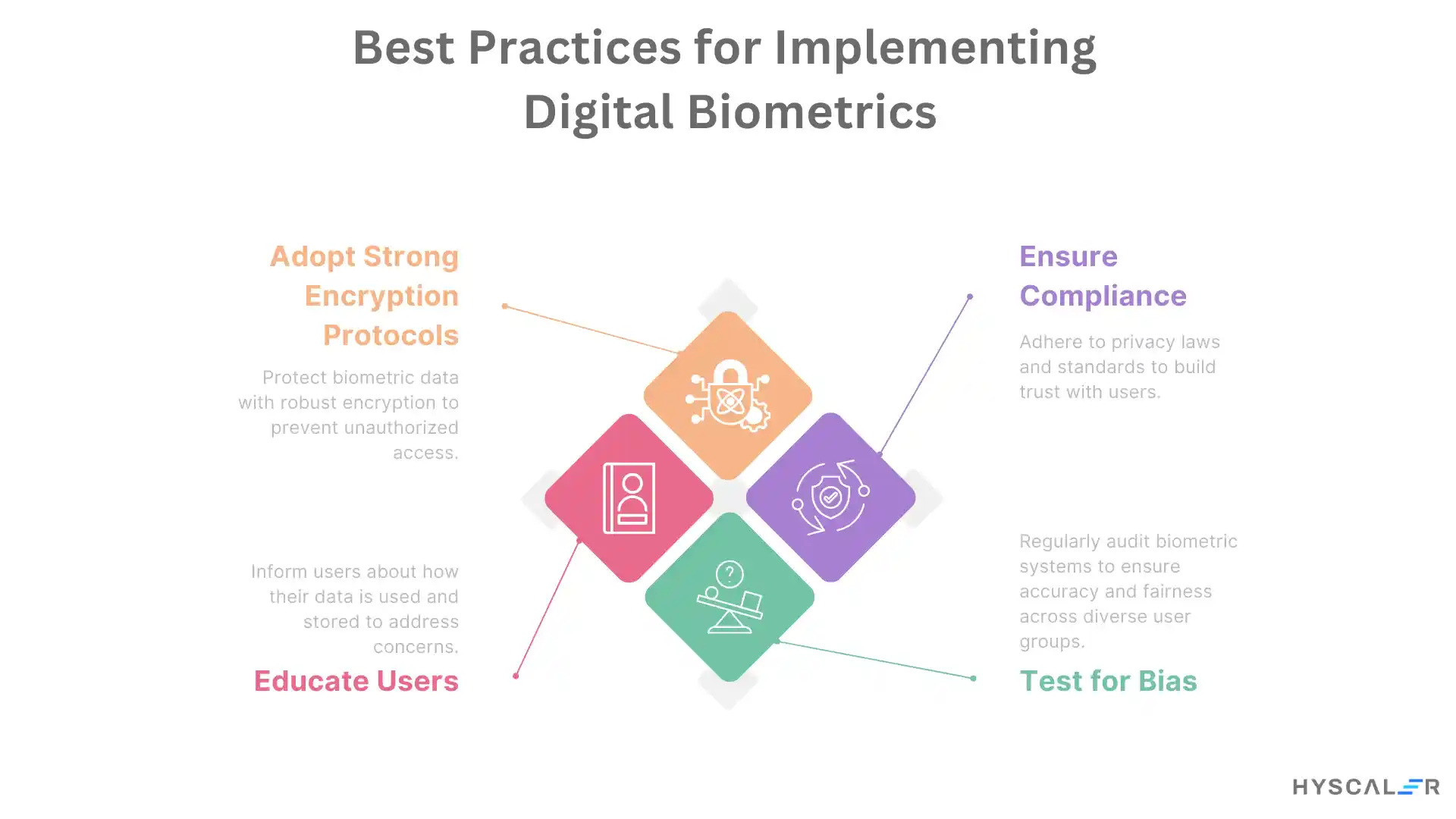
Final Thoughts
Involving a fast-growing number of digital interactions, digital biometrics transforms how we protect the online world. Using the latest innovation, this technology provides a trade-off between security and usability, enabling the sectors to develop trust and simplify user needs. However, with great power comes great responsibility. Proper ethical implementation and overcoming challenges will be the major factors for unlocking the vast potential of digital biometrics in the upcoming years.
The digital biometrics market is poised to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20% between 2023 and 2030, in part due to its mass deployment across industries such as finance, health, and e-commerce.
Ready to transform security with digital biometrics? Begin to explore the ways this technology could make your organization more efficient and secure today.
READ MORE:
AI Rendering: Unlocking the Future of Intelligent Visualization
The Quiet Revolution of Green Hydrogen: Powering a Sustainable Future