Table of Contents
The rise of artificial intelligence has transformed how enterprises operate, but it has also introduced many security risks.
As AI systems become more autonomous, distributed, and powerful, traditional security approaches are proving inadequate.
Enter Zero Trust AI, the security framework that’s becoming the industry standard for protecting enterprise AI deployments in 2026.
What Is Zero Trust AI?
Zero Trust AI is a security model that applies the principle of “never trust, always verify” to artificial intelligence systems.
Just as Zero Trust Network Access revolutionized cybersecurity by eliminating implicit trust in users and devices, Zero Trust AI removes automatic trust from AI models, agents, users, and data access patterns.
In simple terms: every AI interaction, whether it’s a user querying a chatbot, a model accessing training data, or an autonomous agent executing a task, must be authenticated, authorized, and continuously monitored.
Nothing gets a free pass.
Traditional AI security relied on perimeter defenses: secure the data center, lock down the model repository, and trust everything inside.
But in 2026’s landscape of multi-cloud AI deployments, third-party model APIs, and autonomous agents that can access dozens of internal systems, the perimeter has dissolved.
Zero Trust AI acknowledges this reality and builds security into every layer of the AI stack.
Why Zero Trust AI Matters in 2026
Several converging trends have made Zero Trust AI not just relevant, but essential:
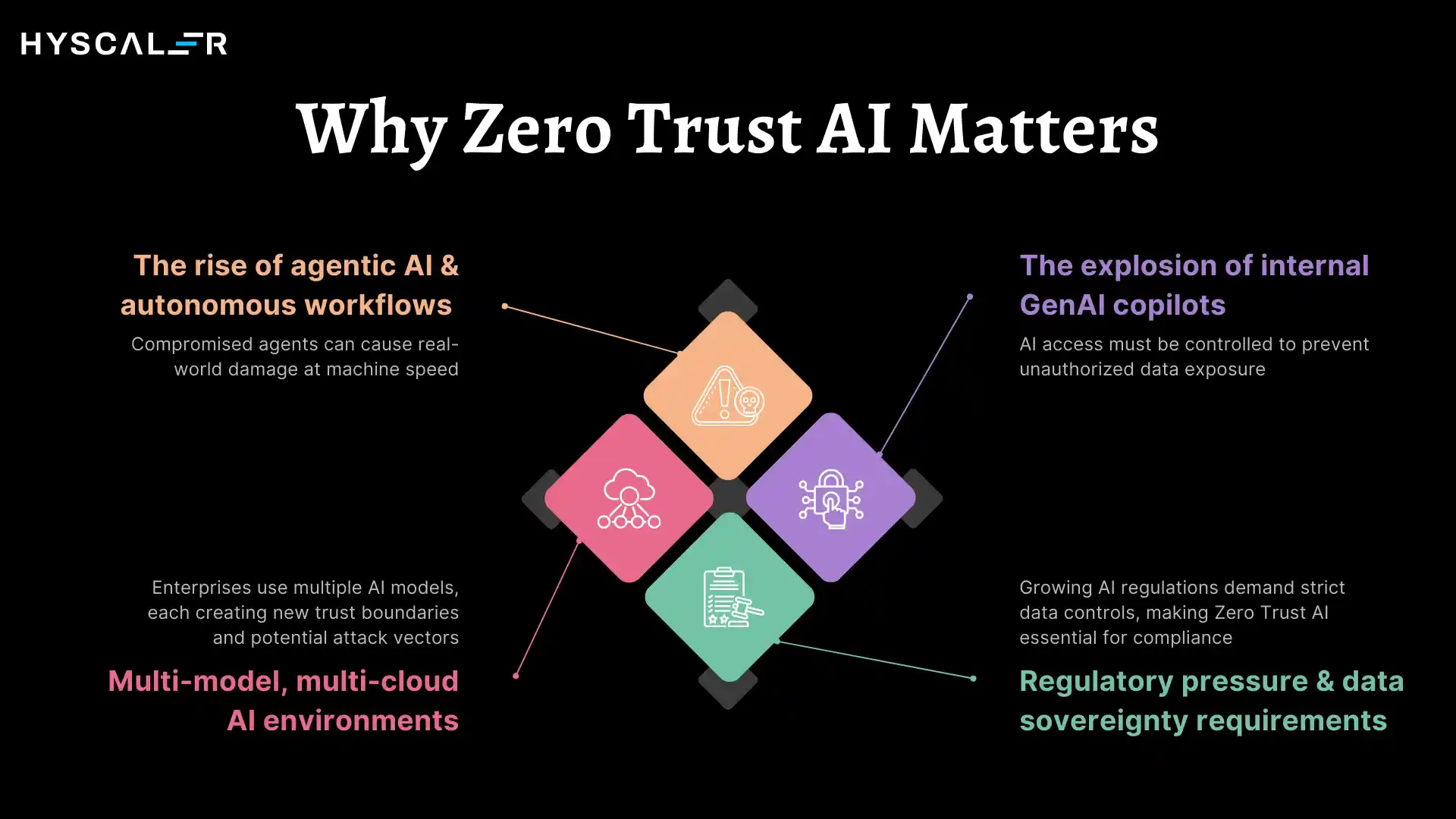
The rise of agentic AI and autonomous workflows has fundamentally changed the risk profile. Today’s AI systems don’t just answer questions; they book meetings, approve purchases, modify code, and manage infrastructure. A compromised or misconfigured AI agent can cause real-world damage at machine speed.
The explosion of internal GenAI copilots means nearly every employee now interacts with AI systems that have varying levels of access to company data. A marketing coordinator’s copilot shouldn’t be able to access payroll data, but without proper controls, it might.
Multi-model, multi-cloud AI environments are now the norm. Enterprises routinely use OpenAI for customer service, Anthropic’s Claude for research, internal fine-tuned models for specialized tasks, and open-source models for experimentation. Each represents a different trust boundary and potential attack vector.
Regulatory pressure and data sovereignty requirements continue to intensify. The EU AI Act, state-level AI regulations in the U.S., and industry-specific compliance frameworks all demand greater control over how AI systems access and process data. Zero Trust AI provides the technical foundation for meeting these requirements.
Core Principles of Zero Trust AI
Zero Trust AI is built on five foundational principles:
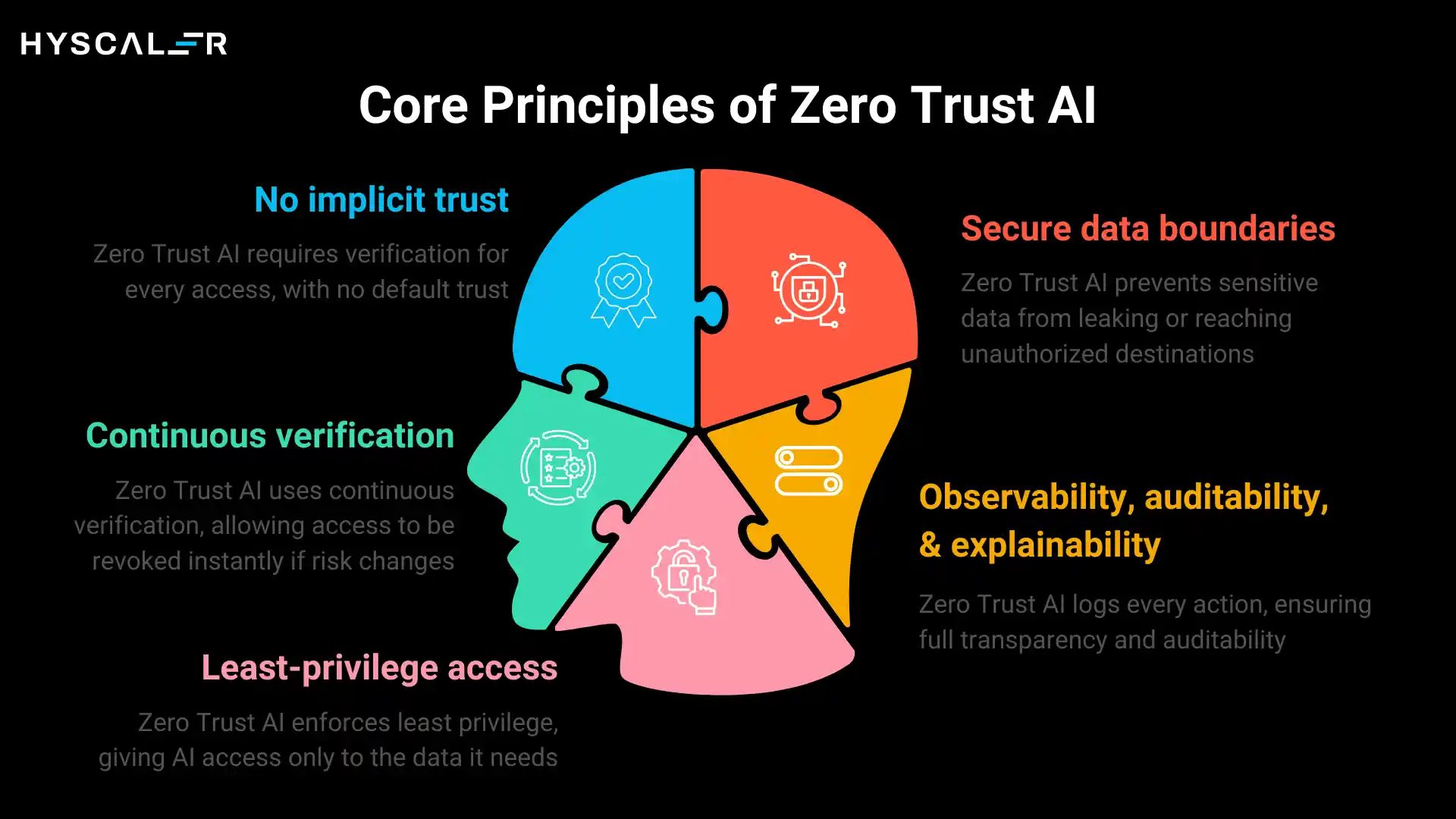
No implicit trust means that users, models, agents, and APIs all start with zero privileges. A model isn’t trusted simply because it’s hosted internally. An AI agent isn’t given full freedom just because the IT team deployed it. Every entity must prove its identity and authorization for each action.
Continuous verification replaces point-in-time authentication. It’s not enough to verify a user’s identity when they log in; their access rights and the AI’s behavior must be continuously evaluated throughout the session. If an AI agent’s behavior suddenly changes or a user’s risk profile shifts, access can be immediately revoked.
Least-privilege access ensures that AI systems have only the data and capabilities they need to perform their functions. A customer service chatbot should access the customer database, not the financial ledger. An HR copilot should see anonymized salary bands, not individual compensation details.
Secure data boundaries prevent data from flowing to unauthorized destinations. This includes technical controls that ensure training data doesn’t leak into model outputs, sensitive information isn’t cached improperly, and data subject to regulatory requirements never leaves designated environments.
Observability, auditability, and explainability create transparency into AI operations. Every prompt, model invocation, data access, and agent action is logged. When something goes wrong, or when regulators come asking, you have a complete record of what happened and why.
Zero Trust AI Architecture (High-Level)
Implementing Zero Trust AI requires rethinking AI infrastructure across several dimensions:
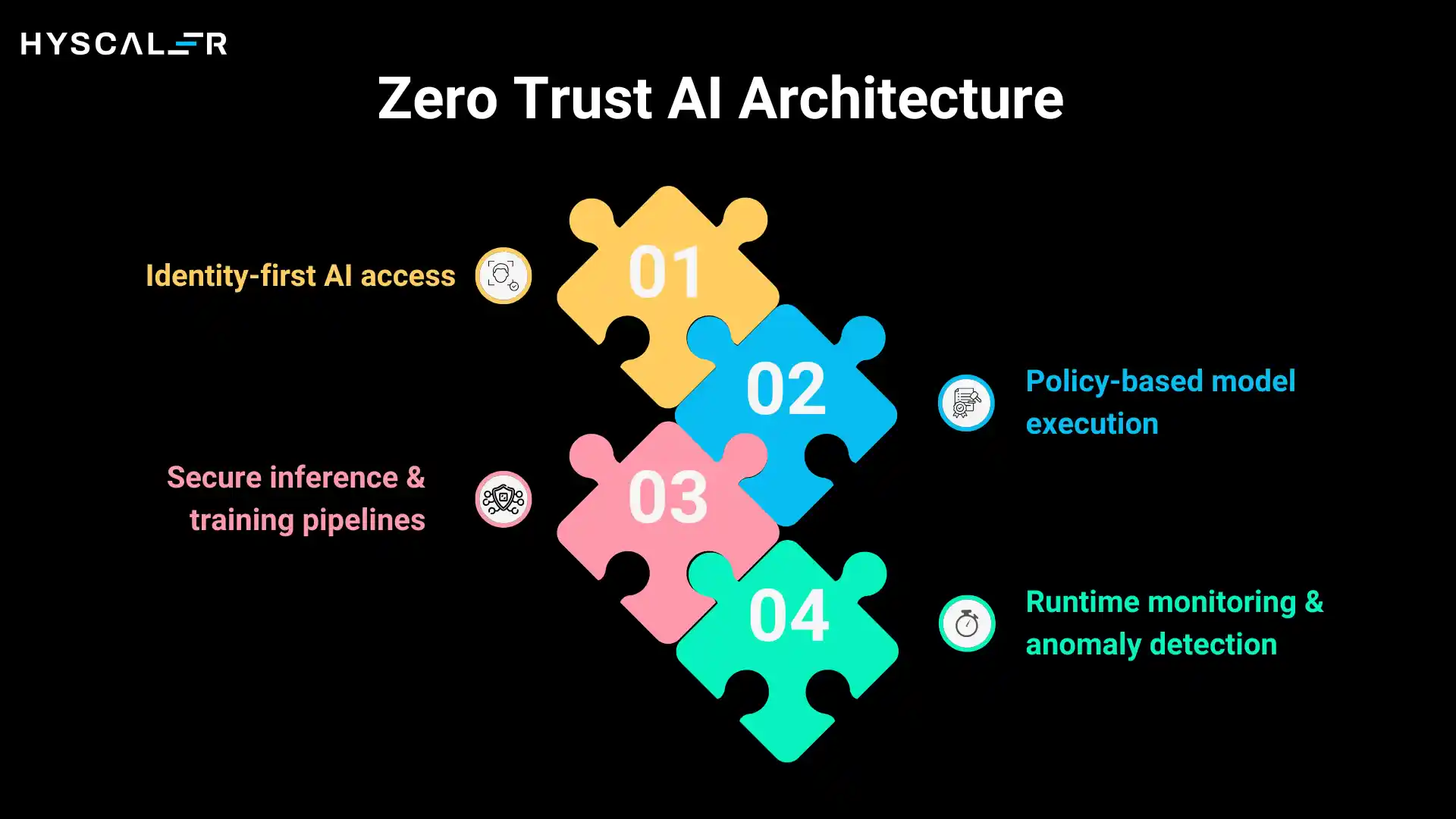
Identity-first AI access treats every interaction as an identity event. Users authenticate through enterprise identity providers, AI models are registered with unique identities and cryptographic signatures, and agents carry digital credentials that specify their capabilities and constraints. Before any AI operation executes, the system validates: Who is making this request? What are they authorized to do? Is this request consistent with their normal behavior?
Policy-based model execution replaces ad-hoc permissions with centralized policy engines. Instead of hardcoding access rules into applications, organizations define policies that govern which models can be used for which purposes, what data they can access, and what actions they can take. These policies are enforced at runtime, ensuring consistency across the entire AI estate.
Secure inference and training pipelines isolate AI workloads and apply defense-in-depth. Training data is encrypted at rest and in transit, models are trained in secure enclaves with access controls, and inference happens in isolated environments where inputs and outputs are monitored for data leakage or adversarial attacks.
Runtime monitoring and anomaly detection provide the continuous verification that makes Zero Trust possible. AI behavior is baselined, and deviations trigger alerts or automatic responses. If a model suddenly starts accessing unusual data patterns, if an agent attempts unauthorized actions, or if output quality degrades suspiciously, the system responds immediately.
2026 Enterprise Examples of Zero Trust AI
Real-world implementations demonstrate how Zero Trust AI works in practice:
Enterprise GenAI Copilots: Large enterprises deploy internal copilots for HR, finance, and engineering.
Zero Trust AI ensures employees only access role-approved data through intelligent context filtering.
When an engineer asks their copilot about a customer issue, the system verifies their role, checks which customer accounts they’re authorized to see, and filters the response accordingly.
Prompts and outputs are logged with full context, who asked, what they asked, what the AI returned, and what data was accessed.
Sensitive data never leaves approved boundaries through a combination of data loss prevention rules and secure multi-party computation techniques that allow AI to reason about sensitive data without ever exposing it directly.
Autonomous AI Agents in Operations: AI agents handle IT tickets, procurement, and cloud optimization tasks.
Zero Trust AI limits which tools an agent can use based on the task context.
A ticket-resolution agent can access the knowledge base and create service requests, but cannot modify production databases.
Every action is verified before execution through a policy engine that evaluates the agent’s request against organizational rules and risk thresholds.
The system prevents agent overreach or rogue behavior by implementing kill switches, action rate limits, and required human approvals for high-impact operations.
Financial Services AI: Banks apply Zero Trust AI to fraud detection and risk models.
Continuous model behavior validation ensures that models perform consistently and haven’t been poisoned or degraded.
Secure access to transaction data means models can analyze patterns without exposing individual customer information to analysts or other systems.
Full audit trails for compliance capture every model decision with sufficient detail to explain outcomes to regulators, including which data was considered, how the model weighted different factors, and what threshold was applied.
Healthcare AI Platforms: Clinical decision support systems must meet stringent privacy and safety requirements.
Zero Trust AI verifies the identity of both users (clinicians) and models (which clinical algorithms are approved for which use cases).
Patient data access controls ensure that AI can only process data for patients currently under a clinician’s care.
Data leakage prevention during inference stops protected health information from being inadvertently cached, logged, or transmitted to unauthorized systems.
Zero Trust AI vs AI Governance (Clear Comparison)
Many organizations confuse Zero Trust AI with AI Governance, but they serve complementary purposes:
| Aspect | Zero Trust AI | AI Governance |
| Focus | Security & access control | Policies, ethics & compliance |
| Scope | Runtime AI behavior | Organizational AI use |
| Core Question | “Can this AI do this right now?” | “Should this AI exist or be used?” |
| Enforcement | Technical & automated | Policy-driven & procedural |
| Examples | Identity checks, access limits | Bias rules, ethical guidelines |
Key Insight: Zero Trust AI implements security at runtime, while AI Governance defines rules and accountability.
Modern enterprises need both.
Governance sets the policy that a customer service AI shouldn’t make decisions about creditworthiness.
Zero Trust AI enforces that policy by blocking the AI’s access to credit scoring systems.
Zero Trust AI vs Traditional AI Security
The shift from traditional AI security to Zero Trust AI represents a fundamental change in approach:
Traditional security was perimeter-based, focusing on securing the boundary around AI systems, the data center firewall, the model repository access controls, and the API gateway.
Zero Trust AI is identity-based, securing individual transactions and continuously verifying that each participant is who they claim to be and is authorized for the specific action they’re attempting.
Traditional approaches relied on static controls set at deployment time: this model has access to this database, period.
Zero Trust AI implements continuous validation, constantly reassessing whether access should continue based on current risk levels, user behavior, and environmental factors.
Traditional security provided limited logs, often capturing only authentication events and major system changes.
Zero Trust AI demands full observability, recording every AI interaction with sufficient detail to detect anomalies, investigate incidents, and meet regulatory requirements.
Benefits of Zero Trust AI for Enterprises
Organizations implementing Zero Trust AI report significant advantages:
Reduced AI attack surface comes from eliminating standing privileges and over-permissioned systems. When AI components only receive the minimum access needed for each specific operation, attackers have fewer opportunities to exploit compromised credentials or vulnerable models.
Stronger data protection results from fine-grained access controls and continuous monitoring. Sensitive data breaches become harder because no single component has broad access, and unusual data access patterns trigger immediate investigation.
Safer autonomous AI adoption becomes possible when organizations have confidence that agents can’t go rogue. Business units that previously resisted AI automation due to security concerns become willing to deploy agents when they can verify and limit what those agents can do.
Better regulatory readiness flows from the comprehensive audit trails and control frameworks that Zero Trust AI requires. When regulators ask how an AI system made a particular decision or whether proper access controls were in place, organizations have detailed evidence readily available.
Higher stakeholder trust emerges when customers, partners, and employees see that AI systems are operating under strict security controls. Transparency about security measures builds confidence in AI deployments.
Challenges & Implementation Considerations
Despite its benefits, Zero Trust AI implementation isn’t without challenges:
Integration with existing MLOps can be complex. Organizations with mature ML pipelines must retrofit Zero Trust controls without disrupting production systems. This requires careful planning, staged rollouts, and often temporary parallel security frameworks during transition.
Performance overhead is a real concern. Every additional verification step adds latency. While well-designed Zero Trust AI systems minimize this impact through caching, async verification, and optimized policy evaluation, some performance trade-off is inevitable. Organizations must balance security requirements against user experience expectations.
Policy complexity grows quickly in large enterprises. When you have hundreds of AI models, thousands of users, and complex data access requirements, defining coherent and maintainable policies becomes challenging. Successful implementations invest in policy management tools and dedicate resources to policy governance.
Change management often proves harder than the technical implementation. Zero Trust AI requires new workflows, different mental models, and changes to how teams develop and deploy AI. Security teams, data scientists, and application developers must align on new practices and shared responsibilities.
Zero Trust AI Checklist (Quick Scan)
Organizations evaluating their Zero Trust AI readiness can use this quick assessment:
AI identity and authentication: Do all AI models, agents, and users have unique, verifiable identities? Can you trace every AI action back to a specific authenticated entity?
Role-based model access: Are permissions to use specific AI models tied to user roles and contexts? Can you prevent unauthorized users from accessing sensitive or powerful models?
Secure data pipelines: Do you have controls ensuring that data used for training and inference meets security requirements? Can you prevent sensitive data from flowing to unauthorized models or users?
Continuous monitoring: Are you logging and analyzing AI behavior in real-time? Can you detect and respond to anomalous AI actions before they cause damage?
Incident response automation: Do you have automated responses to policy violations? Can the system automatically revoke access, quarantine models, or escalate issues without human intervention?
The Future of Zero Trust AI
Looking ahead, Zero Trust AI is positioned to become the foundational security model for enterprise AI:
It will be the default standard for enterprise GenAI, with cloud providers and enterprise software vendors building Zero Trust principles into their AI platforms.
Just as HTTPS became the default for web traffic, Zero Trust will become the default for AI interactions.
Zero Trust AI will be mandatory for autonomous AI systems, as regulators and insurers require verifiable controls before allowing AI agents to operate with minimal human oversight.
Companies wanting to deploy autonomous AI for critical functions will need to demonstrate Zero Trust implementations.
It will serve as the foundation for regulated AI ecosystems, providing the technical infrastructure needed to meet compliance requirements across industries and jurisdictions.
As AI regulation matures, Zero Trust AI will be seen not as a competitive advantage but as table stakes.
Final Thoughts
Zero Trust AI is not optional in 2026; it is the security backbone for scalable, responsible, and enterprise-ready AI systems.
The question facing enterprises is not whether to adopt Zero Trust AI, but how quickly they can implement it.
As AI capabilities grow and attack surfaces expand, the organizations that have invested in Zero Trust frameworks will be positioned to capture AI’s benefits while managing its risks.
Those that haven’t will find themselves increasingly vulnerable, unable to satisfy regulatory requirements, and hesitant to deploy the autonomous AI systems that are becoming essential for competitive advantage.
The journey to Zero Trust AI begins with acknowledging that traditional security models are insufficient for modern AI systems.
It continues with investment in the identity, policy, and monitoring infrastructure that makes Zero Trust possible.
And it succeeds when security becomes not a constraint on AI innovation, but an enabler of it, giving organizations the confidence to deploy AI boldly because they know they can control it precisely.
FAQ
Can Zero Trust AI prevent AI hallucinations or bias?
Zero Trust AI focuses on security and access control, not model quality or fairness. It should be combined with AI governance to ensure AI systems are accurate, ethical, and used appropriately.
How do I get started with Zero Trust AI if my organization has no existing framework?
Start by inventorying AI systems, users, and data flows. Secure high-risk AI first with authentication, logging, and data access controls, then expand using a phased approach: secure, monitor, control, and automate.
What role does encryption play in Zero Trust AI?
Encryption protects AI data at rest, in transit, and in use, enabling secure processing without exposing plaintext. It complements access controls as part of a defense-in-depth strategy.
How does Zero Trust AI handle third-party AI APIs like OpenAI or Anthropic?
Zero Trust AI treats third-party APIs as untrusted, enforcing strict access control, data filtering, and logging. This enables secure AI use while protecting sensitive data.
Is Zero Trust AI only for large enterprises, or can small companies benefit?
Zero Trust AI isn’t just for large enterprises. Startups and small organizations using AI, especially with sensitive or regulated data, should adopt it, as cloud solutions make implementation accessible.
How does Zero Trust AI impact AI model performance?
Well-implemented Zero Trust AI adds minimal overhead, typically 10–50 ms per request. Performance is optimized using authentication caching, pre-authentication, and hardware acceleration.
Do I need to replace my existing AI security tools to implement Zero Trust AI?
Zero Trust AI builds on existing security by adding AI-specific identity controls, policies, and monitoring. It integrates with current network security, encryption, and DLP to enforce Zero Trust principles.
What’s the difference between Zero Trust Network Access and Zero Trust AI?
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) secures application access with “never trust, always verify.” Zero Trust AI extends this to AI, securing models, agents, and data.