Table of Contents
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s a present-day business imperative. Whether it’s responding to customer inquiries, automating internal processes, or driving strategic decisions, AI is enabling businesses to be more efficient and effective.
Central to this transformation are two types of AI systems: AI assistants and AI agents. While both are powerful, their purposes, capabilities, and business applications differ significantly. For business leaders seeking to make informed decisions about AI adoption, understanding these differences is essential.
What Are AI Agents?
- An artificial intelligence (AI) agent autonomously performs tasks for a user or another system.
- It designs its workflow and uses available tools.
- AI agents make decisions, solve problems, interact with environments, and execute actions.
- They sense their environment and apply data for informed decisions.
- Humans set goals, but AI agents independently choose the best actions to achieve them.
- They show reasoning, planning, and memory, learning and adapting over time.
- Generative AI and foundation models provide their multimodal capacity, processing text, voice, video, audio, and code.
- Agents can work with other agents to complete complex workflows.
Types of AI Agents
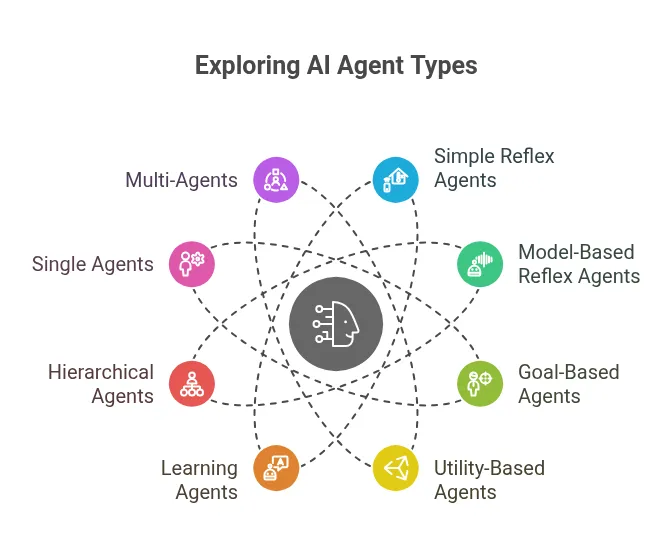
AI agents come in various forms, each suited for different applications:
- Simple reflex agents act solely on the current environment’s state. They follow predefined rules. If the agent encounters an unprepared situation, it cannot respond. An example is a thermostat that turns on the heating at a set time each night.
- Model-based reflex agents use current perception and memory to maintain an internal world model. They update their model with new information. Their actions depend on this model, reflexes, previous precepts, and current state. A robot vacuum cleaner that maps cleaned areas and adjusts around obstacles serves as an example.
- Goal-based agents have an internal world model and a set of goals. They search for and plan action sequences to reach their goals. A navigation system recommending the fastest route illustrates this type.
- Utility-based agents choose action sequences that reach goals and maximize utility or reward. A utility function assigns a value to each scenario based on criteria like goal progression or time. For example, a navigation system that selects a route minimizing fuel cost, traffic, and tolls is a utility-based agent.
- Learning agents possess the capabilities of other agent types but can learn autonomously. New experiences enhance their initial knowledge base. They learn from their environment through precepts and sensors. E-commerce personalized recommendations that track user activity and preferences are learning agents.
- Hierarchical agents are an organized group of agents in tiers. Higher-level agents break down complex tasks for lower-level agents.
- Single agents operate independently to achieve specific goals, often suited for well-defined tasks.
- Multi-agents are multiple AI agents that collaborate or compete to achieve common objectives. They combine diverse capabilities for complex tasks.
How Does an AI Agent Work?
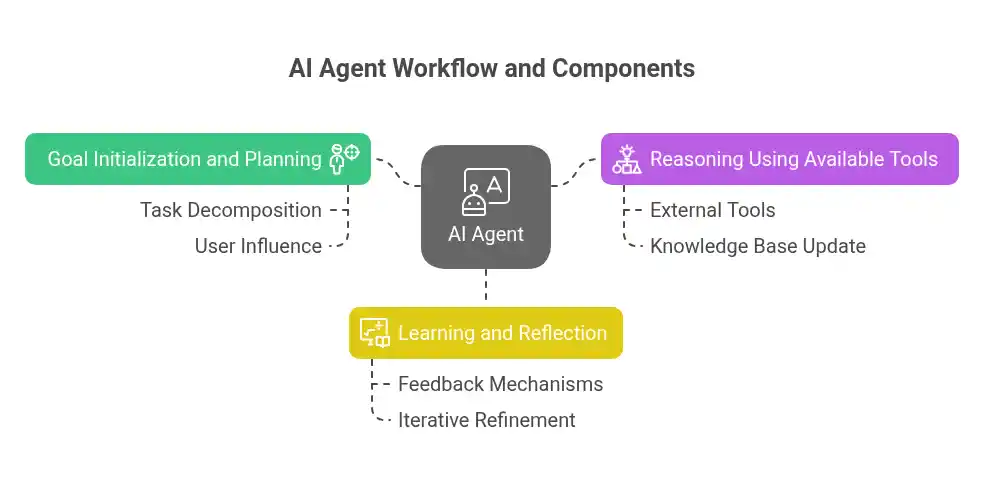
- Large language models (LLMs) are at the core of AI agents. They use external tools, analyze data, generate subtasks, and store memory to adapt over time. Many of the best ai agents follow three major stages:
- AI agents use tools to obtain current information, streamline workflows, and create subtasks autonomously.
- They adapt to user expectations over time by storing past interactions in memory and planning future actions.
- Tool calling occurs without human intervention.
AI agents often work through these three stages or components:
- Goal initialization and planning: AI agents need human-defined goals and rules. Developers, deployers, and users influence agent behavior. The agent performs task decomposition, creating a plan of tasks and subtasks for complex goals. For simple tasks, planning is unnecessary; agents iteratively improve responses without planning next steps.
- Reasoning using available tools: Agents base their actions on perceived information. They use external tools like datasets, web searches, APIs, or other agents to retrieve missing information. They update their knowledge base and reassess their plan, self-correcting for informed decisions. For example, an agent planning a vacation gathers weather data and consults a surfing agent to determine optimal surfing conditions. This information sharing makes AI agents general-purpose.
- Learning and reflection: AI agents use feedback mechanisms, including other AI agents and human-in-the-loop (HITL), to improve response accuracy. They store learned information and user feedback for future performance. Multi-agent feedback reduces human direction time. This continuous improvement is iterative refinement. Agents store solutions to past obstacles to prevent repeating mistakes.
What Are the Benefits of Using AI Agents?
- Task automation: AI agents automate complex tasks that would otherwise require human resources. You achieve goals rapidly and at scale.
- Increased productivity: AI agents streamline tasks, reducing time and effort. You can delegate repetitive tasks, focusing on creative activities.
- Cost reduction: Agents reduce unnecessary costs from process inefficiencies, human errors, and manual processes.
- Informed decision-making: Advanced agents use machine learning to process large amounts of real-time data. This allows you to make better predictions when strategizing.
- Enhanced customer experience: AI agents personalize product recommendations and provide prompt responses. This improves customer engagement and loyalty.
- Greater performance: Multi-agent frameworks outperform singular agents. They combine knowledge and feedback from other agents, facilitating information synthesis.
- Quality of responses: AI agents provide more comprehensive, accurate, and personalized responses than traditional AI models. They achieve this by exchanging information with other agents, using external tools, and updating their memory.
- Improved code quality: Agents automate repetitive tasks and provide recommendations for cleaner, reliable code.
- Security enhancements: AI agents proactively detect and mitigate threats, reducing vulnerability risks.
Difference Between AI Agent and AI Model
- An AI agent is an autonomous system or program that performs tasks, makes decisions, and adapts to its environment. It can initiate actions and design its own workflows.
- An AI model is a mathematical representation of a problem used to make predictions or decisions.
- AI agents often use AI models, such as large language models (LLMs), as their core or “brain” to understand, reason, and act.
- An AI agent possesses a higher degree of autonomy than an AI model. While an AI model provides predictions, an AI agent takes action based on those predictions.
- For example, ChatGPT is a conversational assistant that uses AI models to generate responses, but it is not an AI agent on its own because it does not perform autonomous actions.
1. Defining AI in the Business Context
- AI Assistants: AI Assistants are digital helpers designed to interact with users via text or voice interfaces. They support productivity by responding to commands, handling customer interactions, scheduling meetings, or retrieving data. Popular examples include Google Assistant, Siri, and enterprise chatbots like Intercom or Drift.
- AI Agents: AI Agents go a step further. These are autonomous entities capable of perceiving their environment, making decisions, and acting upon them without continuous human input. Increasingly, businesses are leveraging white label AI agents—customizable, brandable solutions that use machine learning, natural language processing, and reinforcement learning to adapt to dynamic environments and execute complex tasks with minimal oversight.
While AI assistants are tools that support human effort, AI agents can function as semi-independent actors within a system, handling workflows, monitoring performance, and making improvements in real time.
2. Business Applications of AI Assistants
AI assistants can be the first step into automation for many organizations. Here’s how they’re transforming various departments:
- Customer Support: AI assistants are widely used in customer service, automating responses to FAQs, initiating troubleshooting protocols, and escalating cases when needed. This ensures 24/7 availability and quick response times.
- Sales and Lead Generation: Sales chatbots qualify leads, ask questions, provide product suggestions, and even book meetings with sales reps, freeing human employees to close deals.
- HR and Recruitment: AI assistants can schedule interviews, answer employee questions about benefits, and guide new hires through onboarding.
- Marketing Campaigns: From crafting personalized email sequences to managing social media posts, AI assistants help marketers improve efficiency and maintain consistency.
3. Business Applications of AI Agents
AI agents are suited for more complex use cases where automation, adaptability, and decision-making are key.
- Supply Chain Optimization: AI agents predict demand fluctuations, manage inventories, and choose optimal shipping routes. Companies like Amazon rely on such agents for real-time decisions.
- Financial Services: Autonomous agents can detect fraud, automate investment portfolio rebalancing, and forecast cash flows. They’re helping institutions reduce errors and increase ROI.
- Healthcare: Agents analyze patient records, recommend personalized treatments, and flag anomalies that may indicate deteriorating health.Manufacturing and Maintenance: Predictive maintenance agents monitor equipment and schedule maintenance before breakdowns occur, minimizing downtime and costs.
4. Strategic Benefits of Adopting AI Agents and Assistants
- Increased Efficiency: AI systems process data and perform tasks faster than humans, resulting in massive time savings.
- Scalability: AI allows businesses to scale services without proportionally increasing workforce.
- 24/7 Operations: Unlike human employees, AI doesn’t need breaks, offering continuous support and monitoring. Many businesses are now implementing 24/7 phone answering services powered by AI to ensure no customer call goes unanswered, regardless of time zone or business hours.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Both assistants and agents analyze large volumes of data to provide real-time, actionable insights.Cost Reduction: Automation leads to lower operational costs over time, especially when repetitive or analytical tasks are handled by AI.
5. Implementation Guide for Business Leaders
- Step 1: Audit Your Current Processes Start with identifying repetitive tasks, high-volume service interactions, or areas needing real-time data analysis.
- Step 2: Define Objectives Are you looking to cut costs, improve customer experience, or optimize operations? Your goals will determine your AI path.
- Step 3: Choose Between Assistant and Agent Use AI assistants for customer-facing tasks or internal productivity boosts. Choose agents for real-time decision-making, operations, or logistics automation.
- Step 4: Build or Buy? Some AI systems can be purchased off-the-shelf, while others require custom development. When building custom solutions, AI Agent Frameworks can reduce engineering overhead by providing reusable patterns for planning, tool calling, evaluation, and governance. SMEs may benefit from plug-and-play assistants, while enterprises might need tailor-made agents.
- Step 5: Data Strategy Clean, structured, and secure data is vital for AI success. Implement data governance policies early in the process.
- Step 6: Change Management Train employees, build trust in AI systems, and ensure transparent communication about how these tools will be used.Step 7: Measure ROI Set clear KPIs—cost reduction, lead conversion rate, NPS score improvement—and monitor progress continuously.
6. Real-World Case Studies
Retail – AI Assistant: A major fashion brand integrated an AI assistant into its e-commerce site, resulting in a 40% reduction in cart abandonment and a 25% increase in average order value.
Logistics – AI Agent: A shipping giant deployed AI agents for warehouse operations. These agents rerouted deliveries based on weather and traffic conditions, reducing delivery delays by 32%.
Healthcare – Combined Use: A hospital chain implemented AI assistants for appointment scheduling and AI agents for medical data analysis. This led to a 50% improvement in diagnosis turnaround time.Finance – AI Agent: A fintech firm uses AI agents to analyze customer behavior, detect potential fraud, and recommend products, saving over $1M annually.
7. Ethical and Legal Considerations
Data Privacy: Ensure GDPR, HIPAA, and other legal compliance when processing sensitive customer or patient information.
Bias and Fairness: Monitor AI models for biased outputs. Algorithms trained on incomplete or unbalanced data can produce unfair results.
Transparency: Opt for explainable AI, especially in sectors like finance and healthcare. Stakeholders should understand how decisions are made.Job Displacement: AI should be viewed as an augmentation tool. Offer training and redeployment opportunities to employees whose roles evolve due to automation.
8. Future Trends in Business AI
- Agentic Business Operations: Entire workflows managed by AI agents—from procurement to invoicing. This includes specialized applications such as agentic test management, where autonomous AI agents oversee and optimize testing processes in software development and quality assurance, enhancing efficiency and accuracy.
- Personalized AI Assistants: Employees having AI sidekicks to manage meetings, analyze performance, and recommend strategies.
- Cross-Platform Integration: Seamless integration of AI with existing business software (CRM, ERP, HRMS) for unified operations.
- No-Code AI Tools: Empowering business users to build custom AI applications without technical expertise.
- Digital Twins: AI agents modeling real-world business scenarios to simulate the impact of decisions before executing them. This trend is closely tied to advancements in AI agent development, enabling businesses to create more autonomous, intelligent, and adaptive systems.

Core Differences Between AI Agents and Assistants
| Feature | AI Assistant | AI Agent |
| Human Interaction | Required for most tasks | Minimal once deployed |
| Decision-making Ability | Follows pre-set rules | Learns and adapts autonomously |
| Examples in Business | Chatbots, virtual schedulers | Autonomous logistics, intelligent analytics |
| Complexity of Tasks | Simple, repetitive | Complex, multi-step, dynamic |
Conclusion
In the evolving digital landscape, AI assistants and agents aren’t just nice-to-haves—they’re critical business enablers. Assistants simplify interactions and enhance productivity, while agents bring autonomy, intelligence, and scale to core business operations. The key lies in identifying the right balance and roadmap for adoption.
For business leaders, the question is no longer “Should we use AI?” but rather, “How can we use AI most effectively to gain a competitive edge?”
FAQs
How can AI assistants improve customer service?
By offering instant responses, handling routine queries, and providing consistent support around the clock.
What are the cost implications of implementing AI agents?
While more complex and expensive upfront, AI agents often lead to significant ROI through automation, accuracy, and efficiency.
How to ensure data privacy when using AI solutions?
Use secure, compliant platforms, adopt encryption, anonymize sensitive data, and regularly audit AI systems for data governance.
Can AI agents work with existing business software?
Yes, modern AI agents can integrate via APIs and middleware with ERP, CRM, and other business platforms.
Which industries benefit most from AI adoption?
Retail, healthcare, logistics, finance, and customer service are among the top sectors reaping benefits from both AI agents and assistants.
Do small businesses benefit from AI too?
Absolutely. AI assistants are affordable and offer significant gains in productivity and customer service. Agents can be scaled as the business grows
How long does it take to implement an AI system?
Depending on complexity, assistants can go live in weeks; agents may require months of development, testing, and training.