Table of Contents
Chatbots are computer programs designed to simulate conversation with human users, typically through text or speech. They use natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning algorithms to understand user inputs and generate appropriate responses. Chatbots can be programmed for various purposes, including customer service, information retrieval, entertainment, and more.
Core function: Provide information or complete tasks within a specific context, often related to customer service or sales.
Capabilities:
- Answer FAQs and troubleshoot basic issues.
- Gather user information and preferences.
- Direct users to relevant resources.
Strengths: Offer 24/7 availability, handle repetitive tasks efficiently, and personalize interactions to an extent.
Limitations: Reliant on predefined responses, may struggle with complex questions or nuanced requests.
Virtual assistants, on the other hand, are advanced chatbots equipped with artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities that enable them to perform tasks and provide services beyond simple conversation. They can assist users with a wide range of activities, such as scheduling appointments, setting reminders, searching the internet, controlling smart home devices, and even conducting complex transactions. Virtual assistants often integrate with other applications and services to offer seamless user experiences across different platforms and devices.
Core function: Act as a personal assistant, performing a wider range of tasks based on user needs.
Capabilities:
- Manage schedules and reminders.
- Control smart home devices.
- Make calls, send texts, and search the web.
- Integrate with various apps and services.
Strengths: More versatile and intelligent than chatbots, can learn user preferences and adapt responses.
Limitations: It may require more complex setup and training, and privacy concerns around data collection.
Evolution of AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants:-
The evolution of AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants has been marked by significant advancements in natural language processing, machine learning techniques, and the integration of new technologies. Over time, these developments have also given rise to the AI phone call assistant, a specialized form of virtual assistant designed to handle voice-based customer interactions more efficiently. Here’s an overview of their evolution:
Early Days (1960s-2000s): Simple Scripts and Rule-Based Systems
- ELIZA (1960s): Often considered the first chatbot, ELIZA mimicked conversation through pattern matching and pre-programmed responses. While groundbreaking for its time, it lacked true understanding.
- Rise of Rule-Based Chatbots (1970s-2000s): These chatbots followed decision trees and could handle basic tasks with predefined questions and answers. However, they often led to frustrating dead ends if the user strayed from the script.

The NLP Revolution (2000s-2010s): Understanding Human Language
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) Integration: The game changer! NLP allows chatbots to analyze sentence structure, semantics, and user intent behind the words. This enabled more natural conversations and less robotic interactions.
- Machine Learning Enters the Chat (2010s): Chatbots started learning from past interactions. They could identify user preferences and adapt responses, making interactions more personalized and efficient.
The Age of Virtual Assistants (2010s-Present): AI Companions
- Birth of Siri (2011): Apple‘s Siri marked a turning point. It was the first widely adopted virtual assistant using voice commands and offering a wider range of functionalities beyond customer service.
- Alexa and Google Assistant Join the Party (2010s): The competition heated up with Amazon‘s Alexa and Google Assistant entering the scene. These virtual assistants integrated seamlessly with smart home devices and offered even more sophisticated features.
The Future: Continuous Learning and Integration
- Advanced AI for Richer Interactions: As AI continues to evolve, so will chatbots, AI voicebots and virtual assistants. Expect a more nuanced understanding of human emotions, context-awareness, and the ability to handle complex requests.
- Focus on User Experience: The future lies in creating seamless and intuitive user experiences. Chatbots and virtual assistants will become more integrated with our daily lives, acting as true digital companions.
Purpose of implementing chatbots and virtual assistants in businesses:-
Businesses are increasingly adopting chatbots and virtual assistants (VAs) to enhance various aspects of their operations. Here’s a breakdown of the key purposes:
Enhanced Customer Service:
- 24/7 Availability: Chatbots provide first-line support, answering FAQs, troubleshooting common issues, and directing users to helpful resources, even outside of business hours.
- Increased Efficiency: Chatbots free up human agents from repetitive tasks, allowing them to focus on more complex customer interactions.
- Improved Lead Generation and Sales: Chatbots can qualify leads by gathering information and preferences, guiding users through the sales funnel, and even processing transactions.
- Personalized Support: Chatbots can personalize interactions to an extent, remembering past conversations and tailoring responses based on user data.
Streamlined Internal Operations:
- Employee Onboarding and Training: Chatbots can guide new hires through the onboarding process, answer questions, and provide access to relevant resources.
- Improved Task Management: VAs can manage employee schedules, set reminders, and automate tasks, boosting productivity.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Chatbots can collect valuable customer data during interactions, which can be used for market research, product improvement, and targeted marketing campaigns.
Overall Business Benefits:
- Cost Savings: Chatbots and VAs can significantly reduce customer service costs by handling a large volume of inquiries and automating tasks.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: Faster response times, 24/7 availability, and personalized interactions can lead to happier customers.
- Competitive Advantage: Businesses that leverage chatbots, WhatsApp Business API, and VAs effectively can differentiate themselves by providing a superior customer experience.
AI Chatbots vs. AI Virtual Assistants
Distinction between chatbots and virtual assistants:-
Chatbots and virtual assistants share similarities in their functionality but also have distinct characteristics that set them apart. Here’s a breakdown of the key distinctions between the two:
Scope of Functionality:
- Chatbots: Chatbots, often developed using an AI agent builder are primarily focused on facilitating conversations between users and systems. They are often designed to handle specific tasks or inquiries within a limited domain. For example, a chatbot on a retail website may assist customers with product inquiries, help them make purchases, or provide personalized recommendations through conversational AI in retail.
- Virtual Assistants: Virtual assistants are more comprehensive in their functionality and capable of performing a wide range of tasks beyond simple conversation. They can assist users with various activities such as scheduling appointments, setting reminders, providing weather updates, conducting internet searches, controlling smart home devices, and more.

Degree of Intelligence:
- Chatbots: Chatbots typically rely on predefined rules or scripts to respond to user inputs. While some chatbots incorporate basic machine learning algorithms to improve their performance over time, they are generally less sophisticated in their understanding of natural language and context.
- Virtual Assistants: Virtual assistants leverage advanced artificial intelligence (AI) technologies, including natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning, to understand user intents, context, and preferences. They can learn from interactions, adapt to user behavior, and provide more personalized and contextually relevant responses.
User Interaction Channels:
- Chatbots: Chatbots are often integrated into specific platforms or channels, such as websites, mobile apps, messaging applications (e.g., Facebook Messenger, WhatsApp), or customer service portals. Users interact with chatbots primarily through text-based interfaces.
- Virtual Assistants: Virtual assistants are designed to be multi-channel and multi-modal, meaning they can interact with users through various communication channels, including text, speech, and even visual interfaces. They are commonly found on smartphones, smart speakers, and other connected devices.
Use Cases:
- Chatbots: Chatbots are frequently deployed in customer service, sales, and support functions to automate repetitive tasks, handle inquiries, and assist users in completing specific tasks. Similarly, AI phone calls can be leveraged to streamline lead generation, appointment scheduling, and information retrieval.
Virtual Assistants: Virtual assistants have broader applications across personal and professional domains. They serve as digital aides, helping users manage their daily tasks, access information, and interact with digital services more efficiently. Virtual assistants are commonly integrated into smart devices, operating systems, and productivity tools.
Role of AI in propelling automation and productivity in service teams:-
AI is rapidly transforming the service industry, acting as a powerful engine for automation and boosting productivity in service teams. Here’s how AI is making waves:
Automating Repetitive Tasks:
- AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can handle a significant volume of routine inquiries and requests, freeing up service agents for more complex issues. This can include tasks like:
- Answering FAQs
- Resetting passwords
- Scheduling appointments
- Processing simple transactions
By automating these repetitive tasks, AI allows service teams to focus on higher-value interactions that require human empathy, judgment, and problem-solving skills.
Enhancing Customer Experience:
- AI chatbots can provide 24/7 availability, offering immediate support to customers whenever they need it.
- Virtual assistants can personalize interactions by remembering past conversations and tailoring responses to individual needs.
- AI-powered sentiment analysis can gauge customer emotions from text or voice interactions, allowing service agents to prioritize and address frustrated customers effectively.
These features contribute to a more positive and efficient customer experience.
Improving Efficiency and Accuracy:
- AI can automate data entry and analysis tasks, reducing human error and streamlining workflows.
- Machine learning algorithms can identify patterns and predict customer needs, enabling service teams to be more proactive in addressing issues.
- AI-powered scheduling tools can optimize agent workload and ensure appointments are distributed efficiently.
This translates to faster resolution times and improved service delivery.
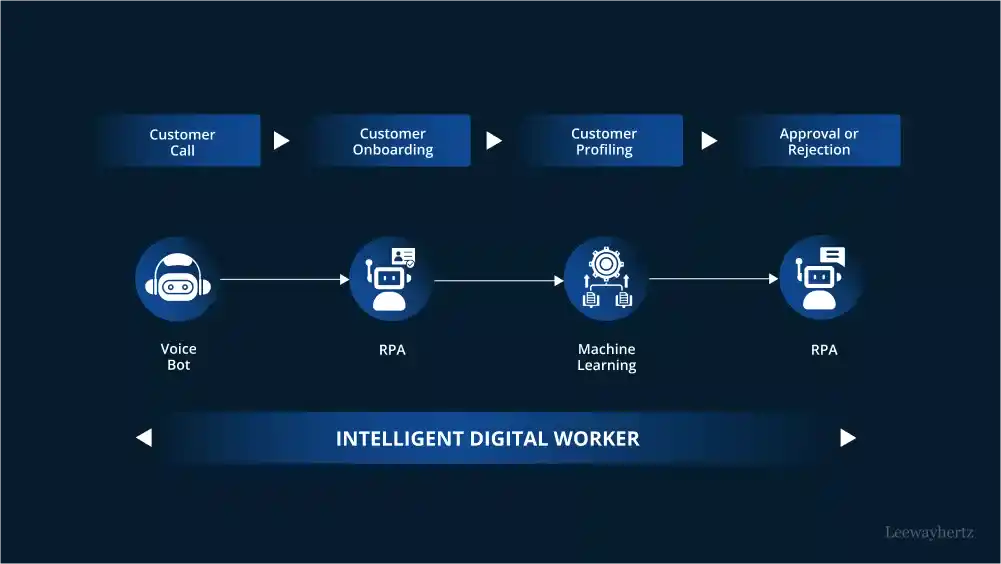
Upskilling the Workforce:
- AI can be a valuable training tool for service agents. Chatbots can simulate customer interactions, allowing agents to practice handling difficult situations.
- AI-powered insights can identify knowledge gaps within the team, enabling targeted training programs to bridge those gaps.
By empowering service agents with the right skills and knowledge, AI fosters a more competent and confident workforce.
Challenges and Considerations:
- The human element remains crucial: While AI automates tasks, the human touch is still vital in service interactions. Empathy, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence are irreplaceable qualities that AI cannot fully replicate.
- Data privacy and security: As AI relies heavily on customer data, ensuring data privacy and security is paramount. Service teams need to be transparent about data collection practices and implement robust security measures.
- Change management: The transition to AI-powered workflows requires careful change management. Service teams need to be involved in the implementation process and adequately trained to leverage AI effectively.
Advancements in AI Technology:-
Upgrading traditional chatbots to advanced AI assistants
Traditional chatbots, while helpful for basic tasks, often lack the sophistication and versatility of advanced GPT AI assistants. Upgrading them can significantly enhance their capabilities and user experience. Here’s a roadmap for this transformation:
1. Leveraging Natural Language Processing (NLP):
- Traditional chatbots rely on keyword matching and predefined responses, leading to stilted interactions.
- NLP empowers chatbots to understand the intent behind user queries, even if phrased differently. This allows for more natural and engaging conversations.
2. Integration of Machine Learning (ML):
- Traditional chatbots lack the ability to learn and adapt.
- Machine learning allows AI assistants to analyze past interactions, identify user preferences, and personalize responses over time. This fosters a more relevant and user-friendly experience.
3. Enhancing Context Awareness:
- Traditional chatbots often struggle with following the flow of conversation or referencing past interactions.
- Advanced AI assistants can remember past conversations and use context to provide more relevant and helpful responses.
4. Dialog Management and Conversational Design:
- Traditional chatbots may lead users down repetitive loops or dead ends if they stray from the script.
- Advanced AI assistants utilize dialog management techniques to navigate conversations smoothly and offer alternative solutions if a user’s request falls outside the initial scope. Conversational design principles ensure a natural flow of interaction.
5. Multimodal Communication:
- Traditional chatbots primarily interact through text-based interfaces.
- Advanced AI assistants can integrate voice commands, visual interfaces, and even sentiment analysis to create a more intuitive and engaging user experience.
Here are some additional considerations for the upgrade process:
- Data Collection and Training: Upgraded AI assistants require a robust training dataset that reflects real-world user interactions and language patterns.
- API Integration: Connect your AI assistant to other business applications and services to broaden its functionality and access relevant data for personalized responses.
- User Testing and Feedback: Continuously gather user feedback to identify areas for improvement and ensure the upgraded AI assistant meets user needs effectively.
Benefits of Upgrading to Advanced AI Assistants:
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: More natural and helpful interactions lead to higher customer satisfaction.
- Increased Efficiency: AI assistants can handle more complex queries, freeing up human agents for higher-value tasks.
- Enhanced Brand Image: A sophisticated AI assistant reflects a forward-thinking and customer-centric brand.
Examples of consumer-oriented virtual assistant AI like Siri and Alexa:-
Several consumer-oriented virtual assistant AI platforms exist, offering functionalities similar to Siri and Alexa. Here are some notable examples:
1. Google Assistant:
- Available on: Android devices, Google Home speakers, smart displays, and many other smart home devices.
- Strengths: Tight integration with Google services (search, maps, calendar, etc.), ability to handle complex requests and multi-step tasks, strong voice recognition capabilities.
- Weaknesses: It might feel less intuitive for non-Android users, and data privacy concerns due to Google’s vast data collection.
2. Bixby (Samsung):
- Available on: Samsung Galaxy smartphones, tablets, and some smart home appliances.
- Strengths: Deep integration with Samsung devices and ecosystem, can control smart home devices seamlessly, good at understanding natural language.
- Weaknesses: Limited compatibility compared to others, still under development compared to more established AIs.
3. Cortana (Microsoft):
- Available on: Windows 10 PCs, Xbox consoles, Android and iOS devices (with limited functionality).
- Strengths: Tight integration with Microsoft products (Office 365, Outlook, etc.), good for task management and reminders, works across multiple platforms.
- Weaknesses: Less feature-rich compared to Siri and Alexa, not as widely adopted by smart home device manufacturers.
4. Baidu Xiaoai (China):
- Available on: Primarily in China on Android devices, Baidu AI speakers, and various smart home devices.
- Strengths: Strong understanding of Mandarin Chinese, integrates with popular Chinese apps and services, well-suited for the local market.
- Weaknesses: Limited availability outside China, language barrier for non-Mandarin speakers.
5. AliGenie (Alibaba):
- Available on: Primarily in China on Alibaba’s smart speaker “Alibaba Genie” and some other smart home devices.
- Strengths: Integrates seamlessly with Alibaba’s e-commerce platform ([invalid URL removed], Taobao), good for online shopping and managing deliveries.
- Weaknesses: Limited availability outside China, language barrier for non-Mandarin speakers.
Core Functionality and Intelligence:-
Varying levels of intelligence between chatbots and virtual assistants:-
The intelligence levels of chatbots and virtual assistants can vary significantly based on their capabilities, functionalities, and underlying technologies. Here’s a breakdown of the varying levels of intelligence:
Basic Chatbots:
- Basic chatbots operate on predefined rules and scripts, providing static responses to specific keywords or commands.
- They have limited intelligence and cannot understand context or engage in meaningful conversations beyond their scripted capabilities.
- Basic chatbots are suitable for handling simple tasks such as answering FAQs, collecting user information, or providing basic customer support.
Rule-Based Chatbots:
- Rule-based chatbots are more sophisticated than basic chatbots and operate on predefined rules and decision trees.
- They can handle more complex interactions by following a set of rules to determine responses based on user inputs.
- However, rule-based chatbots lack the ability to learn from data or adapt to new scenarios, limiting their intelligence and flexibility.

Machine Learning-Powered Chatbots:
- Machine learning-powered chatbots leverage AI algorithms to analyze data and learn from user interactions over time.
- They can improve their performance and accuracy by continuously refining their language understanding and response generation capabilities.
- These chatbots have a higher level of intelligence than rule-based systems and can provide more personalized and contextually relevant responses.
Virtual Assistants:
- Virtual assistants are advanced AI-powered agents capable of performing a wide range of tasks and interacting with users in natural language.
- They leverage advanced NLP, machine learning, and AI techniques to understand user intents, context, and preferences.
- Virtual assistants can learn from user interactions, adapt to new situations, and provide personalized recommendations and assistance across various domains.
- They have a higher level of intelligence compared to traditional chatbots and can perform tasks such as scheduling appointments, making recommendations, and controlling smart home devices.
Conversational AI Platforms:
- Conversational AI platforms provide tools and frameworks for building highly intelligent chatbots and virtual assistants.
- They incorporate advanced AI capabilities such as context management, sentiment analysis, entity recognition, and multi-turn conversation handling.
- These platforms enable developers to create intelligent conversational experiences that mimic human-like interactions and adapt to user needs dynamically.
Applications and Capabilities:-
Multilingual capabilities of AI chatbots and virtual assistants:-
Multilingual capabilities are becoming increasingly important for AI chatbots and virtual assistants (VAs) as businesses strive to reach a global audience. Here’s a breakdown of what you need to know:
Benefits of Multilingual Chatbots and VAs:
- Break Down Language Barriers: Reach a wider customer base and provide support in their native language, fostering trust and better communication using the WhatsApp Business API.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Cater to diverse audiences by offering communication in their preferred language, leading to higher satisfaction.
- Expand Market Reach: Open doors to new markets and demographics, allowing businesses to operate on a global scale.
- Improved Brand Image: Demonstrate inclusivity and cultural sensitivity, projecting a positive brand image.
How Multilingual Capabilities Work:
- Machine Translation: This is the most common approach. Chatbots and VAs use machine translation engines to convert user queries from one language to another and vice versa. Advancements in machine translation are leading to more accurate and natural-sounding conversations.
- Multilingual Knowledge Base: The system needs to have access to information and responses pre-translated into different languages to respond effectively. This requires careful planning and ongoing content creation.
- Language Detection: The AI must be able to identify the language used by the user and switch accordingly. This often involves analyzing the first few words or sentences of the interaction.
Current State of Multilingual Capabilities:
- Progress, but Not Perfect: Machine translation has come a long way, but it can still struggle with slang, idioms, and complex sentence structures. Nuances of humor or cultural references might also get lost in translation.
- Limited Languages: While some chatbots and VAs support dozens of languages, others may only offer a handful. The most commonly supported languages are major global languages like English, Spanish, Mandarin Chinese, French, etc.
- Focus on Accuracy and Fluency: The goal is to provide clear and understandable communication, even if it’s not always perfectly natural-sounding.
Important Considerations:
- Target Audience: Identify the languages most relevant to your customer base and prioritize those for your chatbot or VA.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Ensure translations are culturally appropriate and avoid potential misunderstandings.
- Testing and Training: Test the multilingual capabilities thoroughly to identify and address any issues before deployment. Train your AI assistant on data that reflects the languages you plan to support.
- Continuous Improvement: Machine translation and NLP are constantly evolving. Stay updated and consider retraining your AI assistant with new language data as needed.
The Future of Multilingual AI Assistants:-
We can expect advancements in several areas:
- More Accurate and Natural-Sounding Translations: As machine learning techniques improve, translations will become more nuanced and capture the subtleties of human language.
- Context-Aware Language Processing: AI assistants will be able to consider the context of the conversation and cultural background to deliver more accurate and relevant responses.
- Multilingual Voice Assistants: Voice assistants will be able to understand and respond to user queries in multiple languages, providing a truly global user experience.
Simplifying workplace efficiency and improving productivity:-
In today’s fast-paced work environment, simplifying workplace efficiency and improving productivity are constant goals. Here are some key strategies to achieve them:
Streamlining workflows:
- Identify repetitive tasks: Analyze current workflows to pinpoint repetitive tasks that can be automated or simplified. This could involve using project management tools or workflow automation software.
- Standardize processes: Develop clear and consistent procedures for common tasks. This reduces confusion and ensures everyone is on the same page.
- Utilize technology: Invest in tools that can streamline communication, collaboration, and data management. This can include cloud storage solutions, project management platforms, and communication apps.
Empowering employees:
- Invest in training and development: Provide employees with the skills and knowledge they need to perform their jobs effectively. This can involve training on new technologies, soft skills development, and leadership training.
- Promote communication and collaboration: Create a culture of open communication and collaboration. Encourage teamwork and knowledge sharing to tackle complex projects and solve problems efficiently.
- Provide the right tools: Equip employees with the necessary tools and resources to do their jobs effectively. This includes hardware, software, and access to relevant information.
Optimizing the work environment:
- Minimize distractions: Create a work environment that minimizes distractions and allows for focused work. This could involve designated quiet zones, time management techniques, or noise-cancellation headphones.
- Promote well-being: Encourage healthy habits and work-life balance. This can involve flexible work arrangements, breaks for physical activity, and access to mental health resources.
- Embrace flexibility: Consider offering flexible work schedules or remote work options to accommodate different work styles and personal needs.
Additional Strategies:
- Set clear goals and expectations: Ensure everyone understands the goals and expectations for their role and the team as a whole. This helps individuals prioritize tasks and work effectively.
- Track progress and measure results: Monitor progress towards goals and measure the impact of implemented changes. This allows for adjustments and continuous improvement.
- Recognize and reward accomplishments: Acknowledge and reward employees for their contributions and accomplishments. This fosters a positive work environment and motivates employees to strive for excellence.
Conclusion:-
Overall, chatbots and virtual assistants are not just trends, but impactful tools shaping the future of business-to-customer interactions and internal operations. As AI technology continues to evolve, we can expect these virtual assistants to become even more sophisticated and integrated into our daily lives.
However, it’s important to remember:
- The human element remains crucial: Empathy, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence are irreplaceable qualities that AI cannot fully replicate.
- Data privacy and security: As AI relies heavily on customer data, ensuring data privacy and security is paramount.
- Ethical considerations: As AI assistants become more ingrained in society, ethical considerations regarding bias and transparency need to be addressed.