Table of Contents
Enhanced Understanding of Telemedicine and Its Evolution
Telemedicine allows patients to receive medical advice and counseling from anywhere, at any time, using a phone or computer. This enhances communication between patients and healthcare providers significantly.
The concept dates back to 1876 when Alexander Graham Bell used a telephone to seek medical advice for a sulfuric acid burn. As telephones became common among doctors, concerns arose about potential infection risks from phone use.

Recent studies highlight telemedicine’s effectiveness, particularly for patients facing barriers to in-person visits. In 2014, a third of patients at CVS Minute Clinics preferred tele-video consultations. A 2019 study at Massachusetts General Hospital found 63% of patients perceived virtual visits as equal in quality to office visits. A 2021 study reported no missed diagnoses or adverse outcomes related to telemedicine.
Statistics and Data on Telemedicine Trends
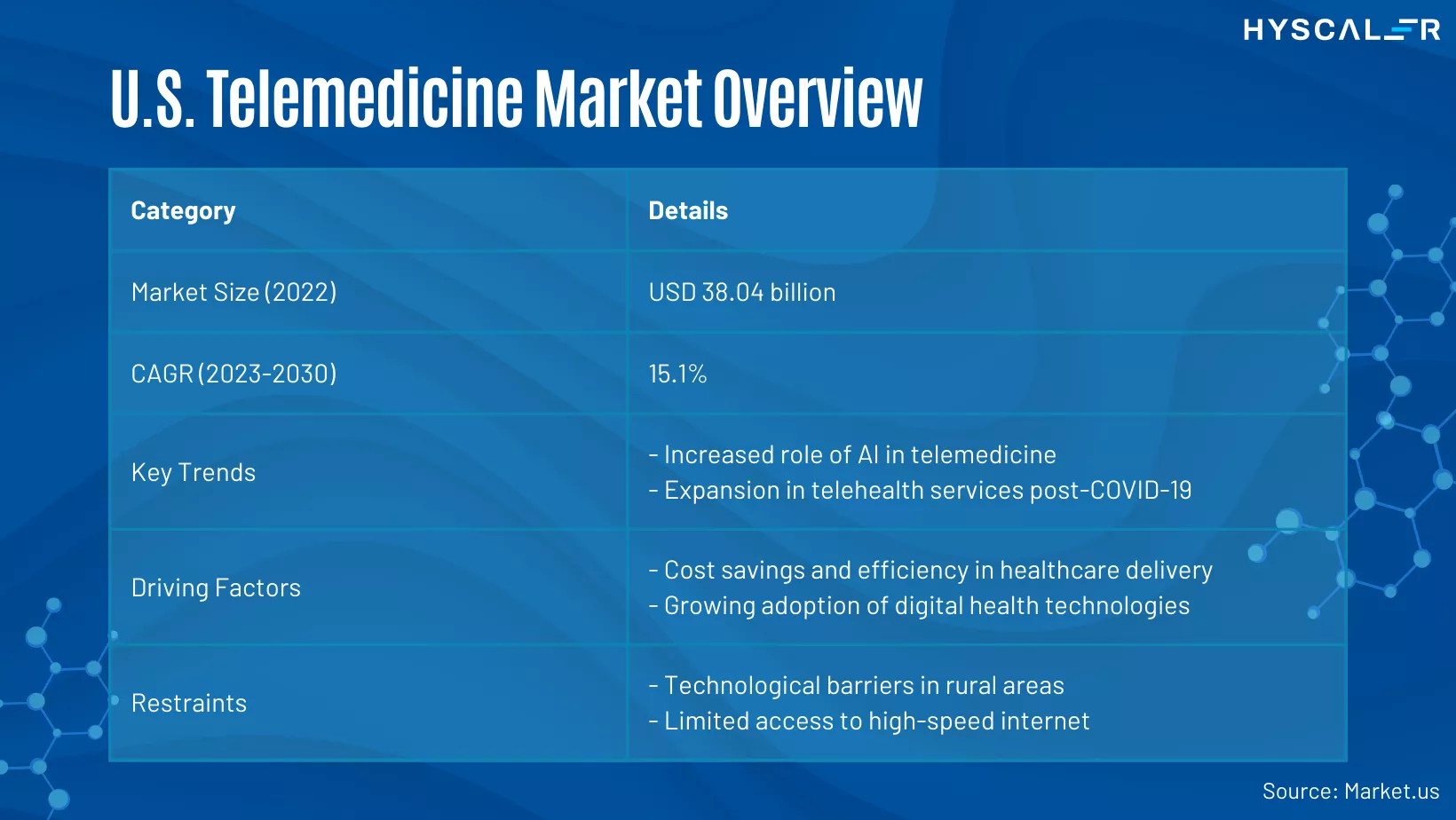
U.S. Telemedicine Market Overview
In 2022, the U.S. telemedicine market was valued at USD 38.04 billion and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 15.1% from 2023 to 2030. Key trends include the increasing integration of AI in telemedicine and the significant expansion of telehealth services due to the pandemic. The main drivers are cost savings and improved efficiency, along with the rising adoption of digital health technologies. However, challenges such as technological barriers in rural areas and limited internet access persist.
Segment Insights:
- Type: Services dominated in 2022, but products are expected to grow significantly.
- Application: Teleradiology leads, with telepsychiatry projected to grow rapidly.
- Modality: Store-and-forward telemedicine is currently dominant, but real-time modalities are set to increase.
- End User: Healthcare facilities are the primary users, with homecare settings also expected to expand.
Accelerated Telehealth Adoption Driven by COVID-19
Key Points:
- COVID-19 has accelerated healthcare providers’ adoption of telehealth and digital technologies to cope up with telemedicine trends.
- Investments are increasing in analytics, automation, IoT, and cloud infrastructure to support scalable care models.
- Pre-pandemic, a 15% increase in digital IT services spending was predicted by 2025, but this is now expected to rise faster.
- New care models like telemedicine require greater digital adoption and integration of advanced technologies.
- Opportunities include data monetization, cloud adoption, compliance with new regulations, and rising consumer expectations for digital healthcare.
Report Insights:
- BigTech companies are entering healthcare, enhancing patient and physician experiences.
- Providers are shifting to value-based care, requiring extensive data sharing.
- New business models and partnerships are forming to improve patient outcomes and reduce costs.
- Increasing consumer expectations for secure and digital healthcare services.
The Rise of mHealth
What is mHealth?
mHealth (mobile health) refers to using mobile devices and wireless technology in healthcare. It primarily involves educating consumers about preventive services, but also extends to disease monitoring, treatment support, epidemic tracking, and chronic disease management.
Why is mHealth Important?
mHealth is especially beneficial in underserved regions with high mobile phone usage. Nonprofits like mHealth Alliance promote its use in developing countries.
Key Benefits:
- Convenience: Wearable devices and mobile apps allow continuous health data tracking without frequent doctor visits. In 2017, there were 325,000 mHealth apps available.
- Improved Communication: Secure messaging facilitates real-time communication between patients and healthcare providers, enhancing care coordination and allowing for timely updates.
Enhanced Accessibility: mHealth tools are making significant strides in bridging healthcare gaps, especially in areas lacking traditional healthcare infrastructure. This technology is transforming how healthcare is delivered by making it more accessible, efficient, and patient-centered, keeping up with the telemedicine trends.
mHealth Applications:
- Preventive Health Education: Educates consumers on preventive care measures.
- Disease Surveillance: Tracks and monitors disease outbreaks.
- Chronic Disease Management: Assists in managing long-term health conditions.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: Enables real-time tracking of patient health metrics.
Impact on Global Health
In developing countries, mHealth initiatives are helping to overcome barriers such as limited access to healthcare facilities, lack of healthcare professionals, and inadequate medical resources. By leveraging mobile technology, these regions can achieve better health outcomes and improved quality of care.
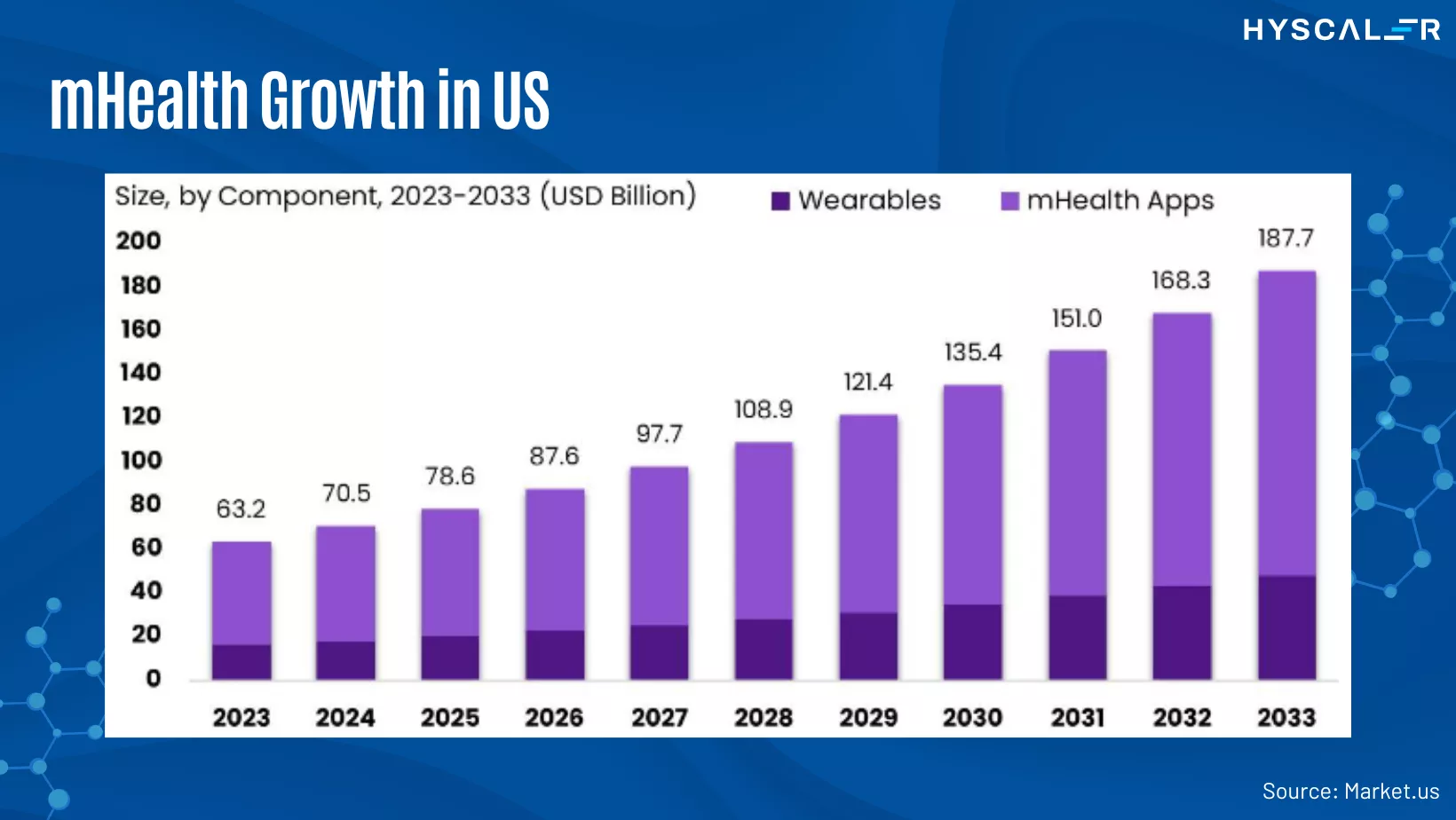
mHealth is revolutionizing healthcare delivery by making it more accessible, efficient, and patient-centered. With ongoing advancements in mobile technology, the potential for mHealth to further transform the healthcare landscape is immense.
5 Telemedicine Trends in 2024
1. AI Integration
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping telemedicine by improving health data analysis and outcome predictions. AI-powered chatbots provide real-time support, answering patient queries and offering immediate advice. For healthcare providers, AI reduces administrative tasks and delivers actionable insights, helping to personalize treatment plans based on individual health data.
2. VR/AR and Virtual Visits
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are enhancing patient and provider interactions. VR/AR can simulate in-person consultations, making virtual visits feel more realistic. Additionally, these technologies offer immersive training for medical professionals, enabling them to practice complex procedures virtually. Patients can also engage in VR-assisted rehabilitation exercises, enhancing recovery outcomes.
3. EHR Integration
The integration of telemedicine platforms with Electronic Health Records (EHR) is crucial for efficient healthcare delivery. This integration allows seamless data sharing across medical facilities, ensuring that healthcare providers have real-time access to comprehensive patient records. It enhances care coordination, reduces errors, and enables the development of personalized treatment plans based on accurate and up-to-date patient information.
4. Wearable Technology and RPM
Wearable devices and Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) technologies are revolutionizing healthcare by providing continuous monitoring of patient health metrics. Wearables track vitals, activity levels, and sleep patterns, sending real-time data to healthcare providers. This allows for early detection of potential health issues and timely intervention. RPM supports post-surgery recovery by closely monitoring patients and ensuring they adhere to their rehabilitation plans.
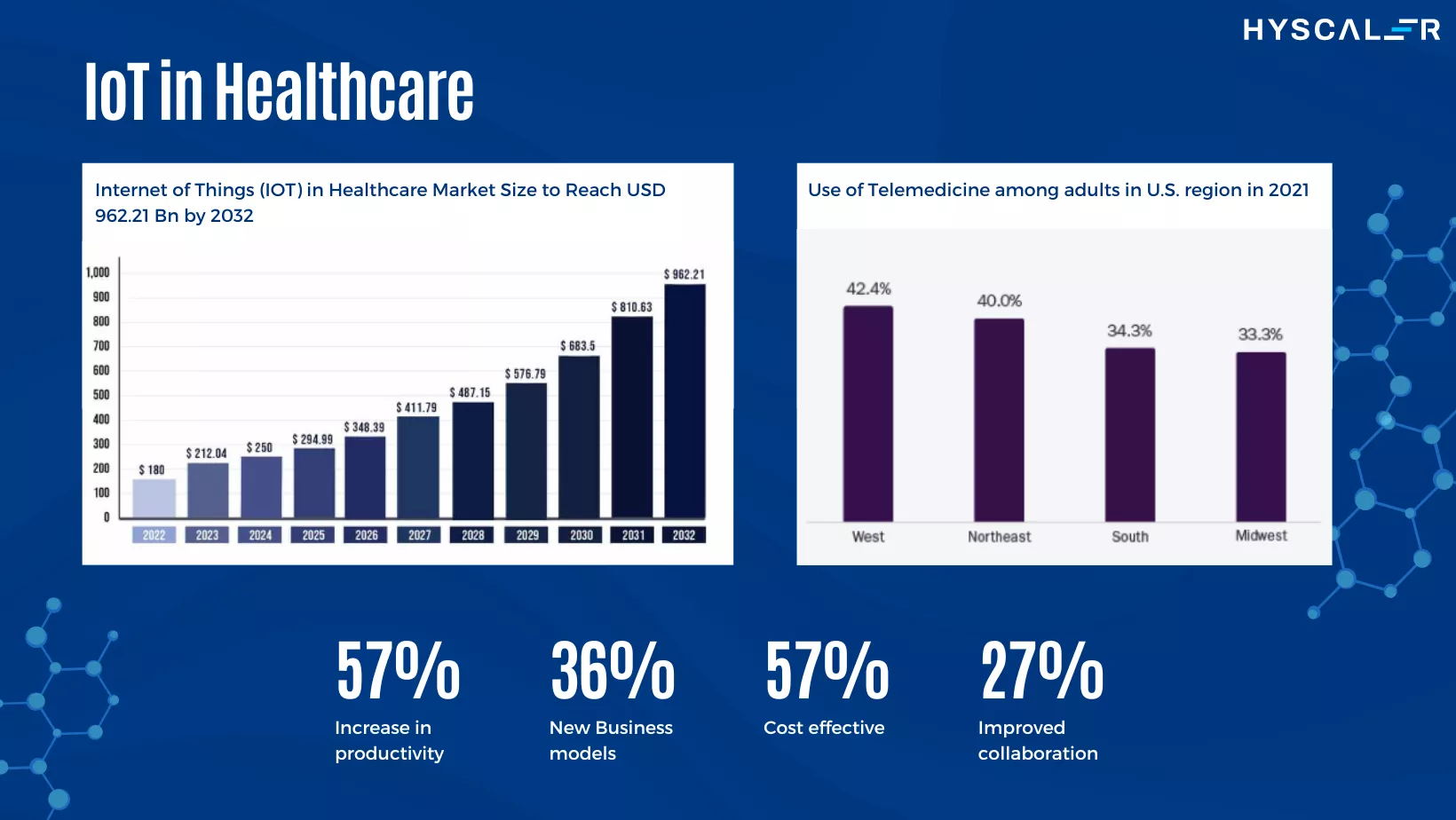
5. mHealth
Mobile health (mHealth) is transforming healthcare by offering patients a wide range of applications and tools to manage their health. mHealth apps provide features such as medication reminders, symptom tracking, and teleconsultation, empowering patients to take control of their health. These apps facilitate better healthcare education, improve patient-provider communication, and enhance overall access to care. The mHealth market is rapidly growing, driven by the increasing demand for preventive healthcare and the rise in investments for mHealth startups.
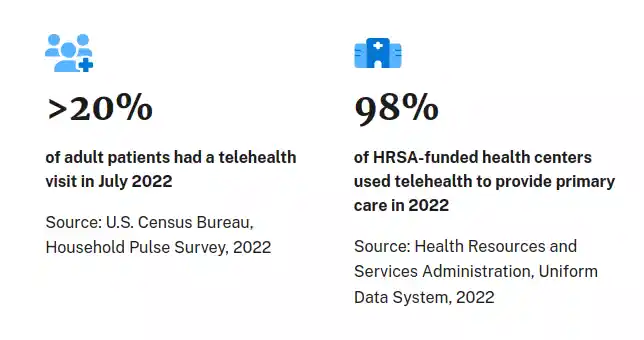
Telemedicine is rapidly evolving with advancements in AI, VR/AR, EHR integration, wearable technology, and mHealth. These trends are making healthcare more accessible, efficient, and personalized, ultimately improving patient outcomes and transforming the healthcare landscape.
What are the Benefits of telemedicine?
Telemedicine offers numerous benefits, such as convenience, cost savings, and improved access to care, especially in underserved areas. However, it also faces challenges like technology requirements and limited scope for physical examinations. As telemedicine continues to evolve, addressing these challenges will be key to maximizing its potential benefits.
- Convenience and Accessibility: Telemedicine allows patients to access healthcare from anywhere, eliminating the need to travel for appointments. This is particularly beneficial for those with chronic conditions or those living in remote areas. According to a Cisco study, 74% of patients prefer easy access to medical services over in-person visits.
- Cost and Time Savings: Telemedicine reduces the time spent on travel and waiting for appointments. A Harvard study found that traditional doctor visits consume around 121 minutes, including travel and waiting time. Virtual visits save this time, making healthcare more efficient.
- Easy Follow-Up: Virtual consultations are ideal for follow-up appointments, allowing patients to stay at home while recovering. Doctors can monitor recovery and decide if further in-person evaluation is needed.
- Labor Cost Savings: Telehealth can significantly reduce labor costs for healthcare systems by cutting down on the need for physical presence. A study indicated telehealth can reduce healthcare system costs by over 50%.
- Increased Access to Care: Telemedicine bridges gaps in care, providing access to specialized services for populations in remote or underserved areas. It allows healthcare systems to deploy specialty consultations as needed, rather than hiring full-time specialists.
- Reduced Provider Burnout: By enabling remote work, telehealth can alleviate some of the pressures on healthcare providers, helping to reduce burnout.
What are the Drawbacks of telemedicine?
- Limited Scope: Telemedicine is often limited to initial consultations and follow-ups. Physical exams and procedures cannot be conducted virtually, making it challenging to assess certain conditions accurately.
- Technology Requirements: Both patients and providers need access to smart devices and a stable internet connection. This can be a barrier for individuals who cannot afford these technologies.
- Internet Dependency: Reliable internet access is crucial for telemedicine. Without it, consultations may be interrupted or delayed, impacting the quality of care.
Conclusion
The telehealth industry is at a pivotal moment, with market potential soaring from $3 billion to a projected $250 billion. If you’re ready to invest in this booming sector, now is the perfect time. Partner with HyScaler, a leading healthcare app development company, to leverage the latest trends and innovations in telehealth. The recent surge in telehealth’s relevance underscores its future growth. Trust in our expertise to develop cutting-edge healthcare applications and position yourself at the forefront of this transformative industry. Your success starts with us.
FAQs
What is the scope of telemedicine?
Telemedicine enables healthcare providers to deliver quality care to patients regardless of their location. This technology bridges the gap, ensuring that even remote areas have access to essential healthcare services.
What are the new technologies in telemedicine?
Innovative technologies like AI, machine learning, cloud computing, IoT, and advanced voice and video communications are revolutionizing telemedicine. These technologies help deliver hospital-level care remotely, freeing up hospital resources for critical patients.
What is the future of digital healthcare?
The future of digital healthcare relies on seamless information exchange between healthcare entities. Interoperability, or the ability of different systems to communicate and share data, is a primary focus for 2024.
Why is telemedicine essential today?
Telemedicine helps control the spread of infectious diseases by allowing doctors to prescreen patients remotely, reducing the risk of exposure to illnesses like COVID-19 and the flu.
Who is the father of telemedicine?
K Ganapathy, a neurosurgeon in India, is often regarded as the father of telemedicine. He established the Apollo Telemedicine Networking Foundation and Apollo Telehealth Services, creating the first telemedicine network between AIIMS, PGIMER, and SGPGIMS.
How does telemedicine enhance patient care?
Telemedicine improves patient care by providing timely access to medical consultations, enabling remote monitoring of chronic conditions, and ensuring continuous patient engagement through virtual visits and follow-ups.
What are the limitations of telemedicine?
While telemedicine is highly effective for many consultations, it cannot replace physical examinations or procedures that require direct contact. Additionally, it requires reliable internet access and appropriate digital devices, which may not be available to everyone.
Can telemedicine reduce healthcare costs?
Yes, telemedicine can significantly reduce healthcare costs by minimizing the need for in-person visits, reducing hospital readmissions, and enabling efficient management of chronic diseases remotely.