Table of Contents
Machine learning is no longer just a concept for the future. It is now the key operational structure for the global financial industry. This technology is changing how banks manage risk, serve customers, and compete in a fast-moving digital world.
This guide will explain machine learning in banking. We will cut through the hype to give you clear facts and real examples of its impact. You will discover its most critical uses that are transforming the sector.
We will cover the main benefits driving its adoption, the big challenges to navigate, and the future trends that will shape the next decade of finance. Let’s explore this intelligent revolution.
What is Machine Learning in Banking and Why is it a Game-Changer?
Among the forces shaping modern finance, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and its subfield, Machine Learning (ML), stand out. These are the most impactful trends in FinTech. These technologies help financial institutions analyze huge, complex datasets. They find valuable patterns that humans cannot detect. This is more than a small improvement; it changes the entire financial sector.
In simple terms, Machine Learning is part of artificial intelligence. Its algorithms learn from data and then make predictions. Instead of being programmed for a specific task, these systems “train” on past information. This lets them automate cognitive tasks, spot trends, and generate insights. Their accuracy increases over time.
Financial institutions are adopting ML for several core reasons that impact their strategy and bottom line:
- Process Automation & Efficiency: ML automates simple, repeated tasks. This includes data entry, document checks, and claims processing. Automation lets employees focus on key tasks. It cuts operating costs and minimizes human mistakes.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: By building models that better understand large amounts of data. This helps companies make smarter decisions. This applies to many areas. Examples include setting the best product prices, managing investment risks, understanding how customers act, and forecasting market changes.
- Competitive Advantage: In a data-rich industry, banks must analyze information faster and more accurately. This ability is a major advantage. ML-powered big data analysis helps banks find new business opportunities. They can respond to market shifts instantly. They make smarter decisions with unmatched speed.
To understand this technology’s impact, look at its practical uses in banking. These applications are powerful and diverse.
5 Key Use Cases of Machine Learning in Banking Operations
Machine learning is changing banking. It is now used in many areas, from back-office tasks like compliance to customer service. Banks use it to be more efficient and create more value. Its uses are vital to key banking functions, including credit, asset management, and cybersecurity.
Here are five of the most important uses today.
1. Fraud Detection & Cybersecurity
Machine learning (ML) algorithms provide a robust, immediate defense against financial crime. They test massive amounts of transaction data in real time. These systems learn from past data.
So, they recognize the subtle, complex patterns of fraud. Traditional security relies on rigid, rule-based systems. These are slow to change.
In contrast, ML models immediately detect anomalies and new threats. They catch what traditional systems miss. Thus, ML creates a dynamic, intelligent security shield.
Real-World Example: HSBC collaborated with Google Cloud. They deployed a machine learning system for anti-money laundering. This new system was much more effective than the old rule-based one. For example, it cut false positives by 60%. Importantly, it also uncovered two to four times more financial crime incidents.
This application improves decision-making for risk management. Also, it boosts operational efficiency. It does this by letting staff focus on the most critical alerts.
2. Credit & Lending: Redefining Risk Assessment
ML transforms the old process of credit scoring and loan approval. Instead of only using FICO scores, ML models analyze thousands of new data points. This creates a clearer, more accurate picture of a borrower’s credit.
The data includes rent payments, utility bills, and social profiles. So, lenders generate more precise risk scores. This also automates loan approvals for more applicants.
Real-World Example: Banco Santander’s US car financing branch uses an ML-powered system. This system assesses the chance of credit default. The solution speeds up loan approvals. Furthermore, it lets the bank rapidly adjust its risk and pricing models as market conditions change.
Faster, more accurate credit checks give Santander a strong advantage in auto lending.
3. Trading & Investments: The Algorithmic Edge
Machine learning (ML) gives traders a critical edge. ML algorithms quickly process huge amounts of real-time market data. They also analyze news sentiment and past trade results. This allows them to forecast market trends and execute trades with speed and high accuracy.
Furthermore, this technology makes investing easier for everyone through “robo-advisors.” These tools use ML to create and manage personalized investment portfolios for everyday investors.
Real-World Example: BlackRock’s Aladdin platform is a top investment technology solution. It uses machine learning to offer advanced analytics for managing trades and cutting investment risk. Moreover, it now uses generative AI. This helps summarize complex portfolio analyses into short, clear reports. As a result, financial advisors gain more power.
This powerful mix of data-driven decisions and automated processes gives BlackRock and its clients a distinct competitive advantage. They expertly navigate complex markets.
4. Customer Experience: The Rise of Personalized Banking
Machine learning drives hyper-personalization. This enables banks to offer tailored, predictive support instead of generic service. Intelligent chatbots and virtual assistants give 24/7, human-like help for common questions.
Examples include Bank of America’s Erica and the Chase Digital Assistant. Furthermore, ML algorithms analyze customer data. They expect needs, offer personalized product recommendations, and deliver proactive guidance. This builds deeper loyalty and engagement.
Real-World Example: Wells Fargo uses its “Customer Engagement Engine.” It analyzes over 150 data points in 350 milliseconds. Thus, the bank provides targeted “next best conversation” suggestions instantly. This increases customer engagement rates by up to 10x.
This ability to deliver personalized insights quickly provides a major competitive edge. Ultimately, it boosts customer retention and revenue growth.
5. Compliance & Operations: Automating the Back Office
ML streamlines regulatory compliance. This area is now called “RegTech.” ML automates Know Your Customer (KYC) operations. Furthermore, it monitors regulatory changes. It also digitizes documents using Optical Character Recognition (OCR). Thus, ML helps banks cut risk and boost efficiency.
These systems analyze customer data to assign risk scores. They also check transactions for suspicious activity. So, they ensure the institution adheres to complex financial legislation more accurately.
Real-World Example: JPMorgan Chase launched a broad AI Research Program. Its goals include eradicating financial crime and perfecting the client experience. Specifically, the bank employs AI-powered compliance monitoring systems. These detect and prevent fraudulent transactions. This ensures adherence to all regulatory standards.
This deep investment in AI-driven compliance sharpens the bank’s decision-making on risk. It also creates massive operational efficiencies in its back-office functions.
These individual applications transform specific banking functions. But, their true strategic power emerges when we quantify the cumulative, bottom-line benefits they deliver to the entire institution.
Quantifying the Core Benefits of ML
Beyond new technology, machine learning offers clear, measurable benefits. These benefits affect all parts of a financial institution. They cut operational costs and grow revenue.

A key McKinsey study estimates that generative AI alone could add $200 billion to $340 billion in annual value to the banking industry. This value comes from increased productivity.
These strategic advantages create several main benefits:
- Enhanced Risk Management: ML uses powerful, data-driven insights. It minimizes credit risk, investment risk, and financial crime. For example, DBS Bank used AI/ML to spot over 95% of its non-performing SME loans. It found these loans at least three months before the businesses faced credit stress. This allowed the bank to act early.
- Improved Operational Efficiency & Lower Costs: Machine learning automates common back-office and customer service tasks. Thus, it cuts operational costs. It also reduces human error and boosts employee productivity. This frees up staff for more important, strategic work.
- Faster, More Accurate Decision-Making: The ability to analyze massive datasets leads to quicker and more reliable decisions. So, customers receive faster loan approvals. Banks achieve more effective algorithmic trading. They also respond to market changes faster.
- Superior Customer Experience & Revenue Growth: ML powers hyper-personalization. This leads to greater customer engagement and stronger loyalty. It also creates targeted cross-selling chances. DBS Bank proves this; it reported a SGD 150 million revenue uplift from its AI/ML projects.
- Always-On Customer Service: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants give customers instant, 24/7 support for their basic needs. This improves satisfaction and eases the load on human support teams.
But, realizing these large benefits demands a clear understanding of the major challenges. Banks must manage this technological shift.
The Challenges & Risks
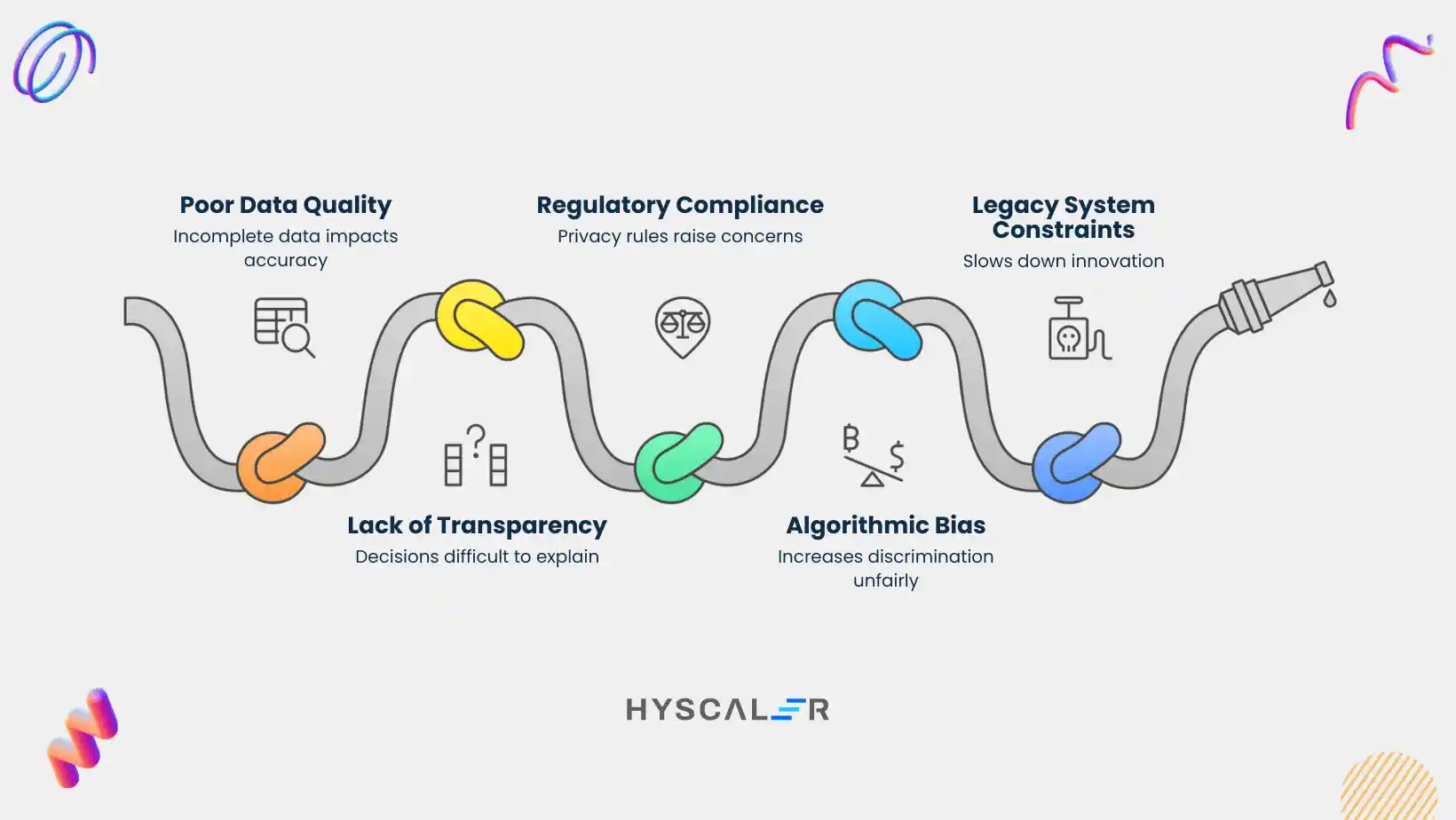
While the promise of machine learning is great, successful implementation faces big challenges. Banks must manage complex issues to use this technology. These challenges involve data, technology, and changing rules.
- Poor Data Quality and Availability: Machine learning models rely on the data they use for training. Banks often struggle with huge amounts of old or incomplete information. This data is scattered across old systems and separate silos. Thus, preparing the high-quality data needed for accurate models becomes hard.
- Lack of Model Transparency (The “Black Box” Problem): Many advanced ML models are very complex. Thus, explaining the exact reason behind their decisions is difficult. This lack of clarity is what leading institutions try to fix. For example, DBS Bank’s PURE Principles demand that every data use case must be Explainable. This “black box” nature creates a major problem for following regulations. Institutions must be able to audit and justify important decisions, like turning down a loan.
- Regulatory Compliance and Security: Using sensitive customer data raises serious concerns about data privacy rules like GDPR. Additionally, institutions must ensure their ML models are fair, auditable, and safe from cyberattacks. Adopting full governance frameworks is vital to using data responsibly and building trust with regulators.
- Algorithmic Bias: If an ML model trains on historical data that has existing biases, it can continue and even increase discrimination. This is a very high-risk area in credit scoring. Biased algorithms could unfairly deny loans to qualified people from certain groups.
- Legacy System Constraints: Many banks use old and inflexible IT systems. Integrating modern, quick ML solutions with these rigid legacy systems is often complex, costly, and takes a lot of time. This situation slows down innovation.
Overcoming these obstacles is key. It helps manage current projects and prepares banks for the next wave of innovation.
What’s Next for Machine Learning in Banking?

The evolution of machine learning in finance is speeding up. Several new advancements will revolutionize the industry further. These emerging technologies will solve current problems. They will also unlock new capabilities for banks and their customers.
- Synthetic Data Generation: Generative AI creates fake but realistic datasets. This helps overcome data privacy and availability problems. This “synthetic data” matches the statistics of real customer data. Crucially, it does not share confidential information. This makes it vital for training fraud detection and anti-money laundering (AML) models.
- Explainable AI (XAI): XAI addresses the “black box” problem. This field develops methods to make AI decisions clear and easy for people to understand. This is key for getting regulatory approval and building stakeholder trust. It also allows for auditing and debugging algorithms effectively.
- Quantum Machine Learning (QML): This new field combines the huge power of quantum computing with machine learning. QML is still in its early stages. But, it promises to solve highly complex problems. For example, it could handle advanced algorithmic trading and portfolio optimization. These problems are too hard for even the most powerful classic computers.
- Generative and Agentic AI: Sophisticated AI agents will transform employee productivity and customer service. Tools like Citi’s Stylus agent support employees with tasks. These include drafting emails and summarizing documents. Furthermore, these agents will serve customers as advanced, conversational virtual assistants. They will manage complex, multi-step financial tasks.
These future trends emphasize building a strategic foundation now. We must capitalize on tomorrow’s innovations.
How to Prepare Your Bank for ML Transformation
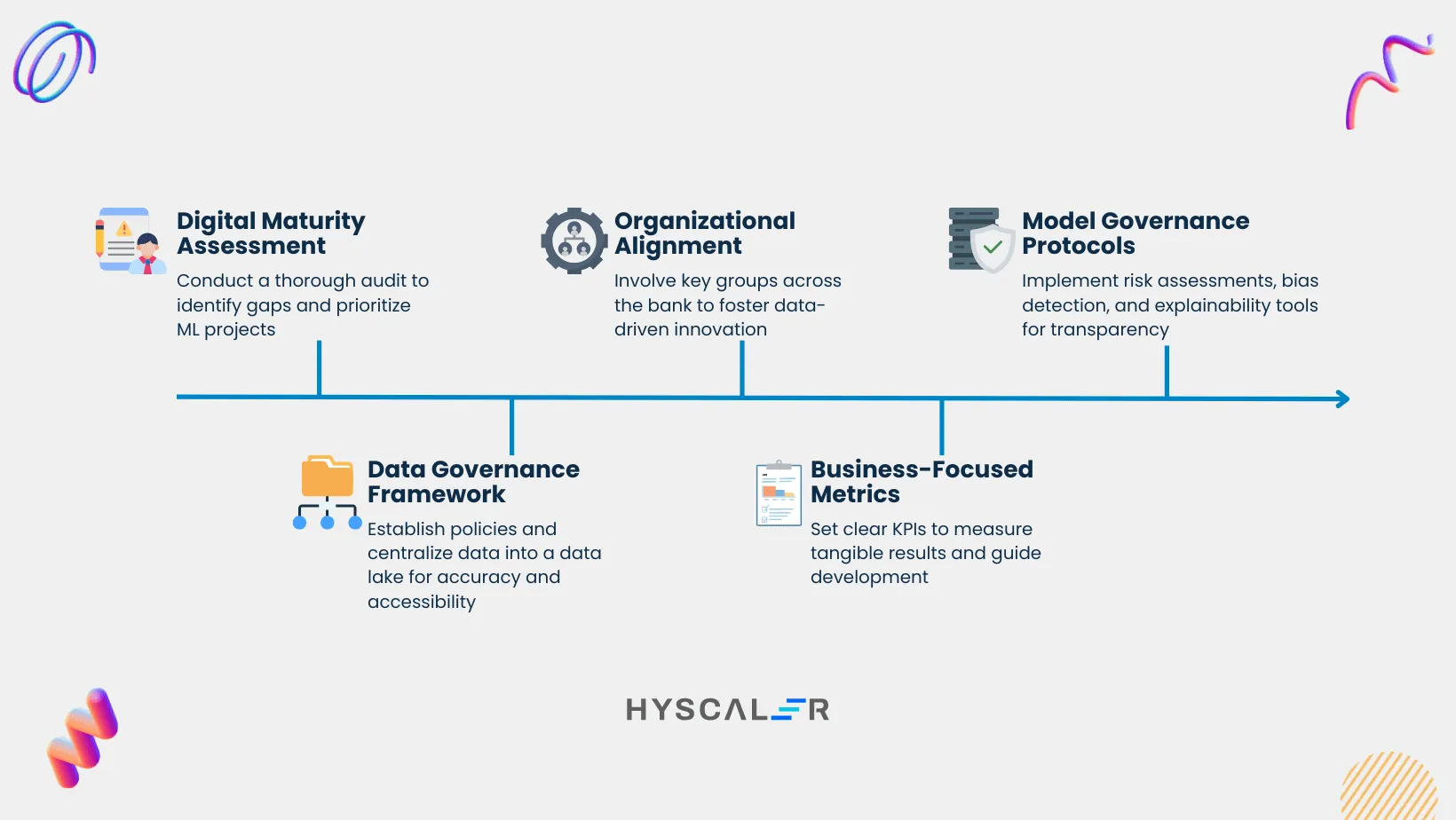
Successfully integrating machine learning is not just a technological challenge. It is a strategic transformation. This transformation requires a clear vision, strong rules (governance), and deep alignment across the organization.
Adopt a deliberate, step-by-step approach. This is essential for lowering risk and boosting the return on investment.
- Start with a Real Audit, Not a Wish List: Real change begins with a careful digital maturity audit. This audit identifies real technology gaps and assesses data readiness. Rank ML projects that offer “quick wins” and high business value. Examples include fraud detection or credit risk assessment. These projects build momentum and secure executive approval (buy-in).
- Build a Strong Data Strategy: A robust data governance framework is necessary. Thus, you must create policies. These policies ensure data is accurate, compliant, and accessible. The critical first step is often to combine data from separate, older systems. Centralize this data into a data lake. This breaks down silos and creates one reliable source of truth for your ML models.
- Create a Coalition, Not Just a Team: Lasting ML initiatives need widespread organizational support. From the start, involve key groups: IT, business lines, legal, and compliance. Align on strategic goals. Define the project scope. Cultivate a culture of data-driven innovation throughout the institution.
- Define Success First: Establish clear, business-focused metrics for each ML model. This proves the value and guides development. These Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) must go beyond technical accuracy. Instead, they must measure tangible results. Examples include cost savings, revenue increase (uplift), or acceptable error rates in a real-world setting.
- Embed Risk Management Immediately: Address the inherent risks of ML proactively. Create strong model governance protocols from the beginning. This means conducting regular risk assessments. Identify potential biases and security flaws. Install explainability tools. These tools ensure transparency for both internal auditors and external regulators.
This blueprint offers institutions a clear path. They move from ambition to execution. They prepare to succeed in an increasingly intelligent financial world.
Conclusion
Machine learning is no longer a theory. It is a present-day reality. This technology now fundamentally redefines the banking industry.
It empowers institutions to operate with greater efficiency. Furthermore, it manages risk with amazing foresight. Banks can also deliver the superior, personalized experiences customers demand. Thus, the question is not if banks should adopt AI. Instead, the question is how they will adopt it.
Based on these applications and strategies, what is the first area where machine learning will make the biggest impact in your organization?
Are there any other exciting use cases of machine learning in banking that we missed? Share your thoughts in the comments below!
FAQs
What does machine learning (ML) mean in banking?
ML is a branch of artificial intelligence. It builds computer programs that learn from data to predict results. These tools find hidden patterns in huge data sets that humans cannot see.
Why is machine learning important in the banking sector?
ML handles massive data volumes that overwhelm people. Consequently, it cuts costs and boosts speed while improving business outcomes. It also discovers deeper links than traditional software.
In which areas of banking and finance is machine learning used?
Banks use ML in credit, payments, and asset management. Moreover, they use it for trading, regulatory tasks, and customer service.
What are the main applications of machine learning in retail banking and finance?
Fraud detection stands as a primary use for retail banks. Additionally, ML judges credit and predicts which customers might leave.
How is machine learning used by banks in day-to-day operations?
Banks automate paperwork and math with ML. These systems also monitor data updates and track customer behavior.
What are the main types of machine learning?
Supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning. These methods teach programs to recognize patterns and make decisions.
How do banks benefit from using machine learning?
Banks boost revenue and lower risks. For example, they spot bad loans three months before a business fails.
How does machine learning add value to banking customers?
Customers receive 24/7 help from smart chatbots. They also get personalized advice and faster loan answers.
Can machine learning improve real-time fraud detection in banks?
Yes, ML identifies strange patterns in transactions as they happen. It blocks scams instantly to save money and protect trust.
What are the most common machine learning problems in the banking sector?
Banks must tackle credit risk and customer loss. They also face “black box” models that are hard for regulators to understand.
How can banks solve machine learning challenges effectively?
Banks fix problems by cleaning their data and hiring experts. Additionally, they use “Explainable AI” to show how models think.
How can machine learning help with regulatory compliance in banking?
ML reads piles of legal documents to track changes. Then, it maps these rules to bank controls automatically to avoid fines.
How is JP Morgan using artificial intelligence and machine learning?
JP Morgan deploys a digital assistant for customer inquiries. They also use AI to stop fraud and research economic shifts.
Does Goldman Sachs use machine learning, and for what purposes?
Goldman Sachs utilizes ML for algorithmic trading. Their tools study market data to trade with high speed and accuracy.