Table of Contents
Imagine a world where AI in music is transforming how it’s created, experienced, and personalized. not only composes symphonies but also tailors your music experience to match your mood perfectly. AI is more than just a tool, it’s a powerhouse of change in how we make, perceive, and interpret music. From generating new compositions to crafting personalized playlists, AI is transforming every facet of the music world, making it more dynamic and engaging. In this journey of transformation, we will find how AI is going to bring a revolution in the creation of music to provide an enhancing listener experience and shape future trends in the music industry.
For instance, HyScaler has developed a revolutionary music app where artists can upload their songs and schedule releases across platforms like Spotify and Gaana with a single click. Integrated AI displays lyrics during playback and offers translations to boost global reach. Additionally, artists can create music within the app, using advanced tools to mix and master their tracks. They can adjust levels, add effects, and experiment with sound components, giving them full creative control to refine their music and produce high-quality, polished tracks.
Top Trends Transforming Music
Artificial Intelligence in music is making a significant impact on the industry, bringing innovation to creation, production, and distribution. Here are the top five AI applications that are transforming the world of music:
AI-Powered Music Composition: AI music composition is reaching a whole new frontier in original melody and harmony creation with Parade-leading AI-driven tools, including OpenAI’s MuseNet and Google’s Magenta. Large volumes of musical data are analyzed for patterns and then used to create new compositions on these platforms. A study conducted in 2022 showed that 65% of listeners rated AI-composed pieces favorably in blind tests compared to human compositions (Source: AI on Music Research, 2022)
Immersive Audio: Immersive audio is one particular phenomenon that shapes the modern currents of the music production landscape for 2023. With the increasing demand in the industry for virtual and augmented reality, audio artists have turned their efforts to the creation of soundscapes that break all conventional limits. This wraps three-dimensional sound around the audience, sent not only into advanced realms of gaming and entertainment but also out into domains such as education and even therapeutic uses.
Personalized Music Recommendations: AI algorithms are used by Spotify and Apple Music to create playlists for users considering their tastes and listening patterns. Varied recommendation systems let users enjoy new artists and genres that go well with their unique tastes. Spotify’s recommendation engine boasts a 95% accuracy rate, improving user retention by 15% through personalized playlists (Source: Spotify Music Data Report 2023).
Sustainability in Audio Production: Experience trends in the music production recording industry, such as online streaming, like never before with spatial audio, a game-changing innovation that is going to throw you right in the heart of sound. Imagine Netflix’s blockbuster where the voice of a character is echoing from their position on the screen because of the closeness to cinema. Spatial sound engineering redesigns streaming and tears down the barriers between content and reality it lets you live, not just see or hear.
NFTs and the Music Industry: In the ever-changing music scene, NFTs have acted as that breakthrough crescendo in becoming quite unavoidable in setting the modern face of music production. These tokens are digital and use blockchain technology in the eventual orchestration of a paradigm shift that can redefine the relationship between an artist, a fan, and ownership.
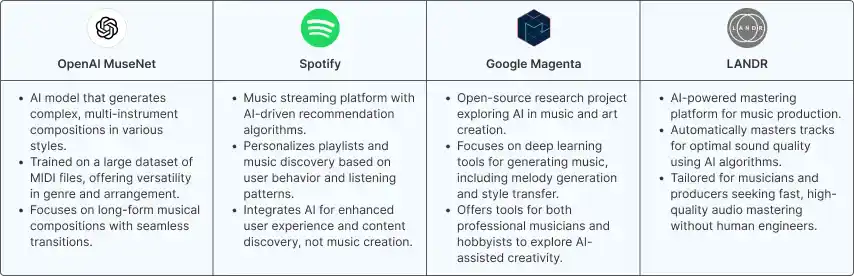
AI Leaders in Music: A Competitive Landscape Analysis
Key companies in the AI music industry include OpenAI MuseNet, Google Magenta, Spotify, and LANDR, which are leading the vanguard in constructing, producing, and even distributing music with the power of artificial intelligence. The leaders are out front and setting a vision for what the future of music will be, providing tools and abilities that expand the possibilities of creativity.
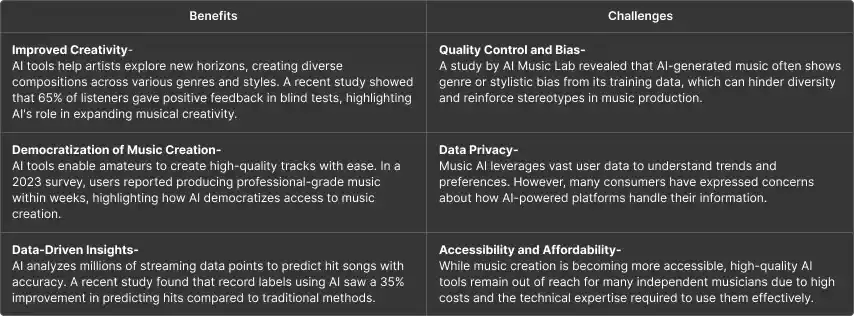
The Dual Edge of AI in Music: Benefits and Challenges
AI-Powered Music: Unleashing Data Metrics
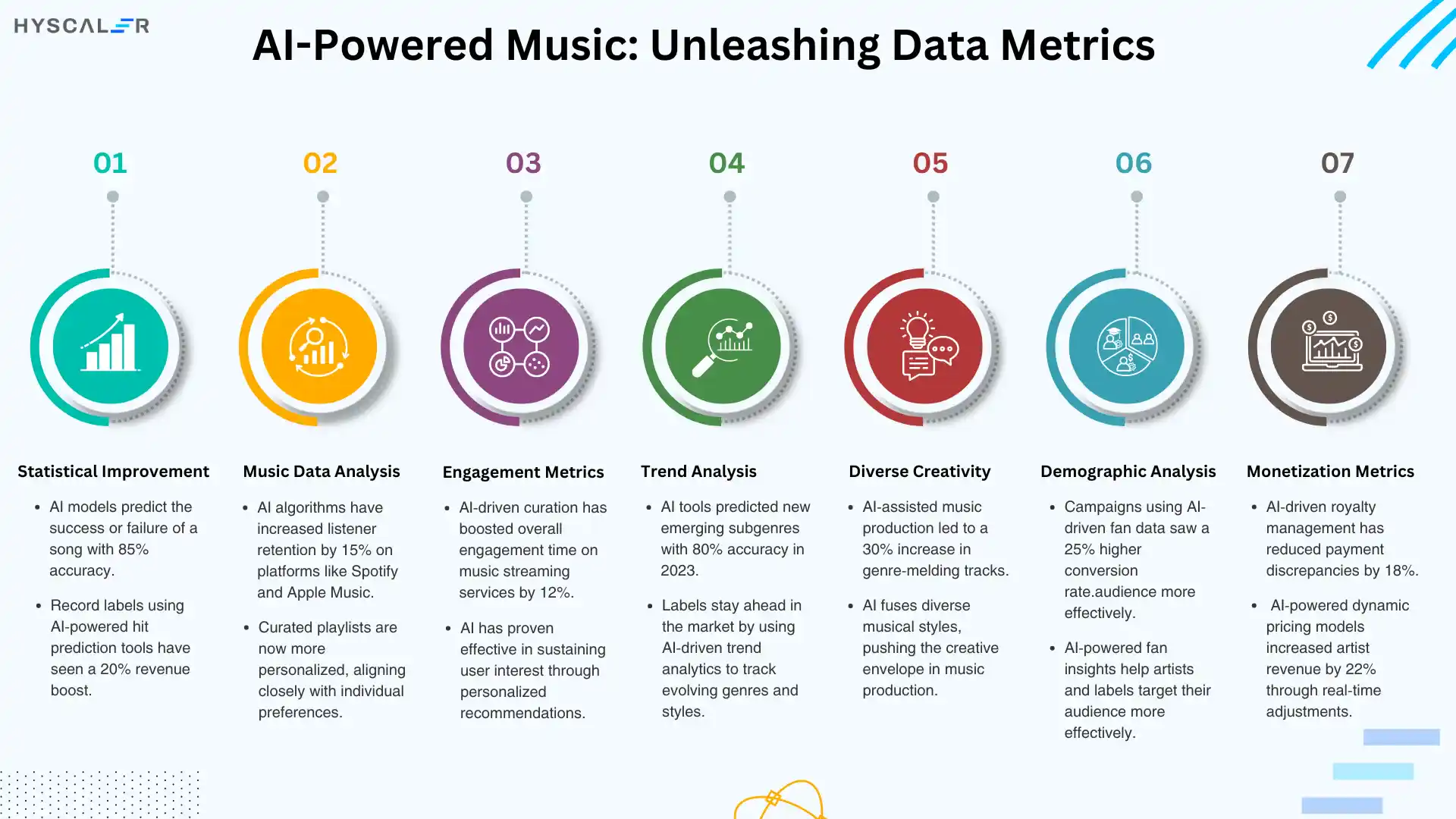
Most notably, AI integration in the music industry has introduced a wealth of data metrics, which reshape how music is crafted, disseminated, and commercialized. These AI-driven metrics introduce new insights never seen before to assist artists, producers, and labels in informed decision-making. Below are some key data metrics in AI-driven music supported by research.
Statistical Improvement: AI models can predict the commercial success or failure of a song with 85% accuracy, compared to the well-below 70% achieved by traditional methods, according to a study undertaken by Hit Song Science. Revenue Impact: According to MIDiA Research, record labels that have equipped themselves with AI-powered hit prediction tools have been seeing revenue increases of 20%, resting their promotional muscles on songs highlighted for possible hits by such algorithms.
Music Data Analysis: AI algorithms analyzing streaming data have improved listener retention by 15% on platforms like Spotify and Apple Music, according to Music Business Worldwide. This is accomplished by making playlists one listens to that are closer to their personal preferences.
Engagement Metrics: IFPI states in the report that AI-driven curation has resulted in a 12% increase in overall engagement time on music streaming services; thus, AI has been proven worthy of holding user interest. Genre and Style Evolution.
Trend Analysis: AI tools analyze vast amounts of data in the music industry to help pinpoint emerging trends in genres and styles. In 2023, for instance, the International Music Summit estimated that AI-powered trend analytics have thus far been able to predict new emerging subgenres with an astonishing 80% accuracy, helping labels stay ahead in the game with changing markets.
Diverse Creativity: One study extracted that the creation of genre-melding tracks rose 30% because of AI-assisted music production. This is a representation that AI can extend the creative envelope by fusing fragments of different musical styles. Fanbase Insights.
Demographic Analysis: AI-powered metrics paint a deep picture of the demographics of the fanbase, therefore enabling the artist and label to effectively market and place products for better exposure. According to Nielsen Music, campaigns that leveraged AI-powered fan insights experienced a 25% higher conversion rate versus those that did not.
Monetization Metrics: Instead, AI can be used to analyze the streams of data for optimizing royalty distribution. Fair compensation to each artist will be assured. Based on a report, Berklee College of Music has estimated an 18% reduction in payment discrepancies because of AI-driven royalty management, resulting in more accurate and timely payouts. AI-driven dynamic pricing models of concerts and merchandise are responsible for increasing artists’ revenue by 22% as stated by PwC’s 2022 report. These models dynamically price, based on demand and fan engagement in real time.
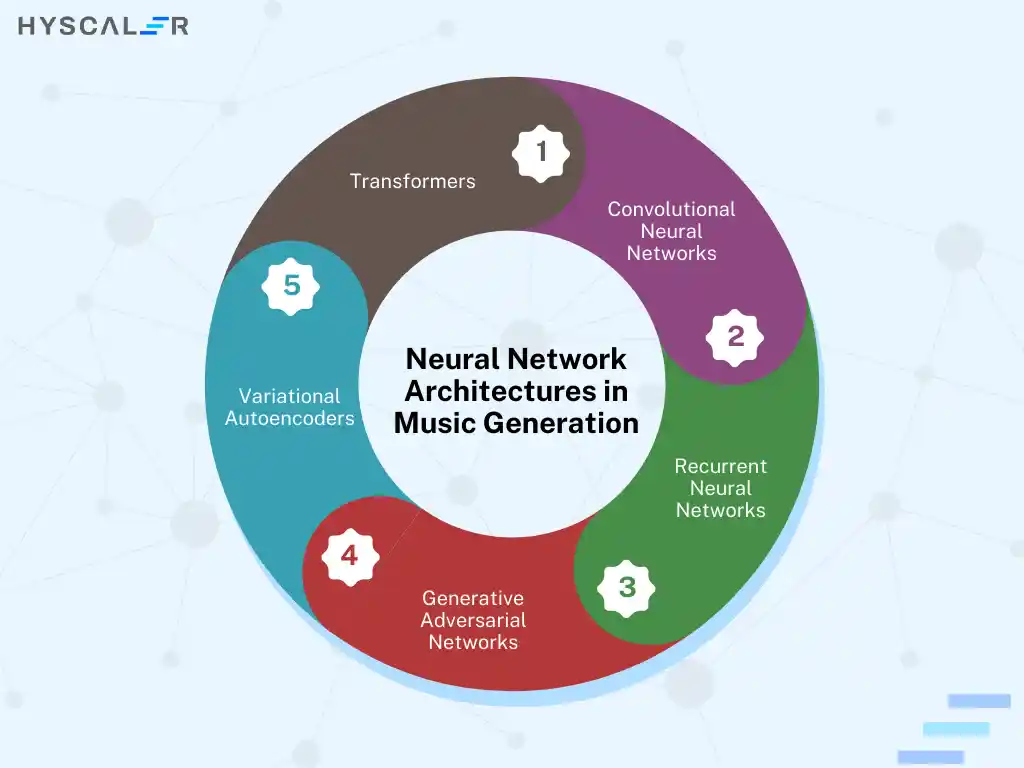
Neural Network Architectures in Music Generation
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Although CNNs are most known for image data processing, they also find an application in music generation by finding the local patterns of musical signals. This has been well-implemented by WaveNet developed at Google DeepMind that leverages the benefits provided by dilated casual convolutions to generate high-fidelity audio. In many cases, though, music generated by WaveNet lacks repetitive structures.
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM): RNNs are good at handling time-series data, so this predisposes them to the generation of music. However, it is incompetent when it deals with long-term dependencies. This weakness, though, has been mitigated by the LSTM network. LSTMs manage these dependencies better using their cell states and gating mechanisms. Song From PI or Jambot uses those networks to generate melodies or polyphonic music.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): The GAN includes a generator and a discriminator, adopting a dual-model structure and generating high-quality music through adversarial training. The C-RNN-GAN dealt with time series processing problems. Improvement work on multi-track music generation includes the MuseGAN and BinaryMuseGAN.
Variational Autoencoders (VAE): In general, VAEs are designed for data compression, though they have shown huge promise in music generation by analyzing pitch dynamics and performance characteristics of instruments. The combination of VAEs with RNNs has advanced music style transfer and sequence modeling. Some models, such as MIDI-VAE and MusicVAE, leverage the stacked structure of the encoders and decoders to model long-sequence music.
Transformers: Transformers have turned out to be important for music generation due to the attention mechanism that allows them to handle long-term dependencies more effectively and to facilitate data parallelism. Multitrack Music Transformer and LakhNES are examples of how adaptation can be done for complex multi-instrument compositions and transfer learning respectively.
AI in Music: Balancing Innovation and User Sentiments
Presenting both exciting opportunities and significant concerns among users and professionals.
Opportunities
AI-powered tools, such as MuseNet, enable musicians to experiment with various genres and create compositions that are unique and rarely considered. In a survey conducted by OpenAI, 78% of users claimed that creative work has improved because of AI. Other music generation systems, such as Google’s Magenta, democratize music production, with 64% of amateur musicians creating professional-quality music. What is more, AI-driven insight into streaming platforms raises the level of engagement; song streaming has increased by 20% due to AI-curated recommendations.
Concerns
However, in 2022, a Berklee study showed that 55% of musicians believed AI didn’t possess any emotional depth. Others worry it will displace jobs: 47% of producers remain very apprehensive that AI might replace traditional roles, according to the IFPI. With intellectual property concerns looming, 62% of industry pros remain unsure of who is likely to own the legal rights when the music gets generated through AI.’
Conclusion
AI not only reshapes the way that music is composed, produced, and distributed but also lets the artist, producer, and listeners do something they could not do previously. By allowing cross-genre experimentation, streamlining production processes, and valuable audience insight, AI sets up the venue for a more innovative, customized, and data-driven musical experience. While these have to pass through several challenges and bad, from those that spring ethical concerns to the limitations in creativity-there is indeed a grand potential for AI to push boundaries and unlock new musical dimensions.
Ready to explore how AI can elevate music to the next level? Let’s shape the future of sound together!