Table of Contents
Explore 7 transformative healthcare trends from the latest EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) updates, shaping health tech, telemedicine, and EHR/EMR compliance by 2025.
This article explores the 7 transformative healthcare trends driven by the EU MDR’s most recent changes, how organizations can adapt to ensure compliance while maintaining market access, and what these changes mean for health tech companies, telemedicine firms, and EHR/EMR providers.
The European Union’s Medical Device Regulation (EU MDR), first enforced in May 2021, has marked a significant shift in the regulation of medical devices within the EU. As the regulation continues to evolve, manufacturers, healthcare providers, and stakeholders must stay informed about its latest updates and their implications.
What is the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR)?
The EU MDR replaced the Medical Device Directive (MDD) and the Active Implantable Medical Devices Directive (AIMDD). It was introduced to establish stricter controls, enhance patient safety, and ensure greater transparency in the healthcare industry.
Key objectives include:
- Stronger Clinical Evidence Requirements: Devices must demonstrate safety and effectiveness through robust clinical data.
- Improved Traceability: The introduction of a unique device identification (UDI) system.
- Greater Post-Market Surveillance: Emphasizing continuous monitoring of device performance after market entry.
- Transparency: A publicly accessible EUDAMED database for device data and performance.
7 Key Healthcare Trends Shaped by the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR)
- Extended Transition Periods: To prevent market disruptions, the EU extended MDR compliance deadlines for certain legacy devices, providing more time for manufacturers to align with new standards.
- Clarifications on Notified Bodies: The capacity and role of Notified Bodies have been expanded to streamline certifications and reduce bottlenecks in device approvals.
- Enhanced Guidance on Clinical Evidence: New guidance documents clarify expectations around clinical data requirements, especially for high-risk products.
- Increased Transparency Requirements: More detailed reporting and data sharing mandates for performance and safety.
- Expanded Scope: The MDR now covers more products, including software used for medical purposes and some aesthetic products.
- Stricter Labeling Requirements: Labels must include standardized symbols and information to ensure clarity for healthcare professionals and patients.
- Digital Transformation in Compliance: Companies are increasingly adopting digital tools to manage compliance data and streamline regulatory processes.
These healthcare trends are essential for balancing patient safety with supply chain continuity, ensuring essential technologies remain available in the market.
Maintaining Medical Device Regulation (MDR) Compliance
To keep up with regulatory requirements, manufacturers must develop a proactive and comprehensive EU MDR strategy that addresses all aspects of device lifecycle management.
Key considerations for ongoing compliance:
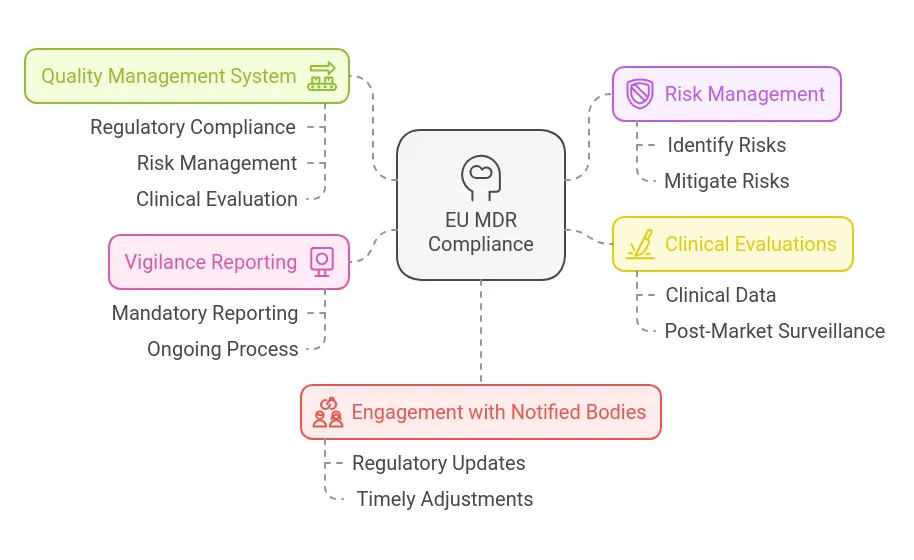
- Develop a Robust Quality Management System (QMS): A strong QMS should cover all production aspects, including regulatory compliance, risk management, and clinical evaluation. Maintain technical documentation, EU declarations of conformity, and certifications for a minimum of 10 years (15 years for implanted devices).
- Implement Proactive Risk Management: Manufacturers must establish a system that identifies and mitigates risks throughout the device lifecycle. This system should be regularly updated to address emerging risks.
- Conduct Clinical Evaluations and Post-Market Surveillance: Companies must demonstrate device safety and performance using clinical data. If necessary, clinical investigations should be conducted, and clinical evaluations should be routinely updated with post-market surveillance data. Periodic safety update reports summarizing post-market findings are also required.
- Maintain Vigilance Reporting: Vigilance reporting is mandatory, and MDR compliance should be seen as an ongoing process rather than a one-time effort.
- Stay Engaged with Notified Bodies: Regulatory changes can affect MDR requirements, making it essential to maintain a good working relationship with Notified Bodies for timely updates and adjustments.
Continuous Compliance and Audits
The EU MDR emphasizes ongoing data collection, documentation, and regulatory audits to ensure consistent compliance across the medical device sector.
Manufacturers and distributors must prepare for audits by meeting several key requirements, including:
- Robust Tracking Systems: Efficient systems for tracking device performance and history.
- Incident Reporting: Prompt reporting of malfunctions, serious injuries, and fatalities.
- Facility Registration: Ensuring all production and distribution facilities are properly registered.
The MDR’s introduction has transformed the medical device landscape, presenting both challenges and opportunities. While compliance can increase operational complexities and costs, it also fosters innovation through digital transformation and better data utilization across the product lifecycle.
These regulatory changes underscore the need for continuous adaptation, balancing compliance with innovation to enhance patient safety and care quality.
How the EU MDR Impacts Manufacturers and Health Tech Companies

The MDR has introduced significant shifts in how manufacturers design, test, and market products. Key impacts include:
- Increased Compliance Costs: Stricter data requirements demand more extensive clinical trials and documentation.
- Product Reevaluation: Legacy products may require reassessment or face market withdrawal if they fail to meet new standards.
- Smaller Manufacturers Facing Challenges: The resource-intensive nature of MDR compliance has posed challenges for small and mid-sized companies.
- Enhanced Risk Management: Companies must implement formal risk management frameworks throughout a product’s lifecycle.
- Heightened Data Management: Maintaining updated, complete, and accessible documentation for regulatory approvals and audits.
Impact on Telemedicine and EHR/EMR Companies
- Telemedicine Companies: Devices used in remote patient monitoring must meet the new regulatory standards, affecting compliance strategies and product availability.
- EHR/EMR Companies: Integration of medical data within EHR/EMR platforms must now align with the enhanced traceability and data security measures mandated by MDR.
Benefits of the EU MDR
Despite the challenges, the regulation brings numerous benefits:
- Enhanced Patient Safety: Stricter regulations ensure that devices on the market are safer for patients.
- Improved Transparency: A publicly accessible database provides critical information to healthcare providers and patients.
- Streamlined Compliance: Digital tools simplify compliance processes, reducing administrative burdens.
What Does This Mean for You?
As a health tech company, telemedicine firm, or EHR/EMR provider, understanding these trends is crucial:
- Stay Up-to-Date: Regularly review the latest MDR updates to ensure compliance.
- Adopt Digital Solutions: Leverage digital tools to streamline compliance and improve operational efficiency.
- Prioritize Patient Safety: Ensure that your products meet or exceed regulatory standards.
Conclusion
The EU MDR’s latest changes have far-reaching implications for healthcare providers, manufacturers, and stakeholders. By understanding these trends and adapting proactively, you can ensure compliance while contributing to safer, more effective medical technologies.
Explore 7 transformative healthcare trends from the latest EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) updates, shaping health tech, telemedicine, and EHR/EMR compliance by 2025.
READ MORE:
Revolutionary Green AI: Making Machine Learning Energy-Efficient
Mental Health 2.0: The Impact of Emerging Technologies on Treatment Outcomes