Table of Contents
Artificial intelligence is transforming rapidly, and at its core lies a skill that’s evolving just as fast: prompt engineering.
As we move through 2025 and look ahead to 2026, the way we communicate with AI systems has become less about memorizing perfect phrases and more about understanding intelligent workflows, context management, and strategic implementation.
What is Prompt Engineering?
Prompt engineering is the art and science of crafting precise instructions to guide AI models like GPT-4, Claude, Gemini, and others toward producing accurate, relevant, and useful outputs.
Think of it as learning a new language, one where clarity, context, and structure determine whether you get exceptional results or mediocre ones.
In simple terms, prompt engineering transforms the “black box” of large language models into controllable, predictable tools that can solve real business problems, automate workflows, and generate creative content at scale.
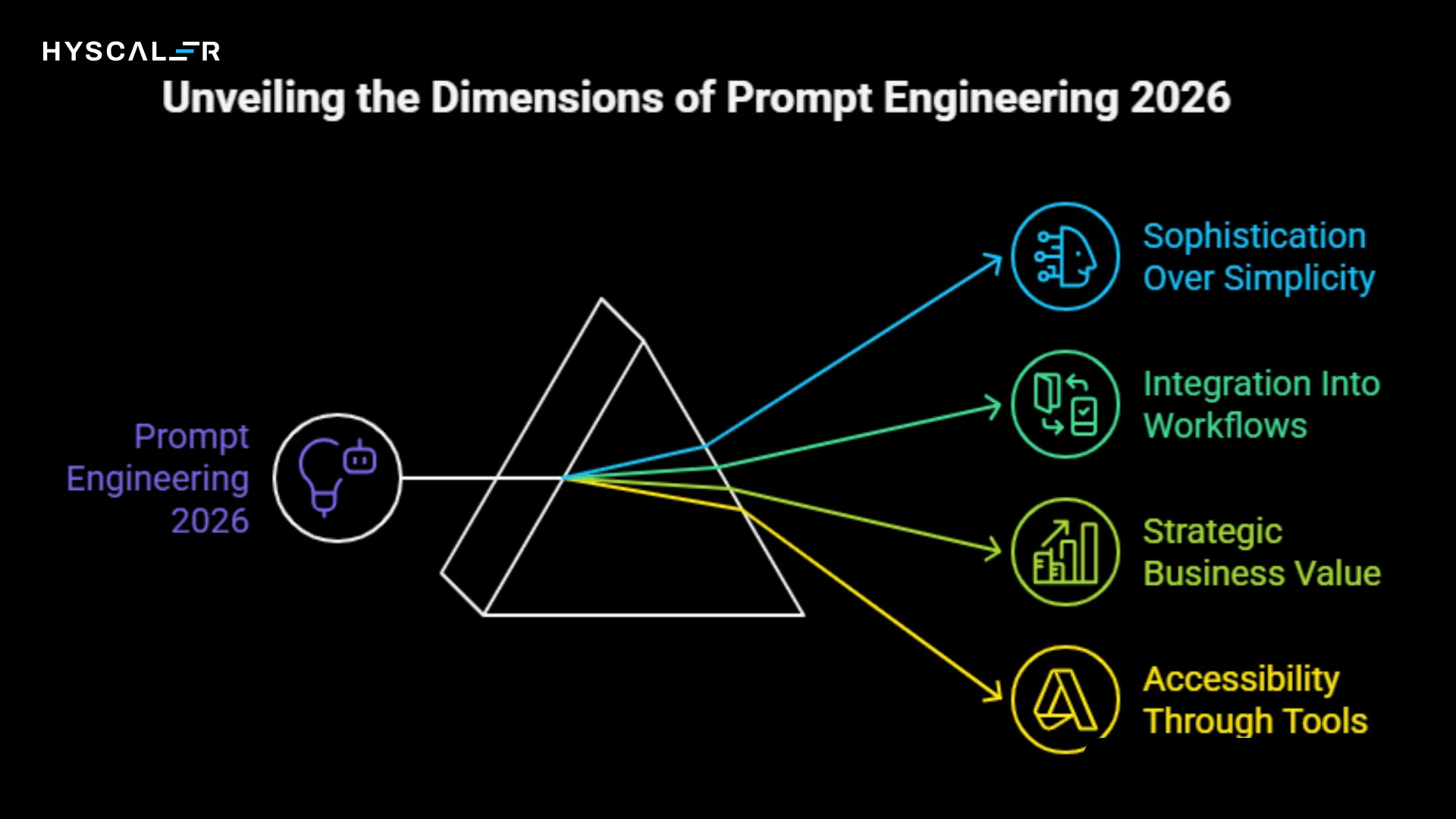
What is Prompt Engineering 2026?
Prompt engineering in 2026 represents a significant maturation from its early days.
Unlike 2023, when people believed dedicated “Prompt Engineer” roles with six-figure salaries would dominate the job market, the field has evolved into something more nuanced and democratized.
Today’s prompt engineering is characterized by:
Sophistication Over Simplicity: Modern AI models have become significantly more intelligent and context-aware. You can provide simple, worded prompts as models understand natural language and user intent.
Integration Into Workflows: Rather than being a standalone skill, prompt engineering has become embedded in product development, content creation, customer service, data analysis, and automation processes. Product managers, marketers, developers, and analysts all need a basic understanding of prompt engineering.
Strategic Business Value: Organizations implementing structured prompt engineering frameworks report productivity improvements averaging 67% across AI-enabled processes. Well-crafted prompts directly impact ROI, operational efficiency, and competitive advantage.
Accessibility Through Tools: No-code and low-code prompt design tools are making the discipline accessible to everyone. Visual interfaces, prompt libraries, and AI-assisted prompt refinement have made it easy to enter.
Prompt Engineering Examples
Understanding prompt engineering becomes easier with concrete examples.
Here are practical applications across different techniques:
1. Zero-Shot Prompting
Zero-shot prompting instructs an AI to perform tasks without providing examples:
Example:
Classify the following text as neutral, negative, or positive.
Text: I think the vacation was okay.
Sentiment:NeutralThe model generates “Neutral” without any prior sentiment analysis examples.
2. Few-Shot Prompting
Few-shot prompting dramatically improves accuracy by showing the model examples of exactly what you want:
Example:
Convert these product names to SKU codes:
Product: Blue Cotton T-Shirt
SKU: BLU-COT-TSH-001
Product: Red Leather Wallet
SKU: RED-LEA-WAL-002This technique can improve accuracy from 0% to 90% in specialized tasks like medical coding or product categorization.
3. Chain-of-Thought Prompting
This technique encourages step-by-step reasoning for complex problems:
Example:
Problem: When I was 6, my sister was half my age. Now I'm 70. How old is my sister?
Let's solve this step by step:
1. When I was 6, my sister was 3 (half of 6)
2. The age difference is 3 years
3. This difference never changes
4. Now I'm 70, so my sister is 70 - 3 = 67 years old4. Role-Based Prompting
Assigning specific roles helps the AI adopt appropriate perspectives:
Example:
You are a cybersecurity analyst with 10 years of experience. Review the following incident report and provide:
1. Risk assessment (High/Medium/Low)
2. Immediate action items
3. Long-term prevention strategies
[Incident details here]5. Structured Output Prompting
Defining the desired format ensures consistency:
Example:
Analyze the quarterly sales data and provide:
**Executive Summary:** (3-4 sentences)
**Key Metrics:**
- Revenue Growth: [percentage]
- Top Product: [name]
- Regional Performance: [breakdown]
**Recommendations:** (3 bullet points)6. Multimodal Prompting
Combining text with images or other media types:
Example:
[Image of product design]
As a UX designer, analyze this interface and provide:
- Three usability improvements
- Color scheme recommendations
- Accessibility concernsWhat is the Future of Prompt Engineering?

The future of prompt engineering is paradoxically both more important and less visible.
Here’s what’s emerging:
Evolution, Not Extinction
While some argue that prompt engineering as a standalone role is becoming obsolete, the skill itself is becoming more critical, just distributed differently.
Instead of specialized “prompt engineers,” we’re seeing prompt engineering expertise embedded into various roles across organizations.
From Prompts to Orchestration
The future belongs to AI orchestration, designing complex workflows where multiple AI agents work together autonomously.
This means:
- Multi-Agent Systems: Instead of crafting single prompts, professionals design systems where AI agents collaborate, delegate tasks, and self-correct
- Workflow Design Over Word Engineering: The focus shifts from perfecting individual prompts to architecting entire AI-powered processes
- Adaptive AI: Systems that learn user preferences and adjust automatically, reducing the need for manual prompt refinement
Conversational Programming
We’re moving toward a world where AI systems understand intent rather than requiring precise instructions.
This “conversational programming” paradigm means:
- Natural language becomes sufficient for complex tasks
- AI handles logic and implementation details
- Iteration happens through dialogue rather than prompt rewriting
Context Over Craft
Modern models with persistent memory and long context windows are changing the game.
Instead of engineering perfect prompts, users provide rich context once, and the AI maintains understanding across sessions.
Key Trends for the Future to Look Out For
As we head into 2026, several transformative trends are reshaping prompt engineering:
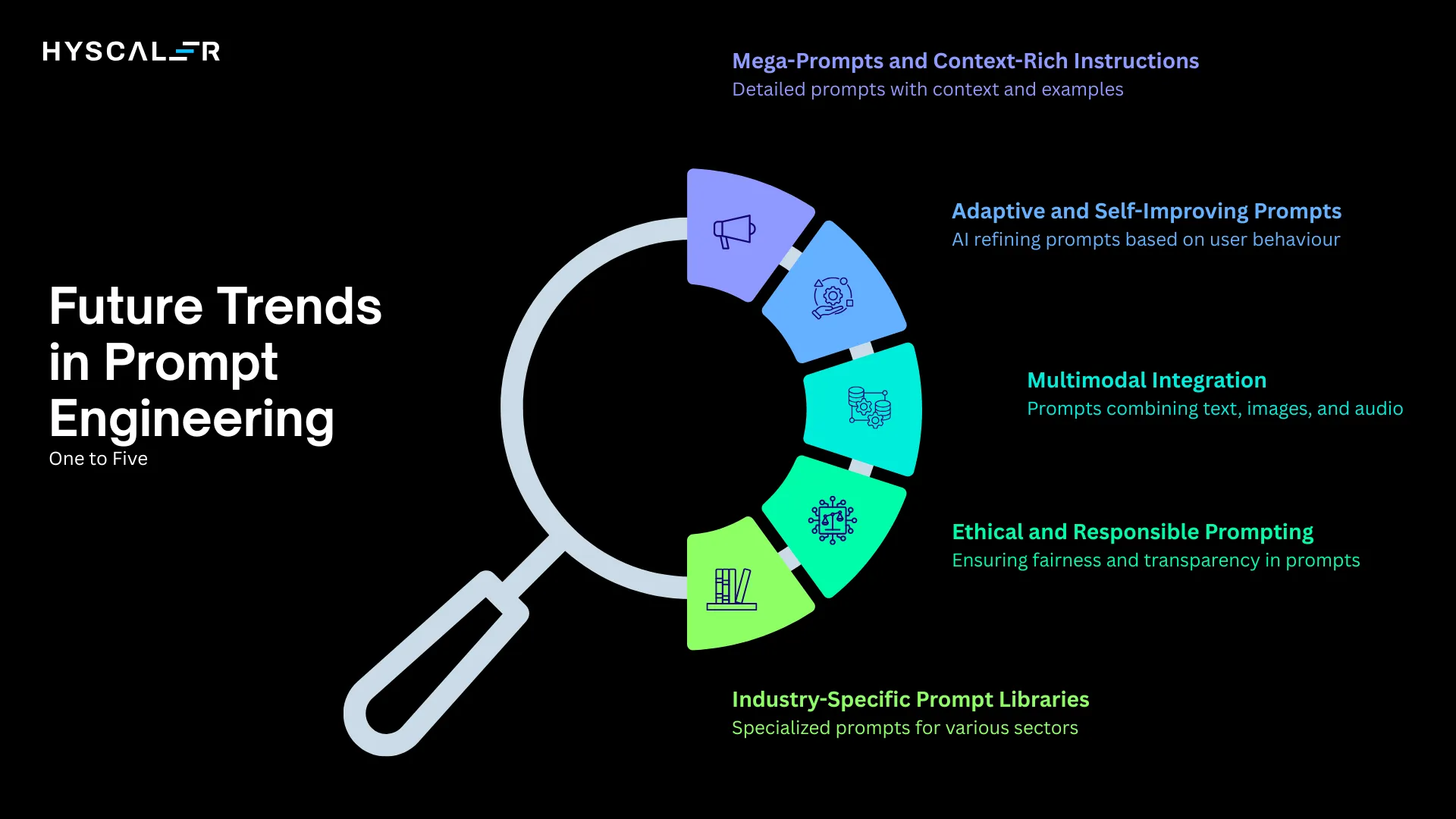
1. Mega-Prompts and Context-Rich Instructions
The trend toward longer, more detailed prompts packed with context is accelerating. Instead of short, clever phrases, effective prompts now include comprehensive background information, examples, constraints, and formatting specifications.
2. Adaptive and Self-Improving Prompts
AI systems are beginning to help refine prompts automatically. Future models will iterate on user queries, generating or adjusting prompts on the fly based on context and user behavior. This creates a feedback loop where the AI becomes your prompt engineering assistant.
3. Multimodal Integration
With models understanding text, images, audio, and video simultaneously, prompt engineering is expanding beyond words. Expect to craft prompts that include visual cues, audio context, and text instructions, working together.
4. Ethical and Responsible Prompting
As AI systems become more powerful, ensuring fairness, transparency, and bias reduction in prompts is critical. Organizations are developing frameworks for ethical prompt design that prevent harmful outputs and maintain compliance with regulations.
5. Industry-Specific Prompt Libraries
Specialized prompt templates and frameworks are emerging for different sectors:
- Healthcare: Diagnostic assistance and patient communication
- Legal: Contract analysis and case research
- Finance: Risk assessment and market analysis
- Marketing: Campaign creation and customer segmentation
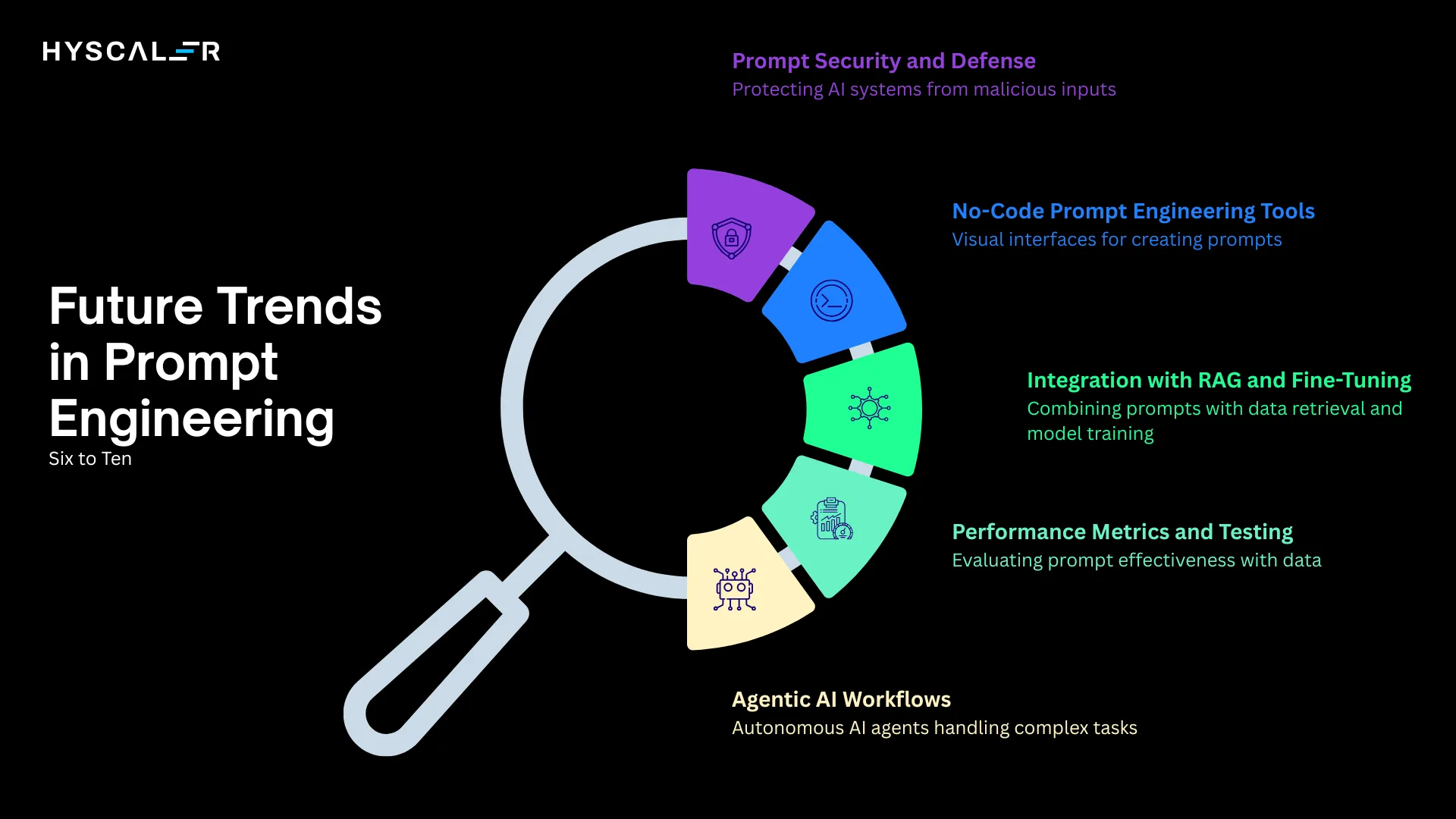
6. Prompt Security and Defense
With the rise of prompt injection attacks and jailbreaking attempts, defensive prompt engineering is becoming essential. Organizations are implementing guardrails, testing frameworks, and security measures to protect AI systems from malicious inputs.
7. No-Code Prompt Engineering Tools
Visual prompt builders, drag-and-drop interfaces, and AI-assisted prompt generation tools are democratizing access. By 2026, creating sophisticated prompts won’t require technical expertise.
8. Integration with RAG and Fine-Tuning
Prompt engineering is converging with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and model fine-tuning. The best results come from combining well-crafted prompts with relevant retrieved data and specialized model training.
9. Performance Metrics and Testing
Systematic evaluation of prompt performance is becoming standard practice. Organizations track metrics like accuracy, consistency, cost-per-query, and user satisfaction to optimize their prompt strategies.
10. Agentic AI Workflows
The biggest shift is toward autonomous AI agents that handle multi-step tasks with minimal human intervention. These agents:
- Break complex problems into subtasks automatically.
- Make decisions based on intermediate results.
- Call external tools and APIs as needed.
- Learn from feedback to improve over time
Skills You Need to Stay Competitive
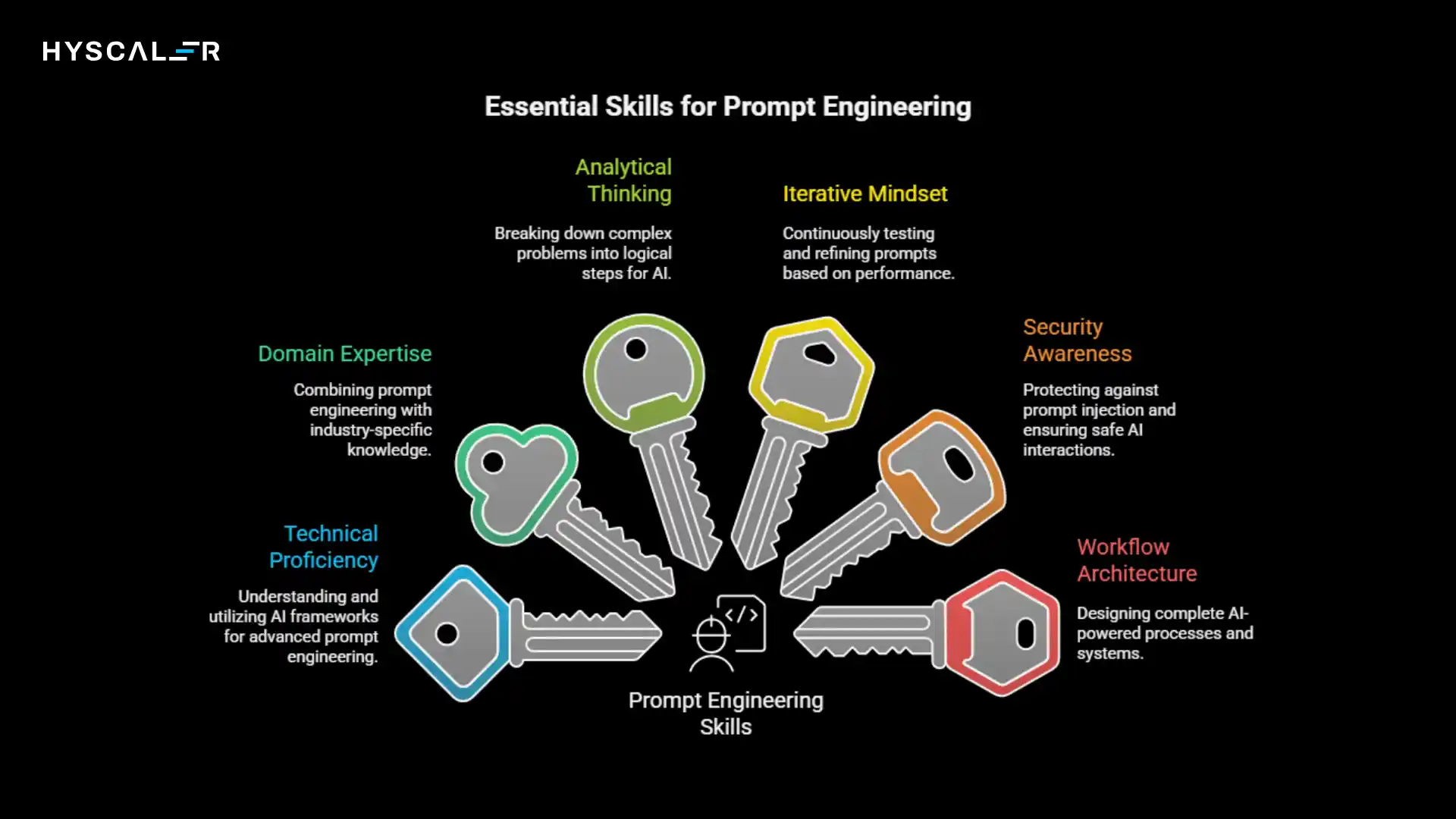
To remain relevant in prompt engineering through 2026 and beyond, focus on developing these competencies:
Technical Proficiency: Understand frameworks like LangChain, CrewAI, and AutoGen for prompt chaining and multi-agent orchestration.
Domain Expertise: Combine prompt engineering with deep knowledge in your industry, healthcare, finance, legal, marketing, or technology.
Analytical Thinking: Develop the ability to break complex problems into logical steps that AI can follow.
Iterative Mindset: Embrace continuous testing, measurement, and refinement of prompts based on real-world performance.
Security Awareness: Learn defensive techniques to protect against prompt injection and ensure safe AI interactions.
Workflow Architecture: Think beyond individual prompts to design complete AI-powered processes and systems.
Conclusion
Prompt engineering in 2026 isn’t about memorizing templates or landing a dedicated “Prompt Engineer” job title.
It’s about understanding how to communicate effectively with AI systems to solve real problems, automate workflows, and create value at scale.
The professionals who thrive will be those who:
- View AI as a collaborative partner rather than a tool to be tricked
- Focus on outcomes and workflows rather than perfect phrasing
- Continuously experiment, measure, and adapt their approaches
- Combine prompt engineering with domain expertise and strategic thinking
- Embrace new paradigms like agentic AI and orchestration
As AI models become more sophisticated and intuitive, the barrier to effective interaction continues to drop.
But the strategic value of knowing how to extract maximum value from these systems, through well-designed prompts, workflows, and architectures, will only increase.
The future of prompt engineering isn’t extinction, it’s evolution into something more powerful, more distributed, and more essential to every organization navigating the AI revolution.
Stay ahead of the curve by treating prompt engineering not as a static skill to master, but as an evolving practice that grows alongside AI capabilities.
The best prompt engineers in 2026 will be those who never stopped learning, experimenting, and adapting.
Is prompt engineering a job?
Yes, and the position or role is called an AI Systems Engineer or LLM Ops Specialist.
What skills do prompt engineers need?
For prompt engineers, they need to have a deep understanding of vocabulary, nuance, phrasing, context, and linguistics.