Table of Contents
The healthcare industry is facing deep digital transformations with AI, telehealth, automation, and IoT, increasing the efficiency and better outcomes in patient care. At the core of this transition is custom medical software development.
The healthcare service providers need to invest more and more in big data, interoperability, and electronic patient record systems to improve digital health.
Healthcare providers are under pressure to provide quality services to the patients, while keeping the costs low and running operations smoothly, making custom healthcare software development important. It helps make things easier to get to, more productive, portable, and scalable.
How Digital Solutions Are Transforming Healthcare in 2025
Healthcare is moving away from a volume-based, fee-for-service model towards a value-based system, prioritizing patient value over profitability. This paradigm shift is being supported by several key trends:
- Enhanced Collaboration: Health plans and healthcare systems are increasingly collaborating. Health plans possess holistic patient datasets crucial for long-term patient care, while providers offer deep clinical effectiveness and care delivery understanding.
- Focus on Wellness: The U.S. healthcare system is shifting from treating diseases to encouraging healthy lifestyles and wellness.
- Virtual Health Adoption: More patients are embracing virtual health options like telemedicine and telehealth, which reduce costs and prevent unnecessary ER visits.
- Patient-Centric Technology: Robotics, AI, big data, and cognitive technologies are automating non-clinical work, giving physicians more time for patient care. This places the patient at the center of the healthcare system.
The healthcare industry is expected to grow due to rising chronic diseases, an aging population, and new technologies. Custom software development is essential to enhance engagement and adapt to these changes.
What Are Mobile Health Apps and Web-Based Medical Platforms?
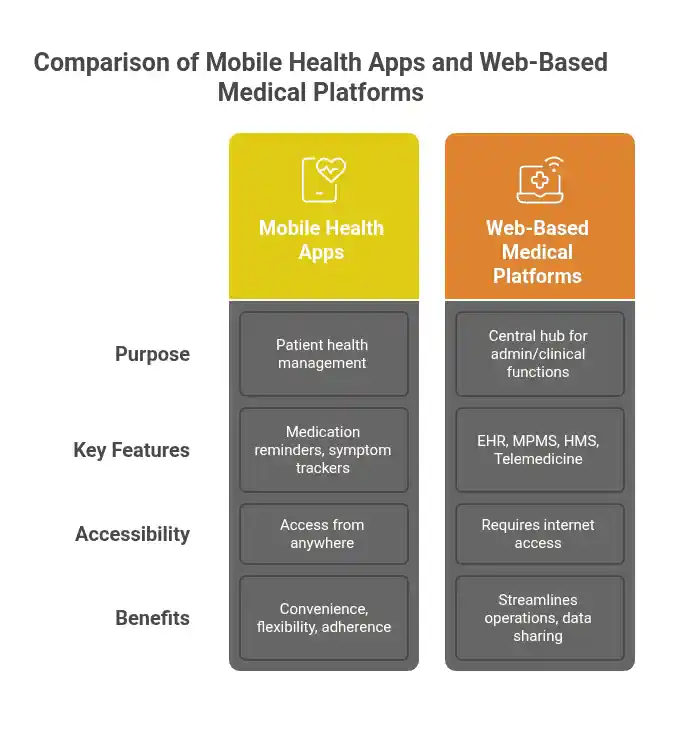
Healthcare software encompasses any software application specifically designed for the medical field. It includes a wide range of tools used by both providers and patients to improve care, streamline workflows, and manage health information electronically.
- Mobile Health Apps (mHealth): Mobile health apps empower patients to actively manage their health with features like medication reminders, symptom trackers, and educational resources. They allow access to personal data from anywhere and help with medication adherence. Urgent care apps enable care without an office visit, offering convenience and flexibility that are driving their popularity.
- Web-Based Medical Platforms: These are often comprehensive systems serving as central hubs for various administrative and clinical functions. Examples include:
- Electronic Health Record (EHR) Software: EHR systems, or Electronic Medical Records, store comprehensive patient data like allergies, lab results, and medical history. They are interoperable, allowing authorized healthcare providers to share information for accurate and timely diagnoses.
- Medical Practice Management Software (MPMS): This software streamlines daily operations for medical facilities, managing everything from appointment scheduling and billing to patient record tracking.
- Hospital Management Software (HMS): A central hub for managing diverse administrative functions within a hospital, including lab management, scheduling, reception, billing, and patient data management.
- Telemedicine Software: This allows remote consultations through video or secure messaging, so you don’t have to travel for appointments.
Both mobile apps and web platforms are crucial components in custom healthcare software development services, allowing organizations to build solutions tailored to their exact needs.
Key Differences Between Mobile Apps and Web Platforms in Healthcare
While both mobile health apps and web platforms are vital to digital healthcare, their primary focus and typical user interactions differ:
- Purpose and Functionality: Mobile apps enhance patient engagement and enable on-the-go health management, while web platforms focus on detailed data management, complex administration, and seamless provider communication.
- Accessibility and Portability: Mobile apps provide superior portability for accessing health data and tools on smartphones and tablets from anywhere. Web platforms, while accessible on any internet-connected device, are better suited for in-office use or dedicated workstations for detailed clinical or administrative tasks.
- User Interface and Experience: Mobile apps prioritize intuitive, consumer-friendly user experiences with touch interaction and quick access to features. In contrast, traditional web platforms, particularly older enterprise systems, often had poor UX but are now being redesigned with end-user involvement for improved usability.
User Experience: Accessibility, Speed, and Interface Design
An easy-to-use design is essential for any healthcare software, whether a mobile app or a web platform. Custom software development is tailored to deliver these.
- Shifting Focus: Enterprise healthcare software historically had a poor user experience because end-users were often excluded from purchasing decisions. This is changing as developers now include doctors and clinicians in the development process to improve UX, similar to consumer software.
- Tailored Design: Custom healthcare software development prioritizes user needs, improving navigation and satisfaction. Patients benefit from easier doctor visits, quick access to medical data, and simplified communication through video chats or messaging.
- Efficiency and Clarity: A good UI and UX for mobile apps and web platforms enhance efficiency. For example, patient portal software provides easy access to medical records, helping to identify errors and empowering treatment plans.
Data Security and HIPAA Compliance
In healthcare, protecting sensitive patient data is not just good practice; it’s a legal imperative. Custom medical software development places paramount importance on data security and regulatory compliance.
- HIPAA Mandate: HIPAA mandates strict requirements for medical data privacy, security, and patient confidentiality. Any software dealing with patient data, electronic or verbal, must comply.
- Built-in Security: A custom healthcare software company can create HIPAA-compliant solutions with strong security measures, such as encrypted data transactions and role-based user access, to protect against hackers.
- Consequences of Non-Compliance: Failing to protect HIPAA data can result in severe penalties from regulators. Ensuring software compliance from the beginning of the healthcare custom software development process is essential.
- Emerging Technologies for Security: Blockchain technology offers a safe, decentralized method to manage sensitive healthcare data, enhancing data integrity and giving patients greater control over their information.
Integration with Medical Devices and EHR Systems
Modern healthcare operates within a complex ecosystem of interconnected systems. For both mobile health apps and web platforms, seamless integration with existing medical devices and Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems is non-negotiable for effective care delivery.
- Essential for Data Flow: Development teams ensure software solutions communicate effectively, enabling smooth data exchange and streamlined workflows for better patient care and operational efficiency.
- Custom healthcare software development services enable seamless data integration with major EHR platforms like Epic, Cerner, and Athenahealth, often through APIs. This allows your solution to directly access patient histories, lab results, and other essential data for enhanced clinical workflows and decision support.
- The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) and wearables enable continuous health monitoring and data collection outside clinical settings. This supports remote patient monitoring and early health issue detection.
For example, a mobile app could share real-time ECG data from a wearable with doctors, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and response times for critical cardiac events. Custom solutions also offer software-as-a-medical-device (SaMD) capabilities, allowing applications to perform medical functions, such as viewing MRI images or collecting patient data for treatment plans.
Cost of Development: Mobile Apps vs Web Platforms
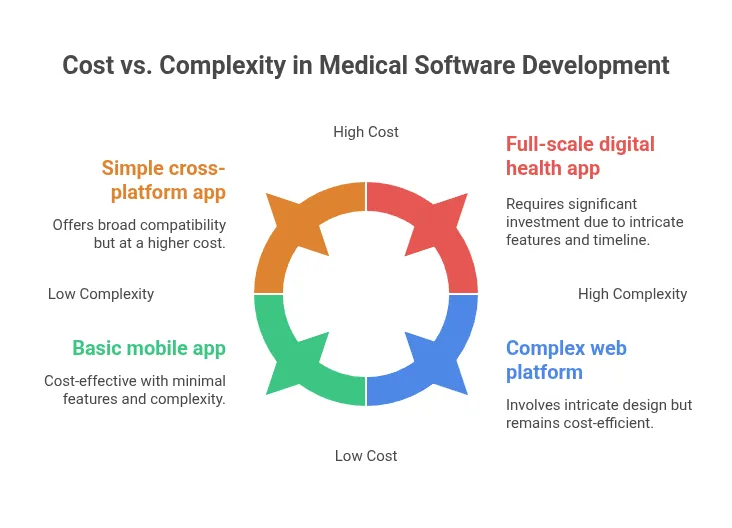
The investment required for custom medical software development varies significantly, whether you opt for a mobile app, a web platform, or a combination of both.
- Factors Influencing Cost: The final cost is highly dependent on:
- Project Complexity: This includes the intricacies of the design, the number of features, and whether you need a cross-platform solution or a simpler app.
- Features and Functionality: More advanced features, integrations with multiple third-party APIs (like payment gateways, EHRs, or telehealth platforms), and sophisticated business logic will increase costs.
- Project Timeline: Generally, the longer a project takes, the higher the cost. A full-scale digital health app can take at least a year to develop.
- Team Composition and Location: The number and specialty of IT engineers involved, and whether you choose in-house development, onshore, nearshore, or offshore outsourcing, all impact the price. Outsourcing can often be more cost-effective than an in-house team.
- Investment Range: A single custom healthcare software development project can range anywhere from $40,000 to over $500,000. This is a significant investment compared to off-the-shelf software, which offers faster implementation and lower initial costs.
- Ongoing Expenses: Beyond initial development, anticipate ongoing maintenance, updates, and support, which typically account for 15-20% of the initial development cost annually. This ensures your solution remains secure, compliant, and performs optimally as technologies and regulations evolve.
Custom development, while a significant investment, provides tailored solutions that align with your organization’s unique needs and compliance requirements—often lacking in off-the-shelf products.
Custom medical software efficiently supports healthcare professionals in managing practices while prioritizing patient well-being. By utilizing advanced technologies like AI, IoT, and mobile health applications, healthcare providers can ensure high-quality care now and in the future.
FAQ
Q1. What do you see as the future of connected devices in healthcare?
Connected devices, referred to as the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), are crucial for the healthcare future. Smart wearable devices and sensors allow us to monitor and collect vital data. This data can be integrated into custom healthcare software solutions for remote monitoring and healthcare management.
As a patient, you can access your medical info anywhere using mobile devices.
Q2. What are the different types of healthcare software?
The healthcare industry utilizes a diverse range of software solutions. Some key types include:
– Medical Practice Management Software (MPMS): Streamlines day-to-day operations like scheduling, billing, and patient record tracking.
– Electronic Health Record (EHR) / Electronic Medical Records (EMR) Software: Manages comprehensive patient data, facilitating precise diagnosis and treatment across authorized providers.
– E-Prescribing Software: Enables electronic transmission of prescriptions to pharmacies, reducing errors and streamlining the process.
– Urgent Care Apps: Allow patients to avoid physical visits while monitoring symptoms and accessing care.
– Hospital Management Software (HMS): Automates record keeping, financial, and administrative tasks for hospitals.
– Healthcare CRM (Customer Relationship Management): Manages patient information, communications, and relationships.
– Medical Diagnosis Software: Uses automation to analyze data for precision in clinical diagnoses.
– Software-as-a-Medical-Device (SaMD): Software that serves a medical purpose independently of hardware, like mobile apps for viewing MRI images.
– Clinical Trial Management Software: Manages and tracks activities in clinical research.
– AI and Robotics Systems: Used for detection, diagnosis, predictive analytics, and even assisting with end-of-life care.
– Patient Portals: Web and mobile apps for patients to access medical records, appointments, and billing information.
– Telehealth/Telemedicine Software: Facilitates remote consultations via video or audio.
– Medical Imaging Software: Helps track, manipulate, and manage medical images.
– Lab Information Management Systems (LIMS): Manages lab-related activities and inventory.
– Population Health Management Software (PHMS): Records, aggregates, and integrates patient data for comprehensive care.
Q3. What are the benefits of custom software development?
Custom healthcare software development offers numerous benefits over off-the-shelf solutions because it is built specifically for your facility or organization to address unique needs.
– Perfect Fit: The software is tailored to match your existing business processes, systems, and workflows.
– Enhanced Outcomes: It helps improve patient outcomes, operational efficiency, and reduces costs.
– Improved Patient Experience: Through patient portals and self-help tools, patients can easily interact with clinicians, leading to higher engagement and satisfaction. You can book appointments remotely and access educational information.
– Increased Efficiency: Automates administrative tasks, freeing up valuable time for medical professionals to focus on patient care and reducing physician burnout.
– Enhanced Security and Compliance: Can be designed with robust security measures specifically for HIPAA compliance and other regulatory requirements, protecting sensitive data.
– Scalability and Flexibility: Custom solutions can adapt and grow alongside your organization’s evolving needs, with new features easily integrated.
– Better Data Management: Improves the accuracy and security of data management, providing insights for informed decision-making and optimizing revenue.Enhanced Outcomes: It helps improve patient outcomes, operational efficiency, and reduces costs.
Q4. What is the role of AI in future software development?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are rapidly transforming healthcare software development. Their role includes:
– Enhanced Diagnosis and Treatment: AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of medical data to identify patterns, leading to earlier, more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment recommendations.
– Predictive Analytics: AI-driven predictive analytics can forecast health risks, predict disease outbreaks, and optimize resource allocation within healthcare systems.
– Automation and Efficiency: AI-empowered workforce modules can automate scheduling, credential checks, and provide instant data access through voice commands, cutting search time for clinicians. Robots can also assist with tasks like medication dispensing and administrative duties.
– Drug Discovery and Clinical Trials: ML can accelerate drug discovery and improve the design and analysis of clinical trials.
– Patient Support: AI chatbots and virtual assistants can offer 24/7 patient information, support, and appointment scheduling. Despite challenges related to data security and bias, AI’s potential in healthcare is immense, promising more innovative applications.
Q5. What is the difference between mobile apps and web apps?
Mobile apps are software designed for smartphones and tablets, and can be native, hybrid, or cross-platform. In healthcare, mHealth apps enable patients to manage their health conveniently, often providing functions like patient portals, remote monitoring, and urgent care.
Web apps are software accessed through web browsers on any internet-connected device, including desktops, laptops, and mobile devices. In healthcare, they manage electronic health records (EHRs), hospital operations, and practice management, enabling remote collaboration.
While both types provide patient access, mobile apps offer a more personalized user experience, whereas web apps are accessible across various devices without specific installations.
Q6. What are the advantages and disadvantages of custom software development?
Choosing custom healthcare software development offers significant strategic advantages but also comes with certain considerations:
Advantages:
– Perfect Fit: Solutions are built from the ground up to meet your organization’s unique requirements, workflows, and existing systems, addressing specific challenges that off-the-shelf products cannot.
– Scalability and Flexibility: Custom software can easily adapt and grow with your healthcare organization’s evolving needs, allowing for seamless integration of new features.
– Enhanced Security and Compliance: Allows for robust security measures tailored to your specific data and ensures strict HIPAA compliance.
– Improved Efficiency and Outcomes: Streamlines operations, reduces administrative burdens, enhances decision-making, and ultimately leads to better patient outcomes and financial efficiency.
– User-Friendly Design: Can be designed with your specific users in mind, improving adoption rates and satisfaction.
– Competitive Advantage: Provides a unique edge by offering specialized functionalities tailored to your specific market needs.
Disadvantages:
– Higher Cost and Investment: Developing custom software from scratch is a significant financial investment, requiring dedicated time, resources, and expertise compared to off-the-shelf options.
– Longer Development Time: Building a custom solution takes more time, potentially delaying implementation compared to readily available products.
– Ongoing Maintenance: Requires continuous updates and support to remain secure, compliant, and functional over time.