Table of Contents
In today’s fast-paced digital world, businesses constantly seek ways to improve efficiency, reduce latency, and enhance user experiences. One technology making waves in this realm is edge computing. This innovative approach processes data closer to the source, bringing numerous benefits and transforming industries across the board. From healthcare to manufacturing, edge computing is revolutionizing how data is handled and utilized. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of edge, its importance, and its transformative impact on various industries.
How Does Edge Computing Work?
Edge computing involves decentralizing data processing by bringing it closer to the source of data generation. Unlike traditional cloud computing, where data is sent to centralized data centers for processing, edge computing processes data on local devices or edge servers. This proximity reduces the time it takes to analyze and act on data, making it ideal for applications requiring real-time responses.
The process begins with data generation, often through IoT devices or sensors. This data is then processed locally by edge servers, which can include gateways, routers, or even the devices themselves. By handling data at the edge, businesses can reduce latency, improve bandwidth efficiency, and enhance overall performance. Furthermore, this approach minimizes the need to transmit large volumes of data to distant data centers, reducing costs and increasing data security.
Why Is Edge Computing Important?
Data is being produced at an exceptional speed worldwide. From wearables tracking our health to sensors monitoring industrial processes, this data holds immense value. But what good is data if it takes too long to analyze? Here’s where edge computing shines.
By processing data locally, edge computing eliminates latency issues. This is crucial for applications that demand real-time responses, like:
- Autonomous vehicles: Cars need to react to their surroundings instantly to avoid accidents. Edge computing enables real-time object recognition and path optimization.
- Industrial automation: Edge servers can analyze sensor data to predict equipment failures and prevent costly downtime in factories.
- Smart cities: Traffic management, resource allocation, and emergency response can all benefit from the real-time insights gleaned from Edge.
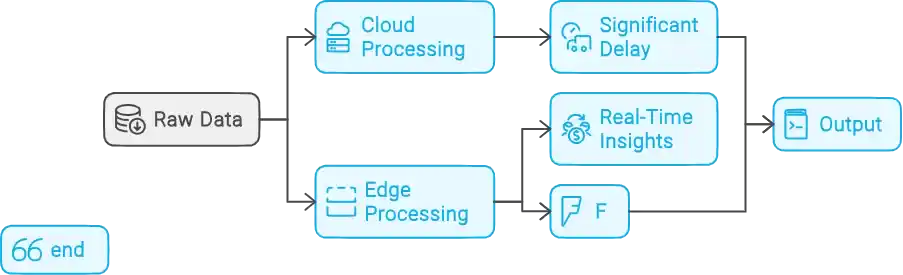
But why is this real-time processing so important? Traditional cloud computing, while powerful, can introduce latency – the time it takes for data to travel to and from centralized servers. A minor delay can result in major impacts.
Consider this: An autonomous vehicle relies on real-time data to navigate safely. If there’s a delay in processing sensor information, the car might not react fast enough to avoid an obstacle. Similarly, a delay in detecting a machine malfunction could lead to a breakdown and production losses in a factory setting.
Edge computing tackles this challenge head-on. By processing data locally, on edge servers, or even on devices themselves, edge computing eliminates latency and enables real-time decision-making. This translates into faster responses, improved efficiency, and better overall performance.
There’s another advantage to local processing: bandwidth efficiency. With billions of devices generating data, the amount of information flowing through networks is immense. Sending all this data to the cloud can strain bandwidth and lead to congestion. Edge computing acts as a filter, processing and analyzing data locally. Only relevant information is then sent to the cloud, significantly reducing the burden on network resources and lowering operational costs.
In essence, edge computing unlocks the true potential of real-time data processing, paving the way for a more responsive, efficient, and data-driven future.
The Role of Edge Computing in Industries
Edge computing is making significant strides across various industries, transforming operations and unlocking new possibilities. For instance, edge computing enables real-time patient monitoring and rapid diagnosis in healthcare. Wearable devices and sensors collect vital signs and health data, which are then processed locally to provide immediate feedback to healthcare providers. This can be life-saving in critical situations where timely intervention is crucial.
In the manufacturing sector, edge computing enhances predictive maintenance and quality control. By analyzing data from machines and equipment in real time, manufacturers can identify potential issues before they lead to costly downtime. Additionally, edge computing facilitates advanced automation, allowing for more efficient and precise production processes. Making quick decisions at the edge reduces delays and improves overall productivity.
Edge vs. Cloud vs. Fog Computing
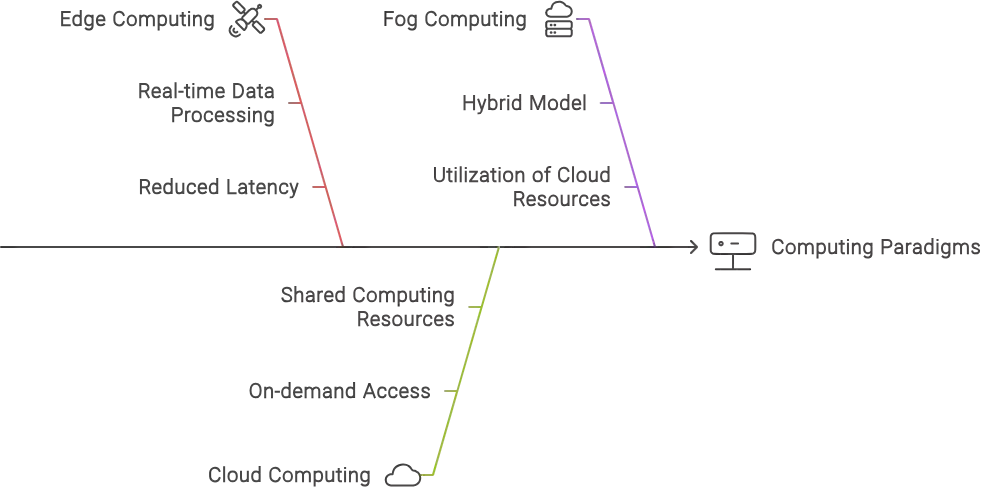
The passage explains the differences between three ways to handle computing tasks: cloud computing, fog computing, and up-and-coming edge computing. Here’s a breakdown:
- Cloud Computing: Imagine a giant warehouse full of powerful computers – that’s the cloud. Your data and applications run on these computers, accessed over the internet. It’s great for scalability (being able to handle more data easily) and offers tons of processing power. However, the data needs to travel to the cloud and back, which can cause delays (latency) for real-time stuff.
- Fog Computing: Think of fog computing as a smaller warehouse closer to your house. It sits between the cloud and the devices that generate data (like sensors). Fog computing can do some processing itself, reducing the amount of data that needs to travel to the big cloud warehouse, which helps with latency.
- Edge Computing: This is where the action happens right at the source of the data. Imagine a mini-computer built into your device itself. Edge offers the fastest possible processing because the data never has to leave the device. This is perfect for real-time applications where speed is crucial.
Here’s an analogy:
- Cloud Computing: You send your laundry to a professional cleaning service (the cloud) – great results, but it takes time.
- Fog Computing: You take your laundry to a local wash-and-fold place (the fog layer) – faster than the professional service, but not as fast as doing it yourself.
- Edge Computing: You wash your clothes at home (the edge device) – the fastest option, but requires your effort.
The best option depends on your needs. If speed is essential, go with edge computing. If you need a lot of storage and processing power, the cloud is a good choice. Fog computing offers a middle ground, helpful when a direct cloud connection is impractical or latency is a concern.
Edge Computing Combined with Other Technologies
This section talks about how combining edge computing with other technologies unlocks even greater potential. Here’s a deeper look:
1. Edge Computing + Artificial Intelligence (AI) = Faster, Smarter Decisions
Imagine a car with both edge computing and AI. Sensors collect data (road conditions, traffic lights, etc.), and the car’s computer (the edge) can analyze it using AI. This allows the car to make real-time decisions (like swerving to avoid an accident) without needing to send data to a distant cloud server for processing. This is crucial for autonomous vehicles where split-second reactions are vital.
2. Edge Computing + Internet of Things (IoT) = Enhanced Efficiency
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to everyday objects with sensors that collect data. Edge computing can process this data locally on the devices themselves, rather than sending everything to the cloud. This is beneficial for:
- Speed: Local processing means faster response times, improving efficiency in areas like smart cities. Traffic lights can adjust based on real-time traffic data, air quality can be monitored and addressed quickly, and energy use can be optimized based on local conditions.
- Reduced Costs: Less data needs to be sent to the cloud, saving on bandwidth costs.
Overall Synergy:
The combination of edge with other technologies like AI and IoT creates a powerful force for innovation. By processing data locally and making quicker decisions, we can achieve greater efficiency and faster responses, and open doors to entirely new applications in various fields.
Use Cases and Examples
This section dives into real-world examples of how different industries leverage edge for their benefit. Here’s a breakdown of the two examples mentioned:
Retail Example: Smart Shelves with Edge
Imagine a grocery store with shelves that are more than just places to store products. These “smart shelves” use sensors to track:
- Inventory Levels: Sensors can detect when items are running low, triggering automatic restocking orders or notifying store staff.
- Customer Interaction: The system might pick up on customers lingering near a specific product, and trigger a display showing relevant information or special offers.
The key point here is that the data from these sensors is processed locally on a device at the edge (perhaps within the shelf itself). This allows for:
- Faster Decisions: Real-time data means quicker actions, like immediately notifying staff about low stock or displaying targeted promotions.
- Improved Efficiency: Automated restocking reduces the need for manual inventory checks, saving time and effort.
Automotive Example: Powering Features in Modern Vehicles
Modern cars are full of sensors and cameras, generating a ton of data. Traditionally, this data might have been sent to a central computer for processing. However, with edge computing:
The car itself can process some of this data locally. This allows features like:
- Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS): Systems like lane departure warnings or automatic emergency braking rely on real-time data to function effectively. Edge computing keeps the processing fast and local for better responsiveness.
- Real-time Navigation: Traffic data can be processed on the edge to provide up-to-the-minute route adjustments and avoid delays.
This is particularly important for the future of:
- Autonomous Vehicles: These vehicles need to make split-second decisions based on their surroundings. Edge computing allows for faster processing of sensor data, enabling quicker reactions and safer operation.
These are just a couple of examples, but they showcase the versatility of edge and its potential to revolutionize various industries.
Advantages
- Faster Processing and Lower Latency: By reducing the distance data needs to travel, edge ensures faster processing and lower latency. This is crucial for applications requiring real-time responses, such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) experiences.
- Enhanced Security and Privacy: Since data is processed locally, there’s less risk of it being intercepted during transmission to distant data centers. This is particularly important in industries like healthcare and finance, where sensitive information must be protected.
- Improved Data Compliance: Edge allows businesses to comply with data sovereignty regulations by keeping data within specific geographical boundaries.
Challenges and Considerations
Here are the challenges of edge computing:
- Managing a Distributed Network: Edge computing thrives on a network of devices scattered across various locations. This makes it difficult to ensure consistent performance, security, and updates for all devices. Businesses need robust management solutions to oversee this complex infrastructure efficiently. Imagine having to keep dozens of tiny computers spread out in different cities all running smoothly and securely – that’s the challenge of managing a distributed edge network.
- Balancing Power and Cost: Edge devices need enough processing power to handle data processing tasks locally. However, cramming more power into smaller devices can be expensive and add complexity to the design. It’s like fitting a powerful engine into a scooter – possible, but not ideal. This creates a balancing act for businesses: ensuring the devices are strong enough to do the job without breaking the bank.
- Keeping Pace with Innovation: The world of edge computing is constantly evolving, with new advancements and best practices emerging all the time. Businesses that want to maximize the potential of edge computing need to stay updated on these developments. It’s like being in a fast-moving field of technology – you need to keep learning and adapting to stay ahead.
Conclusion
Edge computing is undeniably transforming industries by bringing data processing closer to the source. Its ability to reduce latency, improve efficiency, and enhance data security makes it a valuable asset for businesses across the globe. As more industries embrace this technology, we can expect to see even greater innovations and improvements in performance. The future of edge computing looks promising, with endless possibilities for enhancing operations and driving progress.
FAQs
What is edge computing?
Edge computing involves processing data closer to the source, reducing latency, and improving efficiency.
How does edge computing differ from cloud computing?
Unlike cloud computing, which relies on centralized data centers, edge computing processes data locally on edge devices or servers.
What are some common use cases of edge computing?
Edge computing is used in healthcare for real-time patient monitoring, manufacturing for predictive maintenance, and retail for personalized shopping experiences.
What are the benefits of edge computing?
Edge computing offers reduced latency, improved bandwidth efficiency, enhanced data security, and compliance with data sovereignty regulations.
What challenges does edge computing face?
Challenges include managing distributed edge devices, ensuring local processing power, and staying updated with technological advancements.