Table of Contents
Cloud application development is software building that takes place in distant servers. The providers, such as AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud, host the servers. The infrastructure is not needed locally. Resources are controlled, code is run, and data is kept in cloud services. The model has revolutionized organizations’ design, deployment, and scaling of software products.
Traditional applications typically take place on on-premise servers. They need significant up-front capital expenditures in hardware, security, and maintenance.
In comparison, cloud-based software is versatile. You only pay as much as your consumption, and scaling up/down occurs much more rapidly.
What is driving companies to move to the cloud? The answer is simple: speed, cost-effectiveness, and resilience. Cloud platforms deploy applications in many regions, reach global customers, and deploy new features without downtime. This ensures that applications remain competitive as well as meet today’s user expectations.
Have you ever used Google Docs, Dropbox, or Spotify? Those are cloud-based applications. Those products are built on cloud infrastructure. They give individuals instant access across devices while keeping data in sync in real time. That’s what cloud-based application development is about: building applications that are reliable, scalable, and always-on.
Key Benefits of Cloud-Based App Development
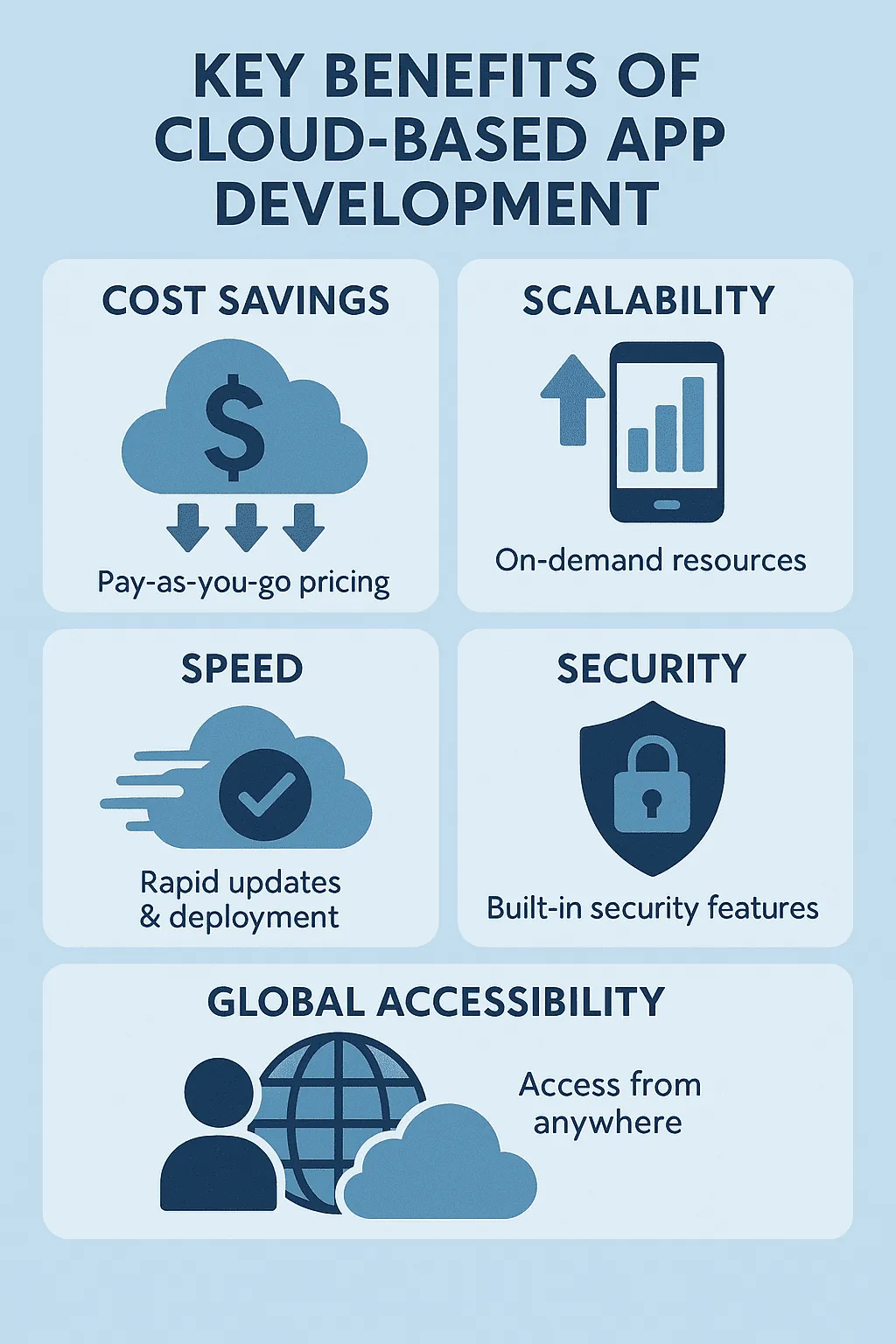
One of the driving forces behind cloud app development is cost savings. On-premise installations need massive upfront capital spending in data centers and servers. That cost goes away with the cloud. You pay what you use, and that model works great in new startup ventures and scaling organizations.
Another big plus is scalability. Say that it’s your e-commerce app, and holiday traffic spikes. You can scale resources in real time on a cloud platform. No downtime, no lost sales. When traffic subsides, scale back down and save money.
Speed matters, too. In the cloud, updates or bugs can be fixed promptly by developers. Changes may be rapidly deployed with continuous integration and delivery pipelines (CI/CD). End-users get new features right away.
Security is also a significant consideration. Leaders like AWS and Azure spend heavily in security. They bundle in encryption, identity, and compliance as capabilities that hardly any organization could reasonably afford in-house. Security is a group effort, and cloud infrastructure is a good baseline.
Another benefit is global accessibility. Workers as well as customers can use apps anywhere using cloud hosting. Groups can work in real time, transfer files, and stay in sync. That flexibility makes cloud apps perfect for telecommuting.
There are cost savings, scalability, speed, security, and worldwide accessibility in cloud app development. Business innovation and growth happen more readily.
Core Components
When building a cloud-based app, several components work together. Let’s break them down:
- Frontend: This is the part users interact with—web or mobile interfaces. Developers often use frameworks like React, Angular, or Flutter. The frontend communicates with the backend through APIs.
- Backend: This includes servers, logic, and APIs. In the cloud, backend services may run on virtual machines, containers, or serverless platforms. For example, AWS Lambda lets you run code without managing servers.
- Databases and Storage: Cloud databases like Amazon RDS or Google Firestore store user data. Object storage solutions, like Amazon S3, handle files, images, and videos. Choosing between SQL and NoSQL depends on your app’s requirements.
- APIs and Integrations: APIs connect your app with third-party services. For instance, payment gateways like Stripe or communication tools like Twilio integrate into cloud-based applications.
- Cloud-Native Services: These tools are offered by cloud vendors. They include AI services, IoT tools, and data analytics. Using them reduces development time and adds advanced capabilities to apps.
Without these components, cloud apps would not function. Every decision—frontend framework, backend language, or database—affects scalability, speed, and user experience.
Popular Cloud Platforms for App Development
When it comes to cloud-based app development, three platforms dominate the market: AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Each offers unique features, pricing models, and ecosystems.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): The largest cloud provider. It offers a massive library of services, from compute and storage to machine learning. AWS is known for reliability and scalability.
- Microsoft Azure: Azure integrates well with Microsoft products. Businesses already using Office 365 or Windows Server often choose Azure. It also has strong support for hybrid cloud setups.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): GCP is popular among developers focused on data, AI, and machine learning. Its tools, like BigQuery and TensorFlow, are strong differentiators.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | AWS | Azure | Google Cloud Platform |
| Market Share | Largest | Second-largest | Growing, strong in AI/ML |
| Strengths | Wide range of services | Microsoft integration | Data analytics & AI |
| Pricing Model | Pay-as-you-go, reserved | Pay-as-you-go, enterprise | Pay-as-you-go, flexible |
| Ideal Use Case | Enterprises & startups | Businesses using Microsoft | Data-heavy & AI-first apps |
When choosing a platform, consider your budget, team expertise, and app requirements. Do you need advanced AI? GCP may be best. Do you already use Microsoft products? Azure could be the right fit.
Cloud-Based Android App Development
Cloud-based Android app development builds mobile apps that use cloud infrastructure for storage, processing, and scaling. Traditional Android apps keep data and tasks on the device. Cloud-based Android apps move heavy tasks to the cloud instead.
Take mobile banking apps as an example. Instead of processing transactions on the device, they use secure cloud servers. This ensures faster performance and safer operations. Again, fitness apps store user data in the cloud, making it accessible across many devices.
Developers use tools like Firebase, AWS Amplify, and Azure Mobile Apps for backend support. These platforms provide authentication, real-time databases, and cloud storage. These features are essential for Android apps.
Testing and deployment are also easier. Cloud testing platforms let you check performance on many Android devices without owning them. With CI/CD pipelines, you can release updates faster.
If you build an Android app today, adding cloud features is almost required. It ensures better scalability, user experience, and reliability. Cloud-based Android app development isn’t a trend—it’s becoming the standard.
Challenges
Cloud-based application development offers many advantages, but it’s not free of challenges. One of the most common issues is security. While cloud providers invest in strong protections, data breaches still happen. You need to set up proper encryption, access controls, and monitoring to keep apps safe.
Another challenge is cost management. Cloud pricing looks cheap at first, but expenses can rise. For example, if your app handles large amounts of data, storage and bandwidth fees can add up. Without tracking usage, you may face unexpected bills.
Vendor lock-in is another problem. Each cloud provider has unique tools and services. Once your app depends on them, switching platforms becomes expensive and time-consuming. This reduces flexibility in the long run.
Finally, there’s the issue of performance consistency. Cloud apps rely on internet connectivity. If users have poor connections, app performance may suffer. Developers need to optimize apps for many conditions, such as low bandwidth or sudden traffic spikes.
You should prepare for these challenges. Use cost calculators to predict expenses. Build apps with multi-cloud or hybrid strategies. Always apply strong data security practices. This way, you cut risks while enjoying the benefits of cloud-based app development.
Steps to Building a Cloud-Based Application
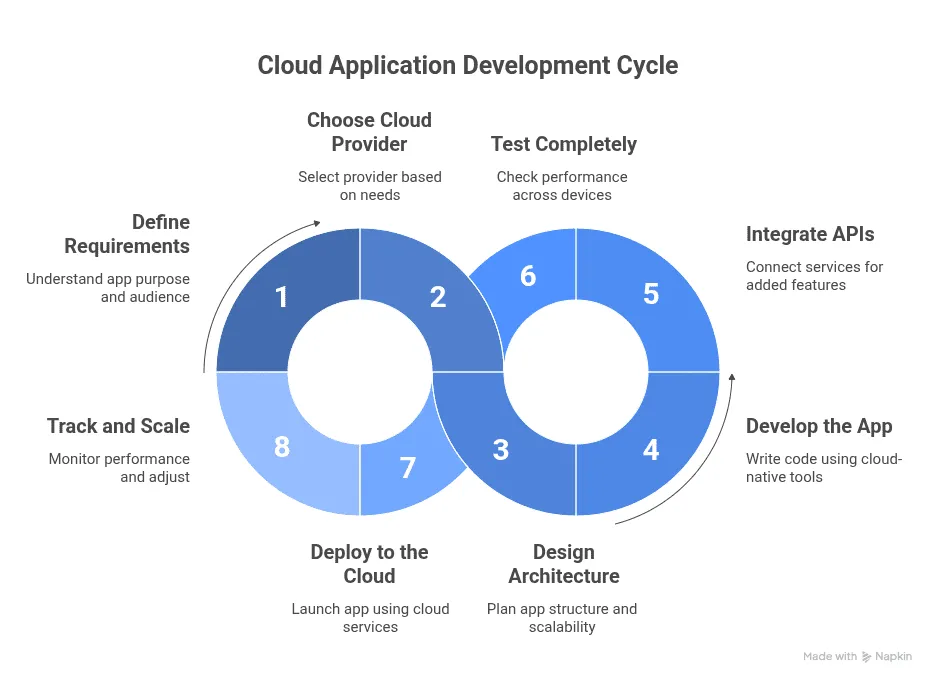
Building a cloud-based application involves a structured process. Here are the main steps:
- Define Requirements: Start by understanding the purpose of your app. Who is the target audience? What problem does it solve?
- Choose a Cloud Provider: Select AWS, Azure, or GCP based on your app’s needs, budget, and technical expertise.
- Design Architecture: Plan how the app will function. Decide on frontend, backend, storage, and APIs. Consider scalability from the start.
- Develop the App: Write code for the frontend and backend. Use cloud-native tools to speed up development.
- Integrate APIs: Connect services like payments, messaging, or analytics. APIs add useful features without building them from scratch.
- Test Completely: Use cloud testing tools to check performance across devices and regions. Fix bugs before launch.
- Deploy to the Cloud: Launch your app using services like AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine, or Azure App Service.
- Track and Scale: Track performance with dashboards. Use auto-scaling to handle traffic spikes.
Each step matters. Skipping testing or ignoring monitoring may cause failures. Following this roadmap ensures your app is reliable, scalable, and ready for real-world use.
Best Practices
To succeed with cloud-based application development, follow proven best practices.
- Design for Scalability: Always plan for growth. Use load balancing and auto-scaling to manage spikes in traffic.
- Focus on Security: Apply encryption for data at rest and in transit. Use identity and access management tools to control who can access resources.
- Automate Deployment: Use CI/CD pipelines. They speed up development, reduce errors, and make updates seamless.
- Optimize Costs: Track usage with tools like AWS Cost Explorer or Azure Cost Management. Choose reserved or spot instances when possible.
- Choose the Right Database: For structured data, go with SQL options. For flexible data, NoSQL is better. Match your choice to your app’s needs.
- Test for Performance: Simulate heavy loads. This shows how your app behaves under stress and helps avoid downtime during peak usage.
These practices may seem simple, but many projects fail because they ignore them. Following them builds a strong foundation for your app’s success.
Security Considerations in Cloud-Based Applications
Security is one of the top concerns for businesses adopting cloud-based app development. Even though providers like AWS and Azure invest in security, you must still take responsibility for your app.
Key practices include:
- Data Encryption: Always encrypt sensitive information. This applies to both storage and data in transit.
- Access Control: Set permissions. Not every user or developer needs full access to resources.
- Regular Monitoring: Use tools like AWS CloudTrail or Azure Security Center to track activity. Early detection of unusual behavior reduces risk.
- Compliance: If your app handles financial or health data, make sure it meets regulations like GDPR or HIPAA. Cloud providers offer compliance certifications, but you must configure systems properly.
- Backup and Recovery: Always prepare for data loss. Automated backups and disaster recovery plans protect your app from unexpected failures.
Think of security as a shared responsibility. The provider secures the infrastructure, but you control app settings, user access, and data protection. Neglecting these areas puts your app at risk.
Cost Management in Cloud-Based App Development
Managing costs is often overlooked in cloud-based application development. Businesses start small, but as traffic grows, so do expenses. Without a plan, budgets can spiral out of control.
One strategy is right-sizing resources. Don’t run large servers if your app only needs small ones. Adjust instances based on demand. Auto-scaling helps with this.
Another approach is using reserved instances. These are long-term commitments with cloud providers, often cheaper than on-demand pricing. If you know your usage will be steady, this saves money.
You should also track usage. Tools like AWS Cost Explorer, Azure Cost Management, or Google Cloud Billing give insights into spending. They show which services consume the most resources.
Finally, avoid unnecessary services. Many teams add tools they never use. Review services and remove what’s not needed.
By managing cloud expenses, you keep your app cost-efficient. This ensures growth doesn’t come with financial stress.
Case Studies
The real-world examples help us better visualize how cloud application development functions. Most of the popular apps rely upon cloud platforms due to speed, scaling, and consistency.
Take Netflix. The firm moved out of localized data centers to AWS. Today, it streams shows to millions of customers worldwide. The cloud services support Netflix by supplying content, providing recommendations, and managing heavy traffic without disrupting service.
Slack is another. The messaging service is hosted on cloud infrastructure. The scalable back end enables global collaboration, file sharing, and integration with thousands of third-party services.
Dropbox also shows the value of cloud adoption. At first, it used physical servers, then it switched to a hybrid cloud infrastructure. The former provided more cost management while offering easy storage and access to files.
The following are real-life cases that show that cloud apps are not ideas, but solutions. Each of these companies made use of the cloud in unique ways: scaling video, facilitating real-time chat, or storing huge datasets. You can emulate such measures in developing your app.
Future Trends in Cloud-Based Application Development
The cloud is evolving, and being up to date with trends is of importance to developers as it is to businesses. One of them includes serverless computing. Code is run without direct server management using functions like AWS Lambda or Google Cloud Functions. The cost decreases, as does development time.
Another trend is multi-cloud strategies. Organizations are no longer tied to one provider. Instead, workloads are distributed across AWS, Azure, and GCP to avoid vendor lock-in and create resilience.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are also driving cloud innovation. Cloud providers offer pre-assembled AI services like image generation, NLP, and predictive analysis. Apps that integrate these features gain a competitive edge.
Finally, edge computing is growing. It brings cloud resources closer to users, reducing latency. For example, apps for self-driving cars or IoT devices need fast, local processing. Edge computing makes this possible.
If you’re building apps today, consider these trends. They shape how cloud applications will function in the next five years.
Cloud-Native vs. Cloud-Enabled Applications
When you hear about cloud apps, you’ll often see two terms: cloud-native and cloud-enabled. They sound similar but are very different.
- Cloud-native apps are for the cloud. They use microservices, containers, and serverless architectures. These apps scale, recover, and update without downtime.
- Cloud-enabled apps are older apps moved to the cloud. They weren’t designed for it, so they don’t enjoy scalability or automation.
For example, an e-commerce site built with microservices and Kubernetes is cloud-native. But a legacy HR system moved from local servers to AWS is cloud-enabled.
If you’re starting fresh, aim for cloud-native. It gives you long-term flexibility and cost efficiency. But cloud-enabled apps are still useful for businesses that want to modernize without rebuilding systems.
Tools and Technologies
Developers have access to a wide range of tools for cloud-based application development. Choosing the right ones can speed up development and improve quality.
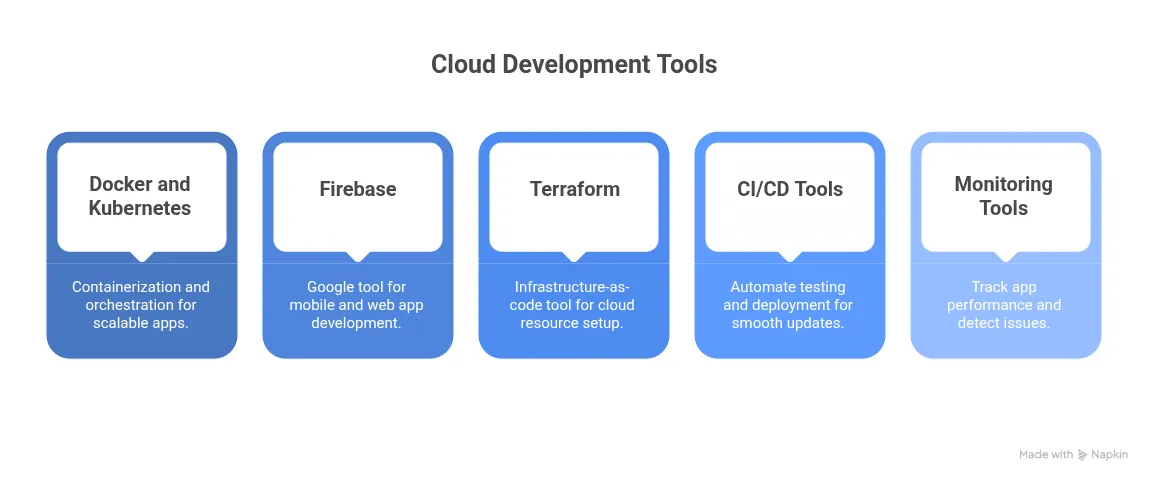
Some popular tools include:
- Docker and Kubernetes: These are essential for containerization and orchestration. They help apps scale and run across environments.
- Firebase: A Google tool for building mobile and web apps. It offers authentication, real-time databases, and cloud storage.
- Terraform: An infrastructure-as-code tool. It lets you set up cloud resources with simple configuration files.
- CI/CD Tools: Jenkins, GitHub Actions, and GitLab CI/CD automate testing and deployment. They ensure smooth updates.
- Monitoring Tools: Services like Datadog, Prometheus, or AWS CloudWatch track app performance and detect issues.
Using these tools reduces manual work. They help you build apps that are reliable, scalable, and easier to maintain.
How to Choose the Right Cloud Provider for Your App
Selecting a cloud provider is a critical step in cloud-based app development. Your choice affects performance, cost, and long-term flexibility.
Here are key factors to consider:
- Service Availability: Does the provider offer the services you need, such as AI, analytics, or IoT support?
- Pricing Model: Compare pay-as-you-go vs. reserved instances. Pick the model that matches your usage patterns.
- Integration: If your team already uses Microsoft tools, Azure may fit best. If data and AI are priorities, Google Cloud is strong.
- Global Reach: Check data center locations. If your users are worldwide, choose a provider with global coverage.
- Support and Documentation: Clear guides, tutorials, and community support make development easier.
Don’t just follow trends—pick the provider that aligns with your app’s goals. Sometimes a hybrid or multi-cloud setup may be the smartest option.
Conclusion
Cloud-based application development has transformed the way businesses build and scale software. When you move from on-premise systems to the cloud, you gain speed, flexibility, and lower costs. Cloud platforms support growth whether you build a web app or a mobile app.
We looked at the benefits, challenges, tools, and best practices. You also saw how companies use the cloud to deliver reliable services around the world. With serverless computing, multi-cloud strategies, and AI on the rise, the future of cloud development looks bright.
Your next step is clear: define your app’s needs, pick the right cloud provider, and start building. Focus on security, scalability, automation, and cost control to set your project on the right track.
Cloud-based application development is not only a trend. It’s the new standard. If you’re serious about building apps that last, the cloud is where you should be.
FAQs
Q1. What is the main advantage of cloud-based app development?
The main advantage is scalability. You can adjust resources to handle changes in user demand, all while keeping costs under control.
Q2. Which cloud provider is best for beginners?
Google Cloud (GCP) is intuitive, thanks to its clear documentation and free tier. AWS and Azure offer broader enterprise features.
Q3. Is cloud-based Android app development different from regular Android development?
Yes. Cloud-based Android apps rely on cloud storage, databases, and APIs instead of keeping everything local. This makes them more scalable and accessible.
Q4. How can I reduce cloud app development costs?
Track usage, use reserved instances, and right-size your resources. Also, remove unused services and set up auto-scaling to prevent waste.
Q5. What is the difference between cloud-native and cloud-enabled apps?
Cloud-native apps are especially for the cloud, using microservices and containers. Cloud-enabled apps are older apps migrated to the cloud with limited flexibility.