Table of Contents
Web development is no longer limited to simple static pages.
In 2026, modern websites must be fast, scalable, secure, and highly interactive, while being built in shorter development cycles.
Web development frameworks make this possible by providing reusable components and best practices for building powerful applications efficiently.
From simple websites to complex, large-scale applications, frameworks are essential.
This guide covers the key web development frameworks in 2026 to help you build faster and smarter.
What is a Web Development Framework?
A web development framework is a pre-built collection of tools, libraries, and best practices that provides a standardized way to build web applications.
Think of it as a blueprint or foundation that handles common tasks like routing, database interactions, authentication, and UI components, allowing developers to focus on building unique features rather than reinventing the wheel.
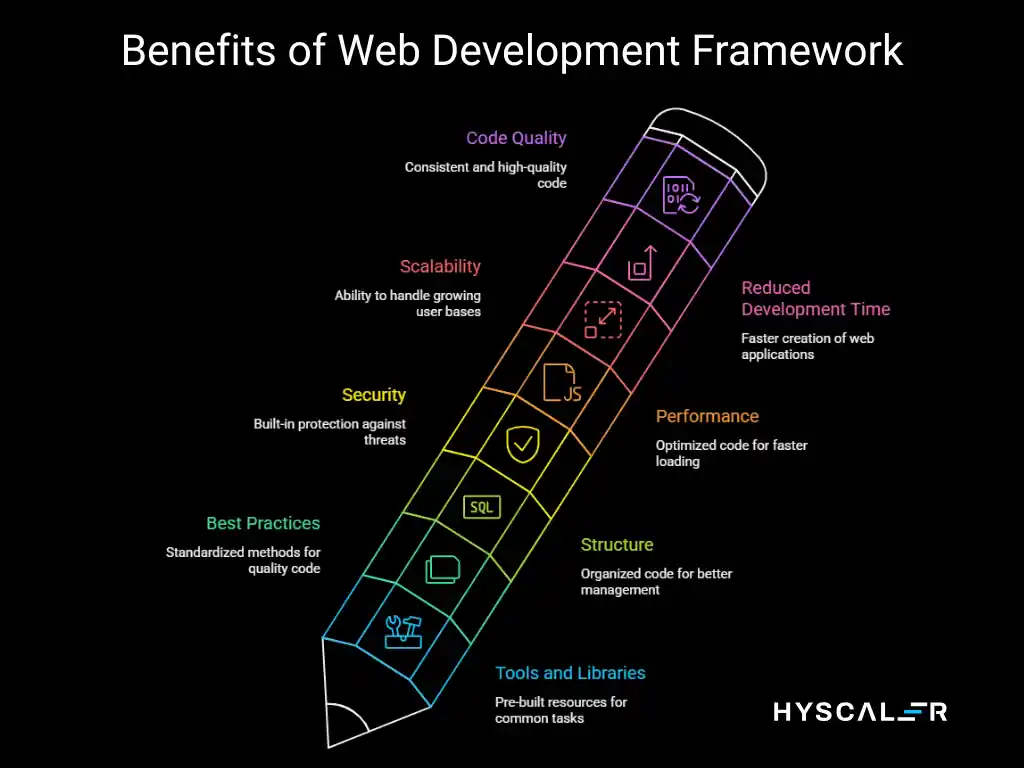
Frameworks provide structure to your code, enforce best practices, and come with built-in solutions for security, performance, and scalability challenges.
They significantly reduce development time and help maintain code quality across teams.
Web Development Framework Architecture
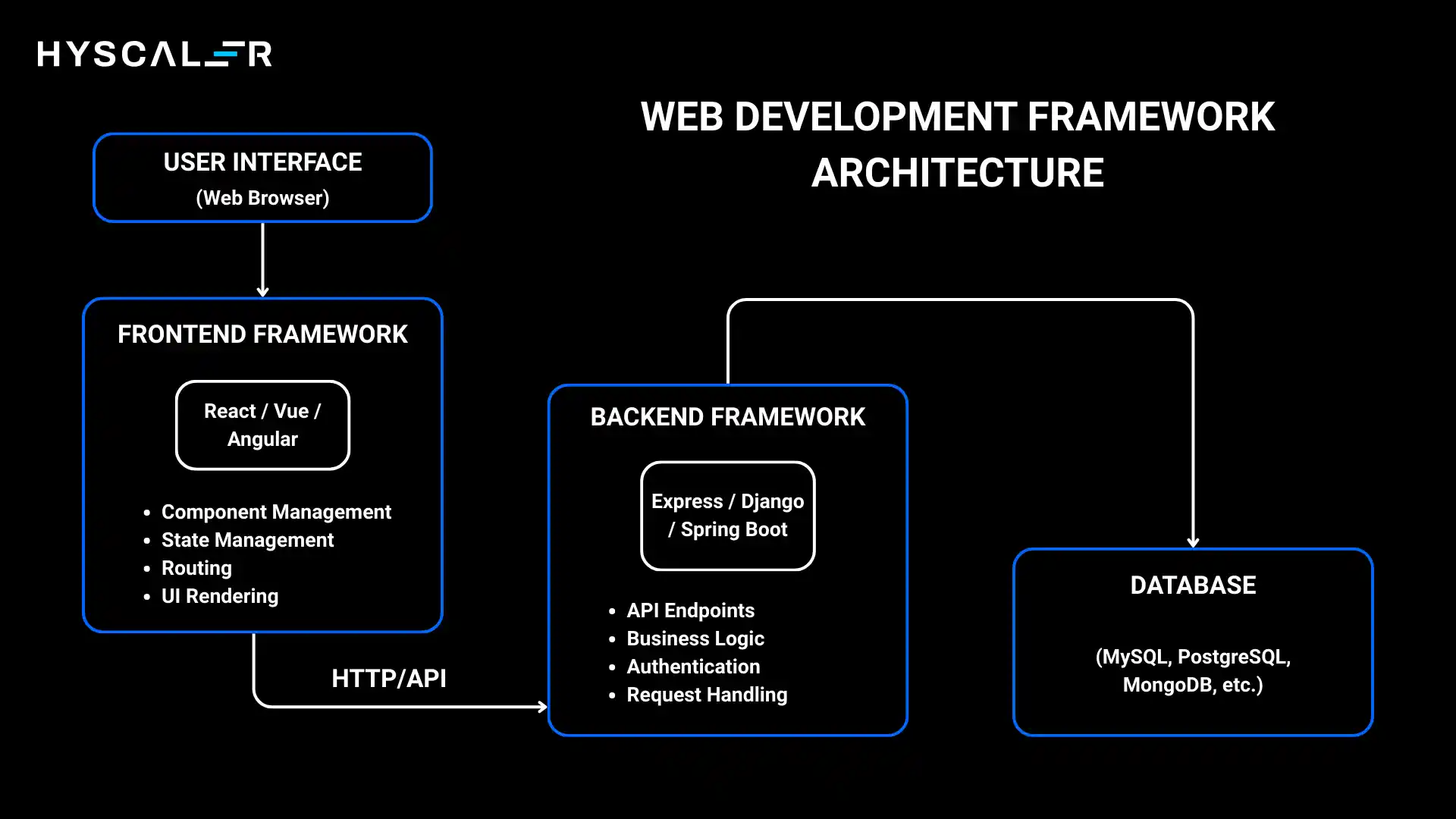
Frontend vs Backend: Understanding the Distinction
Before diving into specific frameworks, it’s crucial to understand that frameworks serve different purposes depending on where they operate:
Frontend Frameworks run in the user’s browser and handle everything the user sees and interacts with. They manage the user interface, user experience, and client-side logic. Examples include Vue.js and Angular (React is also considered, even though it is a library).
Backend Frameworks run on the server and handle business logic, database operations, authentication, and API endpoints. They process requests from the frontend and return appropriate responses. Examples include Express.js, Django, and Laravel.
Full-stack frameworks provide tools for both frontend and backend development, offering an integrated solution for building complete applications. Examples include Next.js, Ruby on Rails, and Meteor.
Benefits of Web Development Framework
Most Popular Web Development Frameworks
Frontend Frameworks
1. React
React, developed by Facebook, has become the dominant force in frontend development. It’s technically a library rather than a full framework, but its ecosystem is so robust that it functions as a complete solution.
Key Features:
- Component-based architecture for reusable UI elements
- Virtual DOM for optimal performance
- Massive ecosystem with tools like Redux for state management
- React Hooks for functional component logic
- Strong community support and extensive third-party libraries
Best For: Single-page applications, complex user interfaces, projects requiring flexibility and customization
2. Vue.js
Vue.js has gained tremendous popularity due to its gentle learning curve and progressive adoption approach. You can use as much or as little of Vue as needed.
Key Features:
- Intuitive template syntax
- Reactive data binding
- Component-based structure
- Excellent documentation
- Smaller bundle size compared to Angular
Best For: Projects of any size, teams wanting an easier learning curve, progressive enhancement of existing applications
3. Angular
Angular, maintained by Google, is a comprehensive framework with everything included out of the box.
Key Features:
- Full-featured framework with built-in routing, forms, and HTTP client
- TypeScript by default
- Two-way data binding
- Dependency injection
- Strong opinions on project structure
Best For: Large enterprise applications, teams preferring structure and convention, projects requiring TypeScript
Backend Frameworks
1. Express.js (Node.js)
Express is the minimalist backend framework that powers countless Node.js applications. Its simplicity and flexibility make it incredibly popular.
Key Features:
- Minimalist and unopinionated
- Excellent for building RESTful APIs
- Massive middleware ecosystem
- Perfect for real-time applications with WebSocket support
- JavaScript on both the frontend and backend
Best For: RESTful APIs, real-time applications, microservices, JavaScript full-stack development
2. Django (Python)
Django is a high-level Python framework that follows the “batteries included” philosophy, providing everything you need out of the box.
Key Features:
- Built-in admin panel
- ORM for database operations
- Strong security features by default
- Excellent documentation
- Rapid development capabilities
Best For: Data-driven applications, content management systems, projects requiring rapid development
3. Spring Boot (Java)
Spring Boot has revolutionized Java web development by simplifying the configuration and setup of Spring applications.
Key Features:
- Production-ready features like metrics and health checks
- Embedded server (Tomcat, Jetty)
- Auto-configuration
- Extensive ecosystem
- Enterprise-grade security and scalability
Best For: Enterprise applications, microservices architecture, projects requiring robust scalability
4. Laravel (PHP)
Laravel is the most popular PHP framework, known for its elegant syntax and developer-friendly features.
Key Features:
- Elegant ORM (Eloquent)
- Built-in authentication and authorization
- Queue management
- Task scheduling
- Blade templating engine
Best For: Web applications with database interaction, rapid prototyping, and teams familiar with PHP
Full-Stack Frameworks
1. Next.js
Next.js builds on React to provide a complete full-stack solution with server-side rendering and static site generation.
Key Features:
- Server-side rendering (SSR) and static site generation (SSG)
- File-based routing
- API routes for backend functionality
- Automatic code splitting
- Built-in image optimization
Best For: SEO-critical applications, e-commerce sites, marketing websites, full-stack React applications
2. Ruby on Rails
Rails pioneered the convention-over-configuration philosophy and remains popular for rapid application development.
Key Features:
- Convention over configuration
- Active Record ORM
- Built-in testing framework
- Rich gem ecosystem
- Scaffolding for rapid prototyping
Best For: Startups needing rapid development, CRUD applications, projects with conventional requirements
3. Nuxt.js
Nuxt.js does for Vue what Next.js does for React, providing server-side rendering and a complete application framework.
Key Features:
- Server-side rendering
- Static site generation
- File-based routing
- Automatic code splitting
- Modular architecture
Best For: Vue.js applications requiring SSR, SEO-friendly Vue apps, full-stack Vue development
The 7 Stages of Web Development
Understanding the web development process helps in choosing the right frameworks and tools for each phase.
Here are the 7 Stages of Web Development:
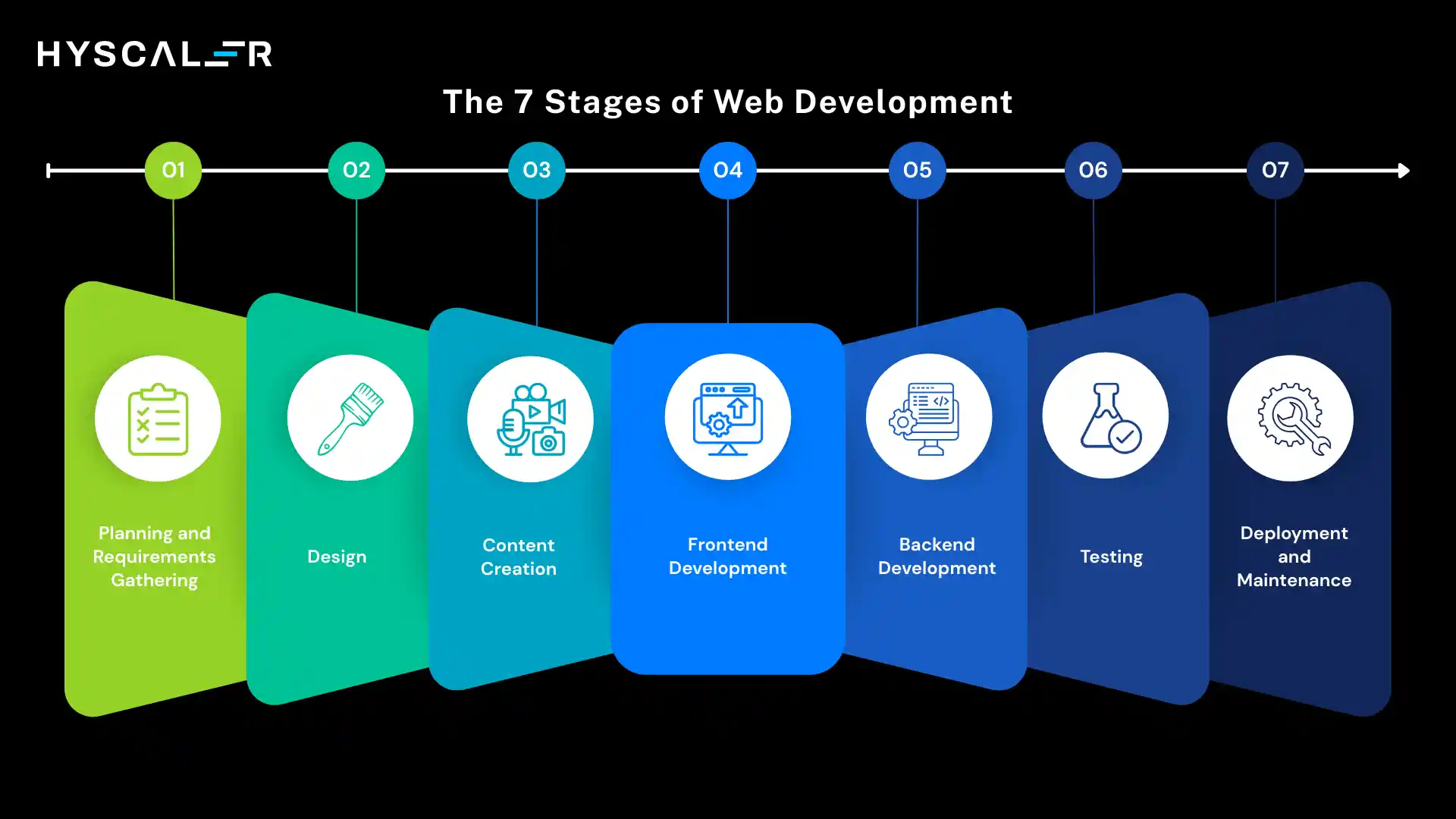
1. Planning and Requirements Gathering
This initial stage involves understanding project goals, target audience, and functionality requirements.
You’ll create wireframes, define user stories, and establish project scope.
During this phase, you evaluate which frameworks align with your project requirements.
2. Design
The design phase focuses on creating the visual layout, user interface, and user experience.
Designers create mockups and prototypes that will guide frontend development.
Framework choice affects design implementation, so designers should understand the capabilities of the chosen tools.
3. Content Creation
Content development includes writing copy, creating images, videos, and other media that will populate the website.
This stage often happens in parallel with design and development.
4. Frontend Development
This is where your chosen frontend framework comes into play.
Developers transform designs into functional user interfaces using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript frameworks like React, Vue, or Angular.
They implement responsive design, animations, and client-side interactions.
5. Backend Development
Backend developers build server-side logic, database structures, APIs, and business logic using frameworks like Express, Django, or Spring Boot.
This stage involves setting up authentication, authorization, data validation, and integration with external services.
6. Testing
Comprehensive testing ensures your application works correctly across different browsers, devices, and scenarios.
This includes unit testing, integration testing, user acceptance testing, and performance testing.
Most modern frameworks include testing tools and utilities.
7. Deployment and Maintenance
The final stage involves deploying your application to production servers and ongoing maintenance.
This includes monitoring performance, fixing bugs, updating dependencies, and adding new features based on user feedback.
Which Framework is Better for Web Development?
The truth is, there’s no single “best” framework.
The right choice depends on your specific needs:
Choose React when:
- You need maximum flexibility and a vast ecosystem
- Building complex, interactive user interfaces
- You want strong community support and abundant resources
- Your team has JavaScript expertise
Choose Vue.js when:
- You want an easier learning curve
- Building projects of any size with a progressive approach
- You prefer intuitive syntax and excellent documentation
- You need good performance with smaller bundle sizes
Choose Angular when:
- Building large enterprise applications
- You prefer a complete, opinionated framework
- TypeScript is a priority
- You want everything included out of the box
Choose Express.js when:
- Building RESTful APIs or microservices
- You want minimalist, flexible backend code
- Real-time features are important
- Your team knows JavaScript
Choose Django when:
- Building data-driven applications quickly
- Security is a top priority
- You need an admin panel out of the box
- Your team prefers Python
Choose Next.js when:
- SEO is critical
- You want React with server-side rendering
- Building e-commerce or marketing sites
- You need a full-stack React solution
Making Your Framework Decision
When choosing a framework, consider these factors:
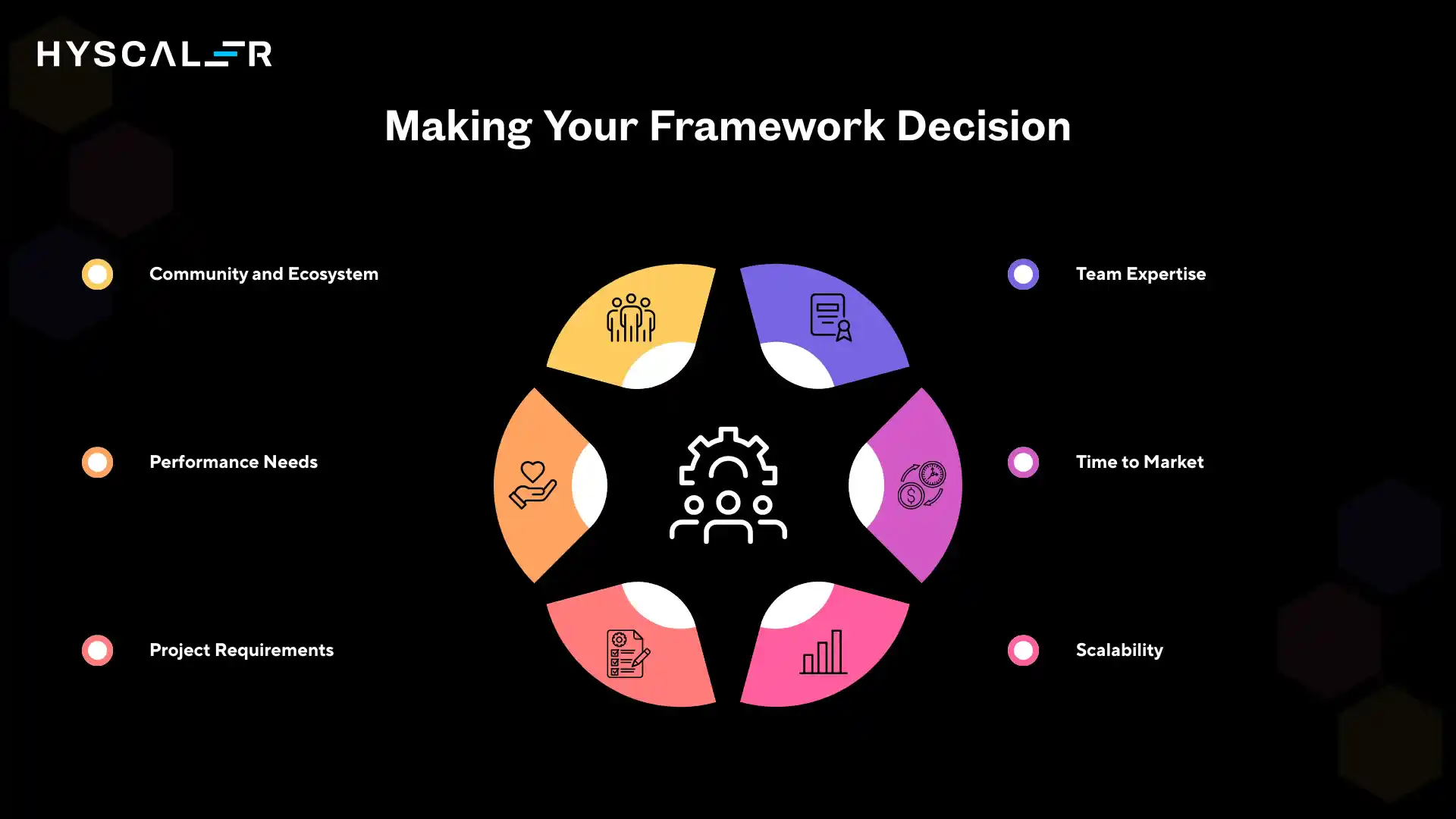
1. Project Requirements: Does your project need server-side rendering? Real-time features? Complex state management?
2. Team Expertise: What languages and frameworks does your team know? Learning curves impact project timelines.
3. Performance Needs: How important are load times, bundle sizes, and server resources?
4. Scalability: Will your application need to handle thousands or millions of users?
5. Community and Ecosystem: Does the framework have active development, good documentation, and available packages?
6. Time to Market: Do you need rapid development, or can you invest time in building custom solutions?
Conclusion
Web development frameworks have transformed how we build applications, making development faster, more maintainable, and more efficient.
Whether you choose React for its flexibility, Django for rapid development, or Next.js for full-stack capabilities, each framework offers unique advantages.
The key is understanding your project requirements, team capabilities, and long-term maintenance needs. Start with the frameworks that align with your immediate needs, but remain flexible.
The web development landscape continues to evolve, and new tools regularly emerge to solve emerging challenges.
Remember, frameworks are tools, not destinations.
The best developers understand multiple frameworks and choose the right tool for each job.
Start learning one framework deeply, then expand your knowledge to others as your projects and career grow.
Happy coding!
FAQs
What are the 7 C’s of a website?
Context – Overall layout and design
Content – Text, images, videos, information
Community – User interaction (comments, forums)
Customization – Personalized user experience
Communication – How the site talks to users (emails, alerts)
Connection – Links to other sites or platforms
Commerce – Buying and selling features (if applicable)
What are three types of web development?
The three types of web development are:
Front-end development – Builds the user interface (what users see)
Back-end development – Handles server, database, and logic
Full-stack development – Covers both front-end and back-end
Is framework frontend or backend?
A framework can be either frontend or backend, depending on its purpose.
Frontend frameworks: Used for UI (e.g., React, Angular)
Backend frameworks: Used for server-side logic (e.g., Django, Spring)
Is Python a web framework?
No. Python is a programming language, not a web framework.
It is used to build web frameworks like Django and Flask, but it isn’t one itself.