Table of Contents
Artificial intelligence has reached a pivotal moment.
While traditional language models have amazed us with their ability to generate human-like text, a new breed of AI systems is pushing boundaries even further.
Enter reasoning models, the next evolutionary step in artificial intelligence that’s revolutionizing how machines think, solve problems, and interact with complex challenges.
What Defines a Reasoning Model?
A reasoning model represents a sophisticated class of AI systems designed to think through problems systematically, just like a human would, before generating responses.
Unlike traditional language models that primarily predict the next word based on patterns, reasoning models incorporate explicit cognitive processes that mirror human problem-solving strategies.
The fundamental distinction lies in their approach: reasoning models use deliberate, step-by-step thinking to break down complex queries, evaluate multiple solution paths, and arrive at well-considered conclusions.
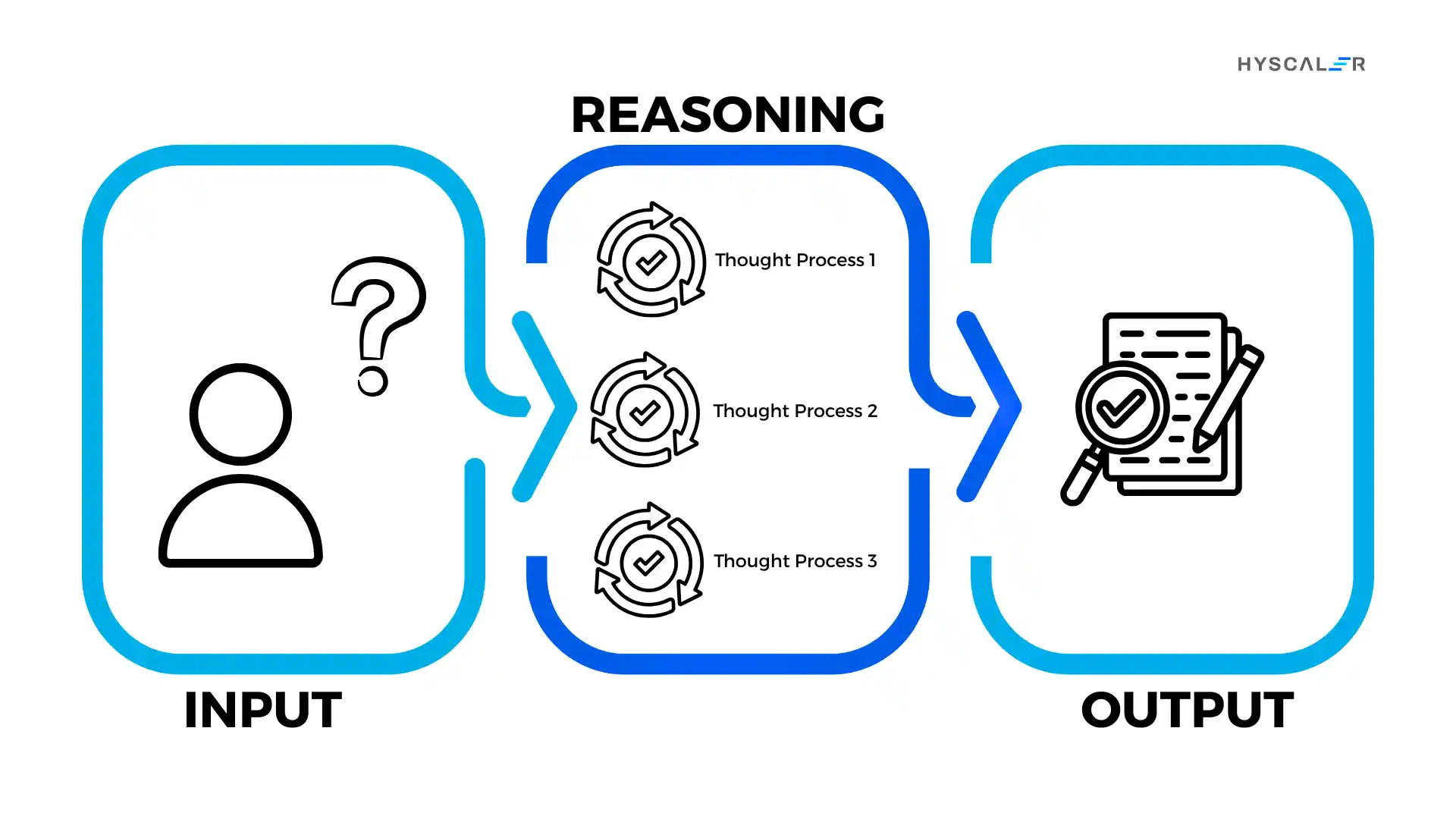
This process often involves chain-of-thought reasoning, where the model articulates its thinking process, making its logic transparent and verifiable.
These advanced systems combine deep learning architectures with structured reasoning frameworks, enabling them to handle tasks requiring logical deduction, mathematical problem-solving, multi-step planning, and nuanced decision-making that goes beyond simple pattern matching.
Reasoning Models vs Traditional LLMs: Understanding the Difference
The distinction is crucial for anyone working with AI technology.
Traditional LLMs function primarily through:
- Pattern recognition from vast training data
- Statistical prediction of likely text continuations
- Rapid response generation with minimal intermediate processing
- Surface-level understanding based on word associations
Reasoning models, in contrast, feature:
- Explicit reasoning chains that show their work
- Multi-step problem decomposition
- Self-verification and error correction mechanisms
- Deeper understanding of logical relationships and causality
- Extended “thinking time” before producing final answers
Think of it this way: traditional LLMs are like students who’ve memorized thousands of examples and can quickly provide answers based on similar patterns they’ve seen.
Reasoning models are like students who actually work through problems step-by-step, checking their logic along the way, even for questions they haven’t encountered before.
Reasoning Models in AI: The Current Landscape
The field of reasoning models in AI has exploded with innovation across multiple platforms and research institutions.
OpenAI’s Reasoning Models
OpenAI has been at the forefront of reasoning model development.
Their approach focuses on training models that can “think before they speak,” allocating computational resources to reasoning processes rather than immediately generating responses.
The O1 series represents their most advanced reasoning-capable systems, designed specifically for complex problem-solving in mathematics, coding, and scientific reasoning.
These models demonstrate remarkable capabilities in:
- Advanced mathematical theorem proving
- Complex code generation and debugging
- Multi-step strategic planning
- Scientific hypothesis formation
Reasoning Models on Hugging Face
The Hugging Face ecosystem has become a vibrant hub for reasoning models, offering researchers and developers access to various implementations.
The platform hosts numerous reasoning-capable models, including:
- Qwen models with extended reasoning capabilities
- The DeepSeek-R1 series is designed for mathematical and logical reasoning
- Reasoning-enhanced LLaMA variants that incorporate chain-of-thought mechanisms
- Various fine-tuned models optimized for specific reasoning tasks
Hugging Face’s collaborative environment allows researchers to share reasoning models, compare architectures, and build upon each other’s work, accelerating innovation in this space.
ChatGPT and Reasoning Capabilities
Is ChatGPT a reasoning model? This question deserves nuance.
Standard ChatGPT (based on GPT-3.5 or GPT-4) incorporates some reasoning capabilities but primarily functions as a traditional language model.
However, newer iterations and specialized versions increasingly integrate reasoning mechanisms.
The advanced models behind ChatGPT can exhibit reasoning-like behavior through:
- Chain-of-thought prompting techniques
- Multi-turn problem decomposition
- Step-by-step explanation generation
That said, ChatGPT’s reasoning is often implicit rather than explicit, verified reasoning found in dedicated reasoning models.
It’s best characterized as a highly capable LLM with emerging reasoning features rather than a pure reasoning model.
What Are Reasoning Model Examples?
Understanding reasoning models becomes clearer when examining concrete examples:
1. OpenAI o1 Series
OpenAI’s o1 models represent purpose-built reasoning systems that excel at complex problem-solving.
They use extended computation time to work through problems methodically, making them ideal for mathematical proofs, advanced coding challenges, and scientific reasoning tasks.
2. DeepSeek-R1
This open-source reasoning model focuses on mathematical and logical reasoning, demonstrating competitive performance with commercial alternatives while being accessible to researchers worldwide.
3. Google’s PaLM with Chain-of-Thought
Google has integrated explicit reasoning mechanisms into its PaLM models, enabling step-by-step problem solving for arithmetic, common sense reasoning, and symbolic manipulation tasks.
4. Anthropic’s Constitutional AI
While not exclusively a reasoning model, Anthropic‘s approach incorporates reasoning about ethical principles and logical consistency into response generation.
5. Specialized Domain Models
- AlphaGeometry: DeepMind’s reasoning model for geometric proofs
- MathGPT: Focused on mathematical problem-solving with explicit reasoning steps
- BioGPT-Reasoning: Medical reasoning models for diagnostic support
Reasoning Models in Academic Research
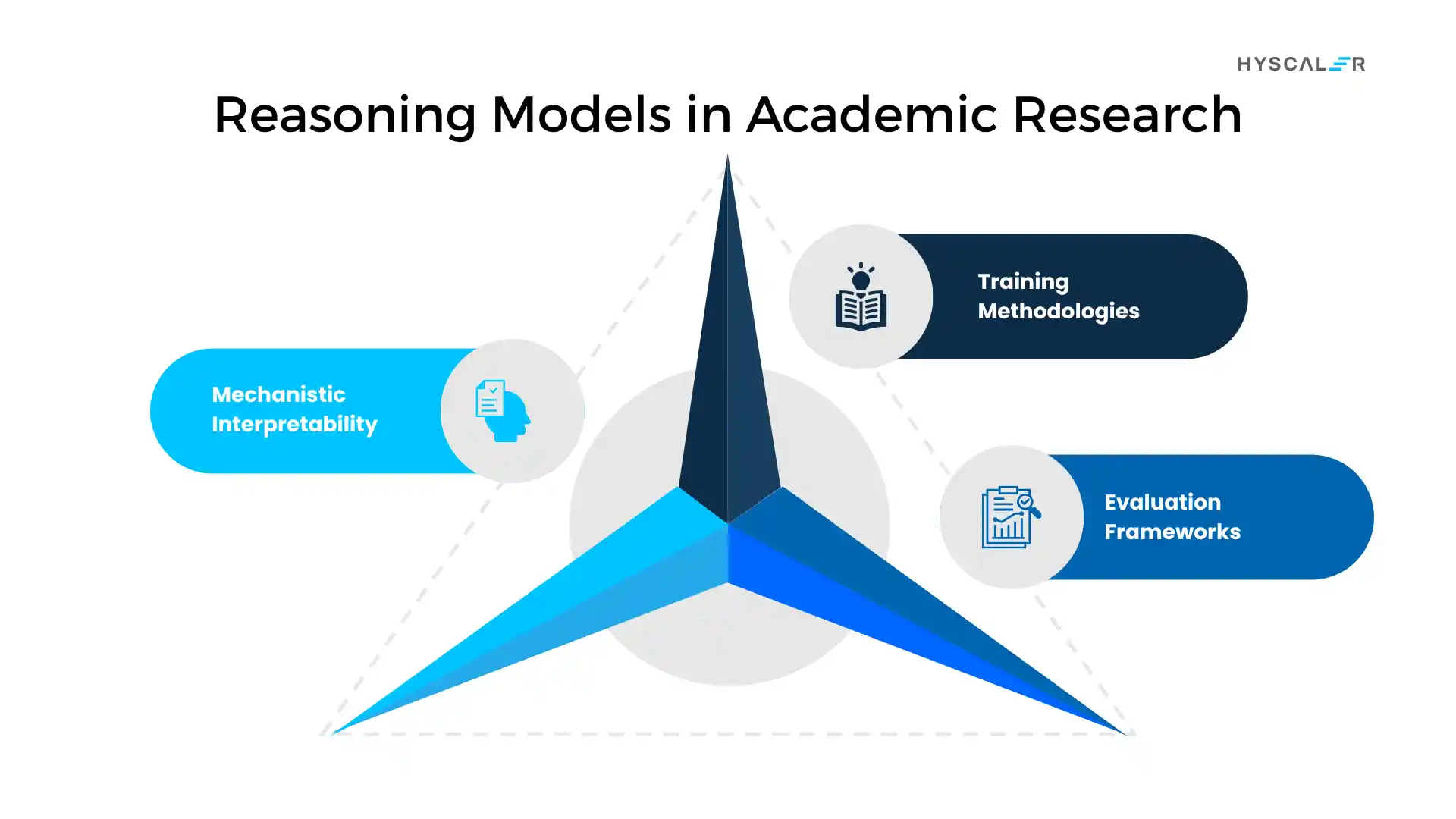
The reasoning models paper landscape reveals fascinating advances in the field.
Key research directions include:
Mechanistic Interpretability
Researchers are working to understand how reasoning emerges in neural networks, examining the internal representations and computational pathways that enable logical thinking.
Training Methodologies
Papers explore various training approaches:
- Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) for reasoning alignment
- Constitutional AI approaches that embed logical principles
- Curriculum learning that gradually increases reasoning complexity
- Self-play and self-correction mechanisms
Evaluation Frameworks
Academic work has established benchmarks like:
- Mathematical reasoning datasets (GSM8K, MATH)
- Logical reasoning challenges (LogiQA, ReClor)
- Multi-step reasoning tasks (StrategyQA, CommonsenseQA)
- Code reasoning benchmarks (HumanEval, MBPP)
Is GPT-5 a Reasoning Model?
Yes, GPT-5 is definitely a reasoning model.
It is a question people ponder because of its capabilities.
Released on August 7, 2025, GPT-5 represents OpenAI’s most sophisticated integration of reasoning capabilities into a production AI system.
GPT-5 functions as a unified system that includes:
- A smart, efficient base model for standard queries
- GPT-5 thinking: A deeper reasoning model specifically for complex problems
- An intelligent router that automatically selects the appropriate mode based on task complexity
Key reasoning features in GPT-5 include:
- Native reasoning effort settings (minimal, low, medium, high) that control how deeply the model thinks through problems
- Extended chain-of-thought processing for mathematical, coding, and logical challenges
- State-of-the-art coding capabilities with 74.9% accuracy on SWE-bench Verified
- Multimodal reasoning that combines visual, textual, and contextual understanding
- Self-verification mechanisms that check reasoning consistency
GPT-5 is now the default model in ChatGPT for all users, replacing GPT-4o entirely.
It represents a paradigm shift where reasoning isn’t an add-on feature but a core architectural component, making it one of the most advanced reasoning models available today.
Practical Applications of Reasoning Models
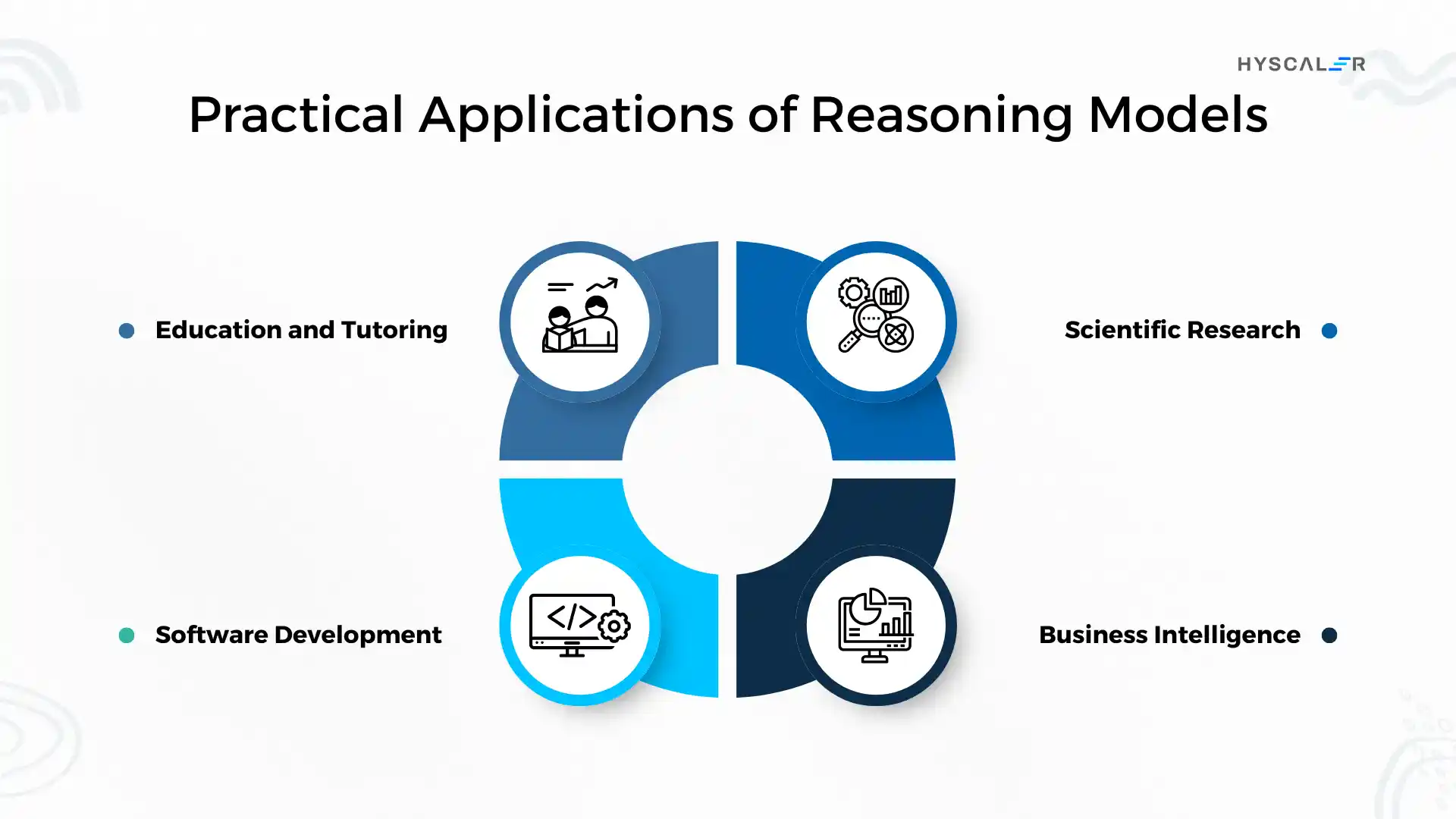
Reasoning models are transforming various industries:
Education and Tutoring
- Step-by-step problem explanations in mathematics and science
- Adaptive learning systems that diagnose conceptual gaps
- Automated assessment with detailed reasoning feedback
Software Development
- Complex debugging with logical error tracing
- Architectural design with consideration of multiple constraints
- Code review with reasoning about best practices
Scientific Research
- Hypothesis generation based on existing literature
- Experimental design with logical optimization
- Data analysis with causal reasoning
Business Intelligence
- Strategic planning with multi-factor consideration
- Risk assessment with explicit reasoning chains
- Decision support systems with transparent logic
The Future of Reasoning Models
The trajectory of reasoning models points toward increasingly sophisticated capabilities:
Near-term developments include:
- Better integration with tool use and external knowledge
- More efficient reasoning that requires less computation
- Domain-specialized reasoning models for specific industries
- Improved interpretability of reasoning processes
Long-term possibilities encompass:
- Truly general reasoning across all domains
- Creative reasoning for novel problem-solving
- Collaborative reasoning with human experts
- Meta-reasoning about reasoning itself
Implementing Reasoning Models: Practical Considerations
For developers and organizations considering reasoning models:
When to Use
Choose reasoning models for:
- Complex problem-solving requires multiple steps
- Tasks where accuracy matters more than speed
- Applications needing transparent decision-making
- Scenarios involving logical constraints or mathematical precision
When Traditional LLMs Suffice
Standard language models work well for:
- Creative content generation
- Conversational interactions
- Simple Q&A applications
- Tasks prioritizing speed over deep reasoning
Integration Strategies
- Start with API access to commercial reasoning models
- Experiment with open-source alternatives on Hugging Face
- Develop domain-specific fine-tuned versions for your use case
- Implement hybrid systems combining reasoning and traditional models
Conclusion: The Reasoning Revolution
Reasoning models represent a fundamental shift in artificial intelligence, from systems that excel at pattern matching to systems that truly think through problems.
As these technologies mature, they promise to extend AI’s reach into domains requiring genuine cognitive depth: scientific discovery, complex engineering, strategic planning, and nuanced decision-making.
The distinction between reasoning models and traditional LLMs isn’t just technical; it’s philosophical.
It reflects our growing understanding that intelligence involves not just knowledge recall but systematic thinking, logical consistency, and the ability to work through unfamiliar challenges.
Whether you’re exploring OpenAI’s latest offerings, experimenting with models on Hugging Face, or reading the latest reasoning models papers, you’re witnessing a transformation in what machines can think and understand.
The age of reasoning AI has arrived, and it’s reshaping our relationship with artificial intelligence in profound ways.
What challenges would you like to solve with reasoning models?
The future of thoughtful AI is here.
Are you ready to harness its potential?
FAQs
How are reasoning models trained?
They are trained similarly to LLMs, with billions of parameters, incorporating a Chain-of-Thought (CoT) process that imitates human problem-solving skills. CoT operates in machine language for self-referencing, then provides output in human language, and is the primary reason reasoning models provide well-structured answers.
What defines a reasoning model?
The well-structured framework or computational method used to process the information, draw inferences, and make decisions based on logic, data, or rules, is what defines the reasoning model. The Chain-of-Thought (CoT) that is incorporated makes it happen.
What is the best model for reasoning?
Among the best reasoning models, OpenAI O3 stands out as the data provided by it is the most structured, with step-by-step reasoning.
What is a traditional LLM?
Large Language Models (LLMs) are sophisticated artificial intelligence systems trained on massive datasets containing billions or trillions of parameters and data. These are designed to understand, generate, and manipulate human language. The “large” designation typically refers to billions of parameters that the model processes and generates text.