Table of Contents
In todays fast-changing market, businesses face a core challenge. They must balance rising pressure for efficiency with security, data privacy, and the risks of vendor lock-in.
This balance drives more companies to choose open-source tools for mission-critical internal work. Open source lets teams inspect, control, and adapt the software to their needs.
Open-source workflow automation tools are software systems with public source code. Teams use them to plan, automate, and track business tasks across many steps and teams.
These tools give teams a clear interface to create automation rules. The rules standardize processes, remove manual work, and now often use artificial intelligence to manage complex logic.
This guide offers a detailed comparative analysis of the leading open-source platforms in 2026. It is designed to inform a strategic technology adoption decision for IT leadership, technical teams, and business stakeholders by evaluating each tool against consistent criteria.
This analysis will evaluate the following 14 platforms:
- n8n
- Activepieces
- Automatisch
- Node-RED
- Apache Airflow
- Prefect
- Windmill
- Kubeflow Pipelines
- Budibase
- Camunda
- Bonita
- Imixs-Workflow
- StackStorm
- Wexflow
The Strategic Value of Open-Source Workflow Automation
Before choosing a tool, grasp its core benefits. These advantages transcend mere technicalities. Indeed, they directly strengthen our security and budget. Open-source also streamlines our long-term strategy. Teams select these workflow tools for compelling, interconnected reasons.
- Stronger Security and Trust: Security-focused organizations demand source code review. Auditing the code is vital. This transparency matters most for workflow tools. Furthermore, these tools touch mission-critical data and systems. Internal engineering teams can, therefore, vet the software for any weaknesses.
- Complete Data Control: Open-source tools usually allow local hosting. Consequently, you avoid relying on a vendor’s cloud. This self-hosting is essential for many teams. They must keep workflow data in their local environment. This ensures compliance with strict privacy rules.
- Saves Money and Provides Flexibility: These open-source platforms are often free to use. Thus, you significantly cut software licensing costs. Moreover, you can modify the source code to fit your exact needs. Proprietary, closed-source tools rarely offer this adaptability.
- Reduces Vendor Lock-In: Adopting an open-source platform limits operational risk. You avoid issues like sudden price hikes. Changes in product direction are not a threat. Also, the risk of a vendor closing operations decreases. This action provides long-term stability for core processes.
- Active Community Support: Many open-source platforms boast active developer communities. Users also form vibrant support groups. These communities provide valuable assistance. They share extensions that boost functionality. In addition, they drive constant innovation. This keeps the tools current and highly effective.
Knowing these benefits provides a clear lens through which to evaluate which platform best aligns with your organization’s specific operational and strategic goals.
Key Criteria for Selecting the Right Platform
The workflow automation market is broad. Platforms target varied user roles, distinct use cases, and technical setups. Therefore, selecting the correct tool demands a clear evaluation framework. This framework hinges on a few essential decision points. Specifically, this section details the key factors to weigh when comparing open-source workflow management platforms.
- Core Experience and Required Skills: Platforms define workflow logic differently. Some platforms utilize simple, visual interfaces. These target non-technical staff in marketing or sales. Other platforms demand code, like Python, to define workflows. Clearly, these tools suit developers and data engineers. Furthermore, these teams need ultimate flexibility and control. Thus, you must align the platform’s interface with your team’s skills. This ensures smooth building and maintenance.
- Integration and Connectivity: A strong workflow platform needs reliable connections. Therefore, it must connect to your existing systems. Assess the platform’s pre-built integration options. For instance, some tools offer vast libraries for popular applications. Conversely, others force you to manually configure APIs for many systems. Ultimately, easy access determines a platform’s value. Connecting to external data and services is paramount.
- AI and Advanced Capabilities: AI now drives most business workflows. Hence, evaluate the platform’s AI strengths. This includes the ability to build and monitor AI agents. Additionally, platforms must allow human-in-the-loop oversight. The best platform integrates with specific AI models. Furthermore, it configures agent behavior efficiently. Significantly, seek support for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). Teams can then craft genuinely intelligent automations.
- Deployment, Licensing, and Support: Practical factors like deployment and support demand attention. Many platforms offer a free, open-source version. Consequently, paid cloud or enterprise editions provide additional features. You must understand the specific open-source license, such as MIT or Apache 2.0. Similarly, scrutinize the commercial offering’s pricing models. Always ensure enterprise-level support exists. Also, demand robust Service Level Agreements (SLAs).
Applying this framework will help clarify which platform is the best strategic fit for your organization’s unique requirements.
Top Open-Source Workflow Automation Tools: A Comparative Analysis
This section details the best open-source workflow automation tools. We provide a complete breakdown. Clearly, we simplify the platform selection process. Therefore, we organize tools by core strength and audience. These range from general app connectors to specialized developer engines.
Further, for professionals looking to build these technical skills, online coding bootcamps offer structured training in software engineering, automation-ready backend systems, and AI-powered workflows, helping developers move from theory to real-world automation implementation.
General Purpose & “Zapier Alternatives”
We tackle the challenge of “SaaS sprawl.” Crucial business data fragments across countless cloud apps. Consequently, these tools become your central nervous system. They powerfully connect disparate platforms. For example, they link CRMs, marketing systems, and communication tools. This automation drives cross-functional business processes. Therefore, they offer strong open-source alternatives to proprietary platforms like Zapier or Make.com.
1. n8n
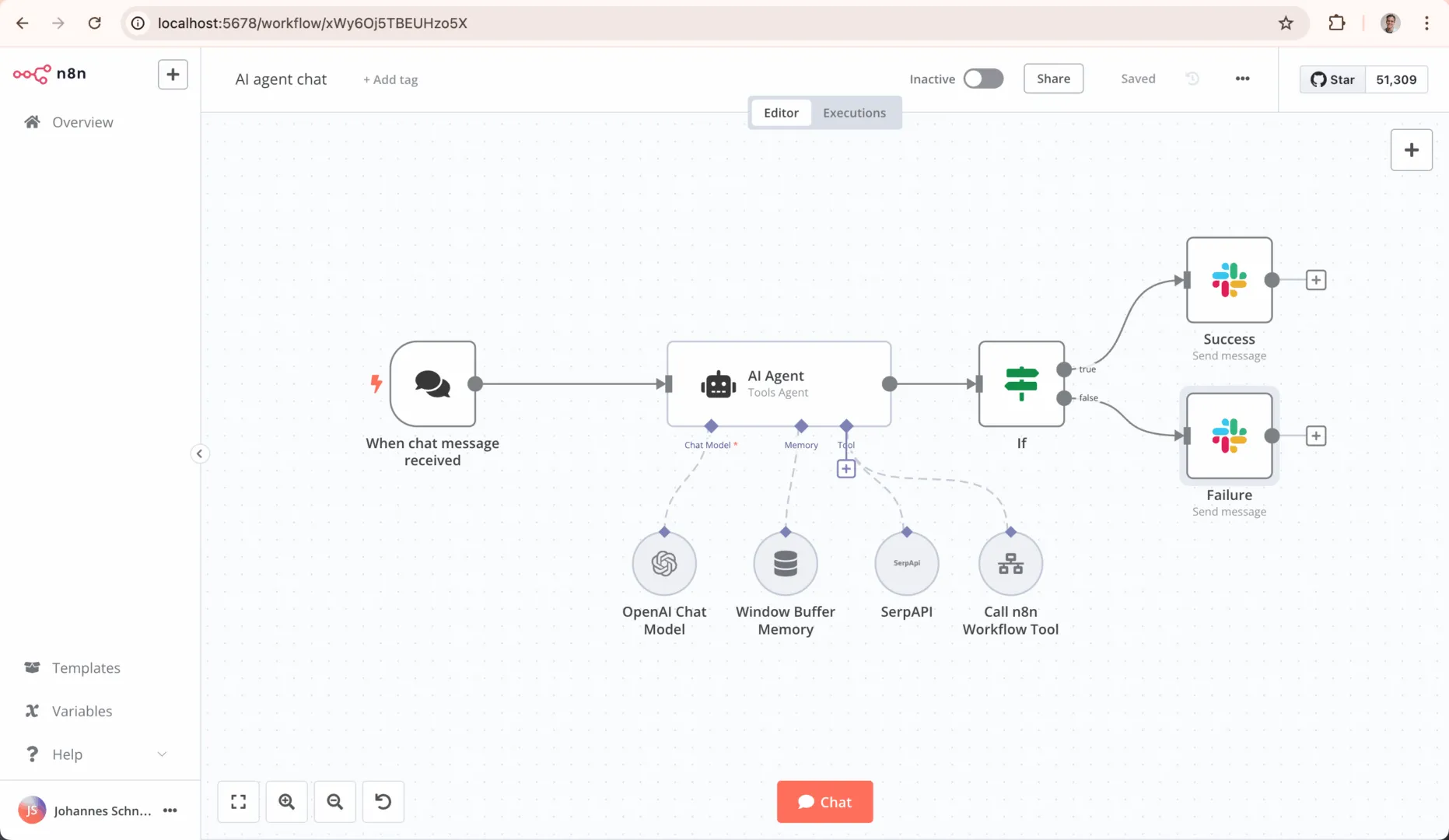
- Overview: n8n is a prominent workflow automation tool designed for technical teams, distributed under a source-available, fair-code license. It uniquely combines an intuitive visual interface with the power to implement custom code, making it both accessible and highly flexible.
- Key Features:
- Low-Code Visual Building: Offers a rapidly growing library of over 400 official integrations and an intuitive visual editor, enabling teams to build complex workflows without manually configuring most API requests.
- Pro-Code Flexibility: Provides extensive opportunities to implement custom JavaScript and Python code directly within workflows, offering ultimate control when needed.
- AI-Native Platform: Features robust capabilities for building and managing AI agents, including flexible model selection, human-in-the-loop guardrails, and RAG functionality.
- Ideal Use Cases & Target Persona: n8n is particularly popular with technical user personas and teams who need to build powerful, AI-driven automations connecting to a wide array of business tools, from IT operations to sales and marketing.
- Licensing and Deployment: n8n is licensed under a fair-code model, which makes the source code available but includes commercial restrictions, differentiating it from purely permissive open-source licenses like MIT or Apache 2.0. Its Community Edition can be self-hosted for free, and it also offers paid cloud and enterprise plans based on the number of workflow executions.
2. Activepieces
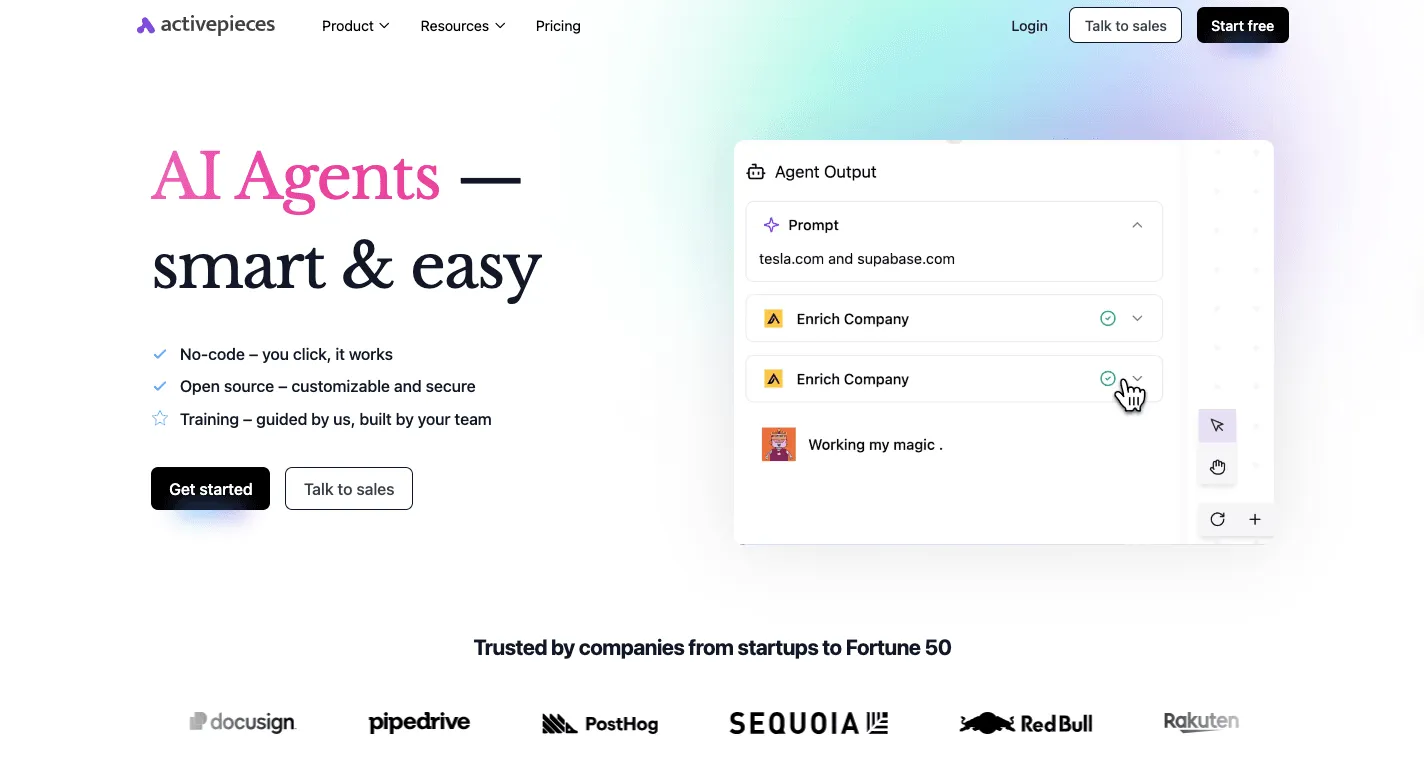
- Overview: Activepieces is a no-code, AI-first automation tool positioned as a true MIT-licensed open-source alternative to Zapier. It is designed to empower business users to automate processes securely in-house without requiring technical expertise.
- Key Features:
- No-Code Builder: Features a clean, drag-and-drop flow designer that allows non-technical users to automate complex workflows without writing any code.
- AI Automation: Enables the creation of intelligent workflows using AI agents, models, and natural language inputs to automate decision-making.
- Developer-Friendly Framework: Built in TypeScript, it allows developers to easily customize or build their own integrations, with all connectors being open source and available on npm.
- Ideal Use Cases & Target Persona: Activepieces is ideal for marketing, sales, HR, and operations teams needing to automate repetitive tasks without coding. Its self-hosting capability also makes it a strong choice for organizations with strict data privacy and security concerns.
- Licensing and Deployment: Activepieces is MIT-licensed, making it completely free and open for everyone. It can be self-hosted and offers a free version alongside cost-effective paid plans.
3. Automatisch
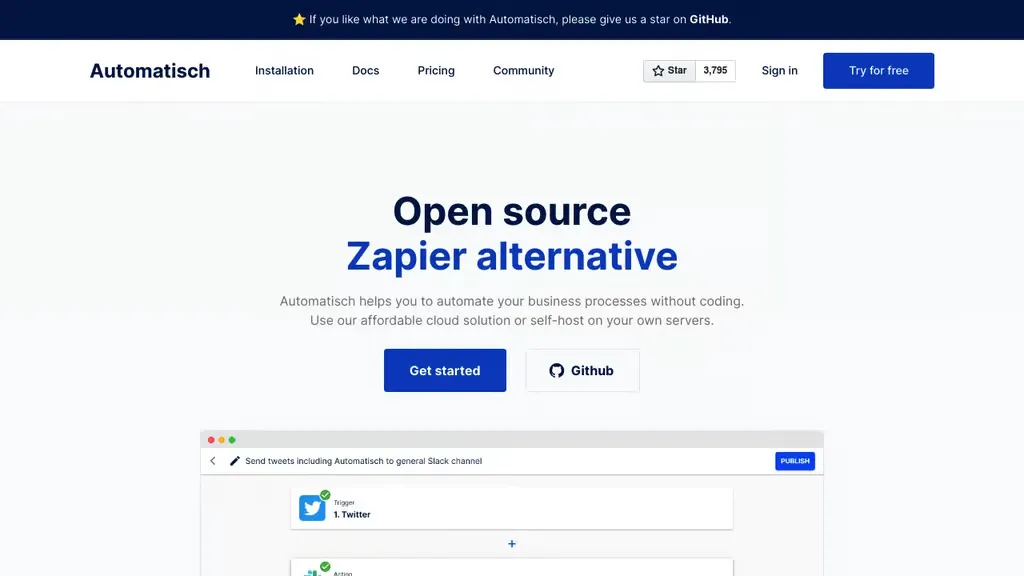
- Overview: Automatisch is a no-code workflow automation platform that positions itself directly as an open-source Zapier alternative, focused on empowering non-technical users to create custom automation logic.
- Key Features:
- Intuitive No-Code Interface: Offers a sleek and familiar interface for connecting tools and configuring workflow triggers and actions without code.
- Pre-built Integrations: Provides a set of pre-built integrations for common business applications, though its library is less extensive than n8n’s.
- API Connectivity: For tools without a pre-built connector, users may need to manually configure API requests to achieve broader integration.
- Ideal Use Cases & Target Persona: Its target audience consists of teams and non-technical users who need an open-source, self-hosted solution for custom workflow automations without relying on development skills.
- Licensing and Deployment: Automatisch is an open-source, self-hosted platform. The specific license is not specified in the source material.
4. Node-RED
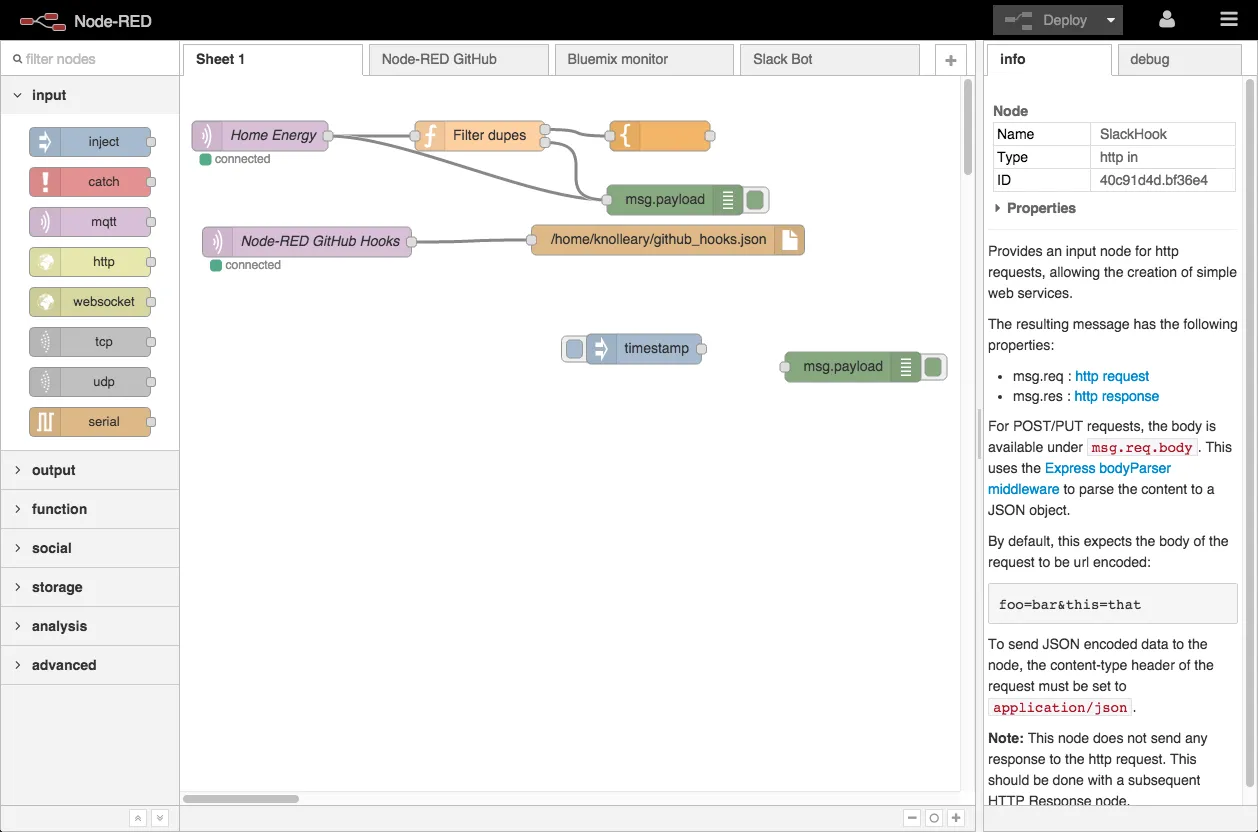
- Overview: Node-RED is a mature, flow-based development tool created for wiring together hardware devices, APIs, and online services. It is widely used for Internet of Things (IoT) and other event-driven applications.
- Key Features:
- Visual Flow-Based Editor: Utilizes a browser-based, drag-and-drop interface where users place and connect “nodes” on a canvas to design data flows.
- Extensive Node Library: Boasts a huge community-contributed library of over 5,000 nodes, covering integrations from hardware protocols to cloud services.
- Node.js Foundation: Built on Node.js, making it lightweight, efficient, and easily extensible with custom JavaScript modules.
- Ideal Use Cases & Target Persona: Node-RED is ideal for a wide range of users, from home hobbyists and industrial operators to enterprise teams, focused on IoT projects, real-time event processing, and connecting a heterogeneous mix of devices and services.
- Licensing and Deployment: Node-RED is part of the OpenJS Foundation, licensed under Apache 2.0. It is self-hosted and can run anywhere Node.js is supported, including on low-cost hardware like the Raspberry Pi.
Developer & Data-Centric Platforms
These platforms solve the engineering challenge of orchestrating complex, scheduled, and often mission-critical data operations. They are powerful, code-centric frameworks designed for developers, data engineers, and DevOps teams to manage data pipelines, machine learning models, and infrastructure automation where programmatic control, reliability, and observability are paramount.
5. Apache Airflow
- Overview: Apache Airflow is a leading open-source platform for programmatically authoring, scheduling, and monitoring complex data workflows. It treats workflows as Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs), making it a de facto standard for data engineering.
- Key Features:
- Pure Python Workflows: Pipelines are defined entirely in Python, allowing for dynamic generation, version control, and ultimate flexibility in creating complex logic.
- Rich Web UI: Provides a robust web interface for monitoring, managing, and scheduling workflows, with full insight into task status, logs, and historical runs.
- Extensible and Scalable Ecosystem: Features a modular architecture with a large library of ready-to-use operators for connecting to services like AWS, GCP, and Azure, which can be extended with custom plugins.
- Ideal Use Cases & Target Persona: The primary users are data engineers and developers who need to create and manage complex, scheduled data workflows, ETL jobs, and machine learning pipelines.
- Licensing and Deployment: Airflow is an Apache 2.0 licensed project. It is typically self-hosted or available through managed cloud services like AWS MWAA and Google Cloud Composer.
6. Prefect
- Overview: Prefect is a modern, Python-first open-source workflow orchestration platform positioned as a direct alternative to Airflow, designed to handle dynamic, data-intensive workloads with a focus on developer experience and security.
- Key Features:
- Modern and Dynamic Python Workflows: Workflows are written as pure Python functions with simple decorators, and Prefect excels at creating tasks based on data and conditions at runtime without static DAG definitions.
- Hybrid Execution Model: Separates the orchestration control plane from the execution layer, ensuring that user code, data, and secrets remain securely within the user’s infrastructure.
- Built-in Observability: Includes comprehensive monitoring tools and real-time dashboards for debugging and performance analysis out of the box.
- Ideal Use Cases & Target Persona: Prefect is built for data engineering, ML, and AI teams that require dynamic, event-driven workflows and prioritize security, data control, and a modern developer experience.
- Licensing and Deployment: The open-source framework is licensed under Apache 2.0, with a commercial Prefect Cloud platform available for managed orchestration.
7. Windmill
- Overview: Windmill is an open-source developer platform and high-performance workflow engine designed to turn scripts into production-grade webhooks, workflows, and UIs, blurring the line between low-code and pro-code.
- Key Features:
- Multi-Language Scripting with Visual Composition: Supports creating automation logic in Python, TypeScript, Go, Bash, and more, and offers a visual tool (
Flows) for chaining scripts into complex logic. - Autogenerated UIs: Automatically generates user interfaces from script parameters, enabling the rapid creation of simple internal tools and apps.
- High-Performance Engine: Claims to be a highly performant workflow engine, positioning itself as a faster alternative to platforms like Airflow for certain use cases.
- Multi-Language Scripting with Visual Composition: Supports creating automation logic in Python, TypeScript, Go, Bash, and more, and offers a visual tool (
- Ideal Use Cases & Target Persona: Windmill targets developers and technical teams who want to leverage existing scripts to build internal tools, data pipelines, and scheduled cron jobs within a unified, production-grade platform.
- Licensing and Deployment: Windmill is open-sourced under the AGPLv3 license (which has strong copyleft provisions that may affect proprietary derivative works). It can be self-hosted via Docker or Kubernetes and offers a commercial enterprise edition.
8. Kubeflow Pipelines
- Overview: Kubeflow Pipelines is an open-source platform specifically designed for building, deploying, and managing end-to-end machine learning (ML) workflows on Kubernetes.
- Key Features:
- Containerized Components: Each step in a pipeline runs as an independent, portable container, promoting reusability and reproducibility across different environments.
- Python SDK for Authoring: Data scientists can create and manage ML workflows directly in Python, integrating pipeline definitions into their existing development practices.
- Metadata Tracking and Lineage: Automatically logs inputs, outputs, and parameters for each run, providing full visibility and lineage for auditing and reproducibility.
- Ideal Use Cases & Target Persona: Its core users are data science and MLOps teams tasked with building, deploying, and managing reproducible and portable machine learning pipelines at scale.
- Licensing and Deployment: Kubeflow Pipelines is an open-source platform built to run natively on Kubernetes, licensed under Apache 2.0.
Business Process Management (BPM) & Internal Tools
This category is tailored to solve the problem of automating structured business processes that often require human interaction. These platforms excel at modeling and executing workflows like approvals, reviews, and ticketing, and often include capabilities to build the internal applications that employees use to participate in these processes.
9. Budibase
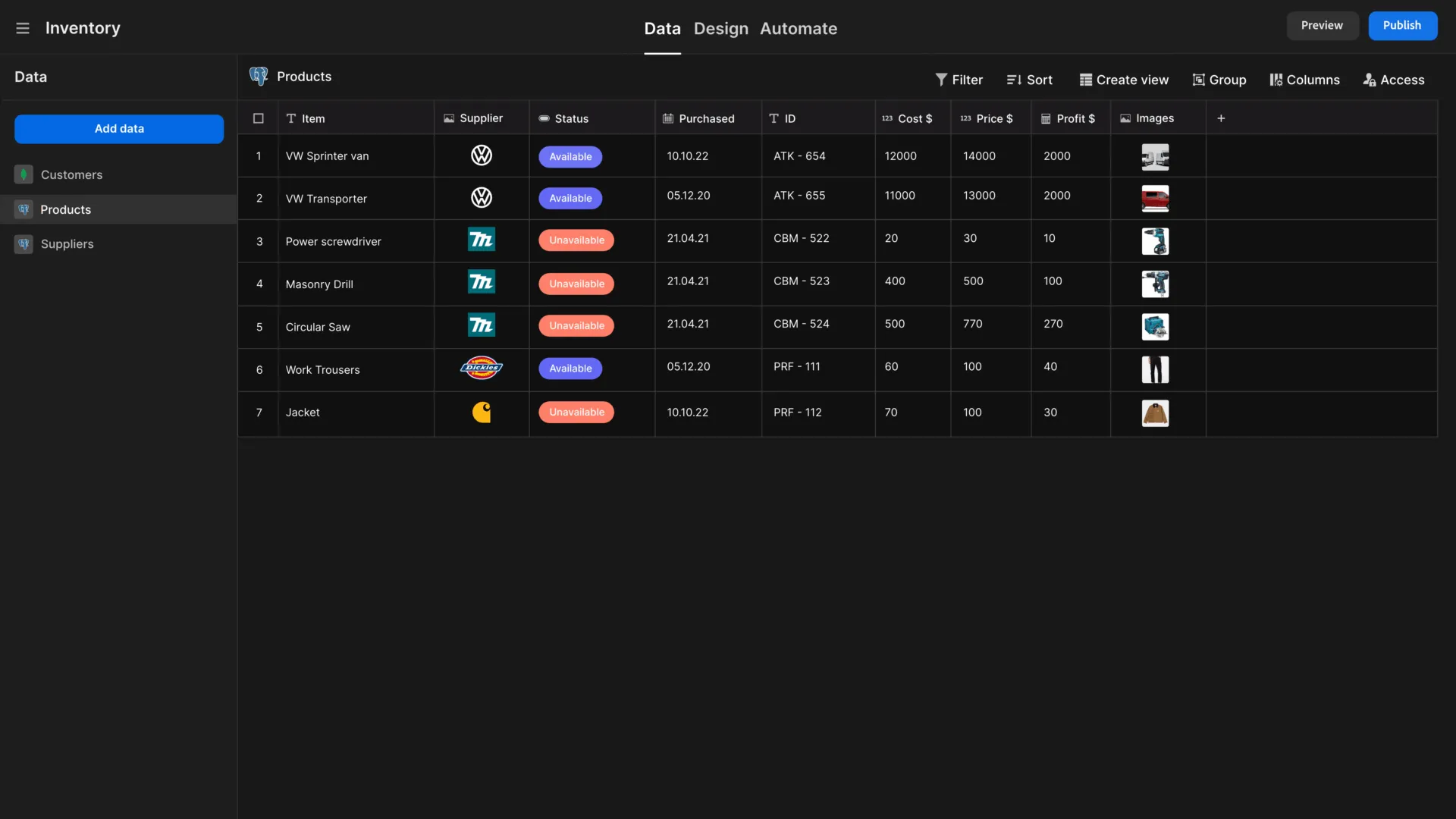
- Overview: Budibase is an open-source, low-code platform that empowers IT teams to build secure internal tools and automate workflows, complete with powerful AI capabilities.
- Key Features:
- Rapid App Building: Offers extensive connectivity to data sources (RDBMS, NoSQL, APIs) and can automatically generate user interfaces, making it fast to build internal tools.
- AI-Powered Automations: Provides a range of AI capabilities, including pre-built operations and custom prompts powered by BudibaseAI, OpenAI, or Azure.
- Enterprise-Grade Security: Features granular custom Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and supports self-hosting and air-gapped deployments for maximum security.
- Ideal Use Cases & Target Persona: Budibase is optimized for busy IT teams that need to rapidly and securely build internal tools for workflows like approvals, ticketing systems, request management, and service management.
- Licensing and Deployment: Budibase offers a free and unlimited self-hosted open-source plan under the GPL v3 license, alongside paid cloud and enterprise tiers.
10. Camunda
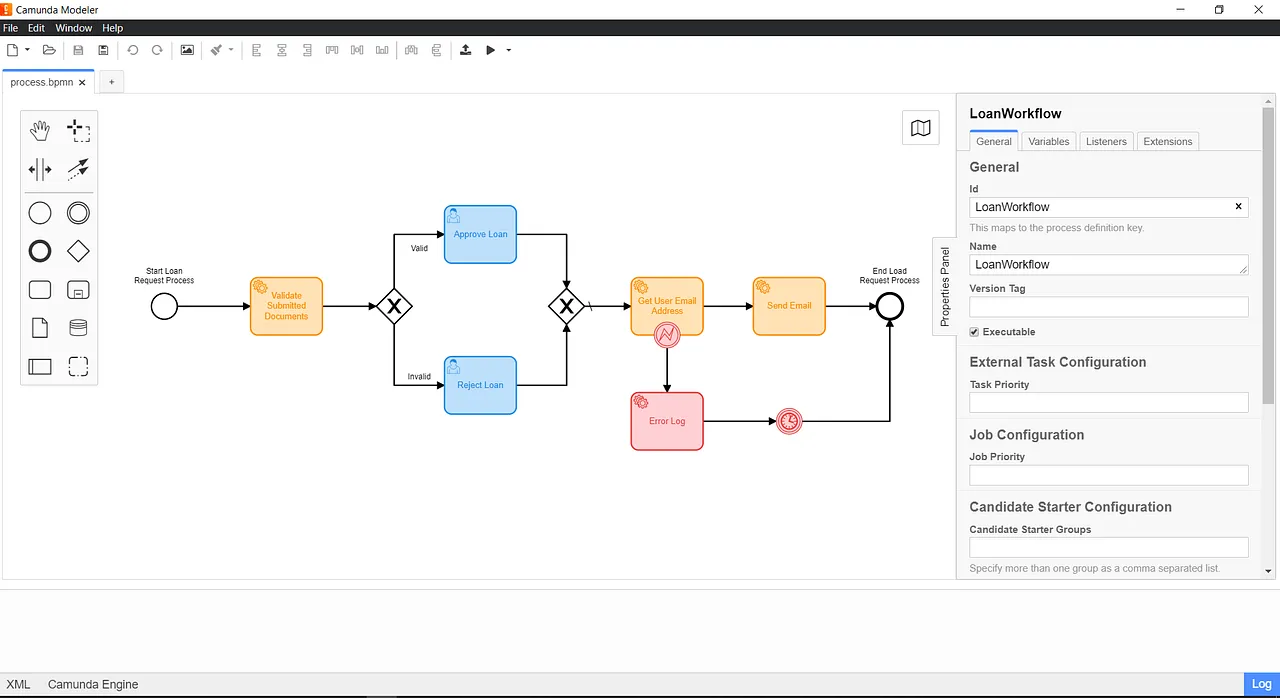
- Overview: Camunda is an open, cloud-native automation platform designed to orchestrate complex processes across people, systems, and devices using the industry standards BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) and DMN (Decision Model and Notation).
- Key Features:
- Standards-Based Modeling (BPMN/DMN): Uses visual, industry-standard languages that allow business stakeholders and IT teams to collaborate effectively on process design and automation.
- Universal Process Orchestration: Provides extensive integrations and a cloud-native engine (Zeebe) to orchestrate tasks across people (via its
Tasklist), systems, and devices. - Cloud-Native Architecture: Built on a scalable, event-driven engine designed for high-throughput, distributed environments.
- Ideal Use Cases & Target Persona: Its users include developers, architects, and business leaders collaborating to automate complex, end-to-end business processes in large enterprise environments.
- Licensing and Deployment: Camunda offers free versions for modeling (SaaS) and non-production use (Self-Managed), with custom-priced Enterprise plans available for production deployments.
11. Bonita
- Overview: Bonita is an open-source business process management (BPM) and low-code platform for building comprehensive, process-based applications that automate and optimize operations.
- Key Features:
- Visual Process and UI Design: Allows users to graphically design business processes using the BPMN standard and build customized, responsive user interfaces for applications tied to those processes.
- Java-Based Engine: Its robust BPM engine is written in Java and executes process definitions, making it highly extensible for developers.
- Continuous Delivery Support: Offers add-ons for automatic provisioning with tools like Docker and Ansible to support DevOps and CI/CD pipelines.
- Ideal Use Cases & Target Persona: It is used to create “Living applications” for IT operations, finance, and compliance, enabling close collaboration between business analysts and developers to deliver complete solutions.
- Licensing and Deployment: Bonita is open-source (GPLv2) and can be downloaded for free. Commercial offerings with additional features and support are available from Bonitasoft.
12. Imixs-Workflow
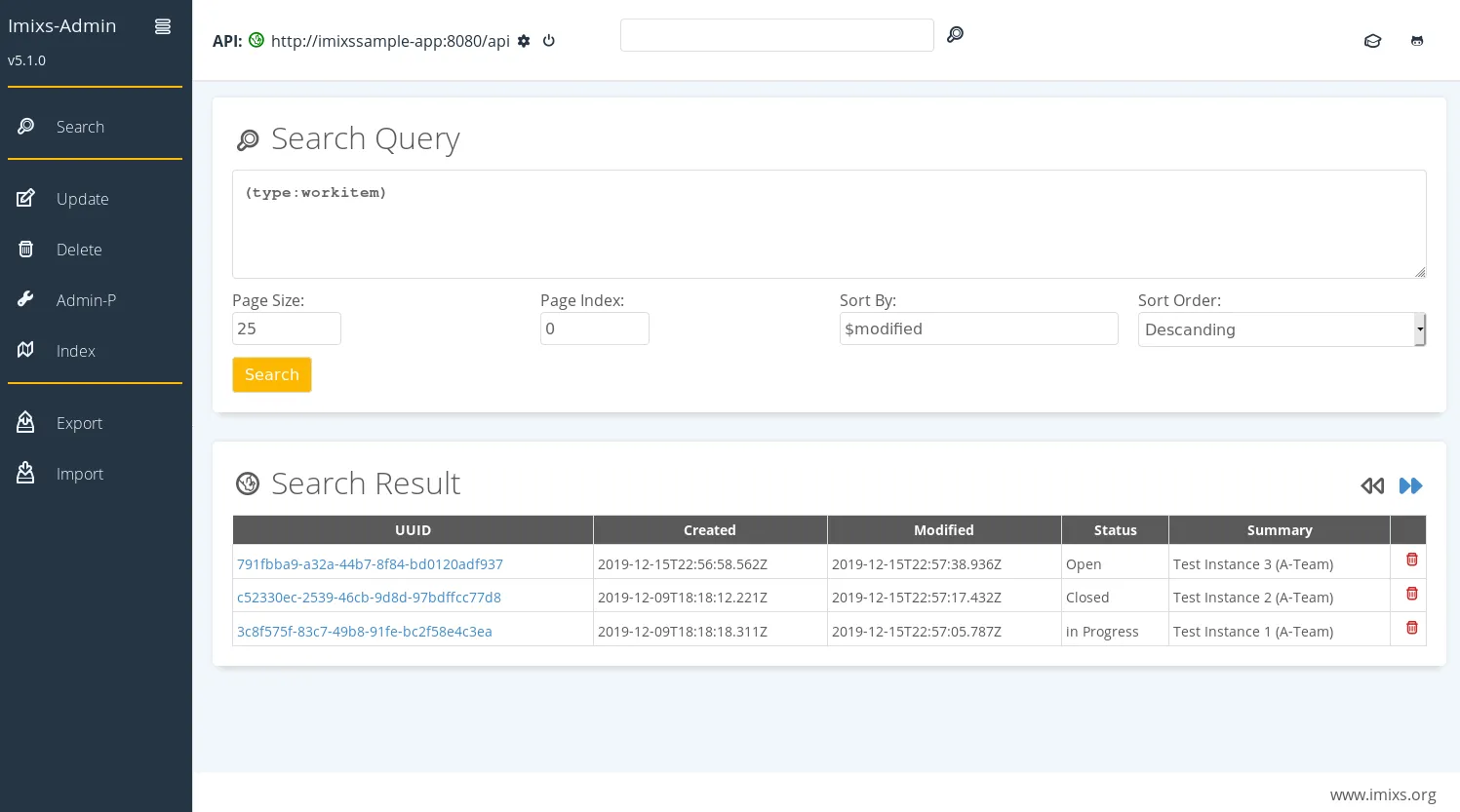
- Overview: Imixs-Workflow is an open-source workflow engine designed for building human-centric business process management solutions using the BPMN 2.0 standard.
- Key Features:
- Human-Centric Design: Focuses on workflows that require human decision-making and interaction, using events and approvals to trigger state transitions.
- Enterprise Java Foundation: Built on the Jakarta EE standard, ensuring enterprise-grade scalability, security, and transaction management.
- Microservice Architecture: Provides a RESTful API and is well-suited for deployment in containerized environments like Docker and Kubernetes.
- Ideal Use Cases & Target Persona: It is ideal for creating transactional business processes that involve human decision points, such as case management and compliance workflows, particularly in regulated industries.
- Licensing and Deployment: It is licensed under the Eclipse Public License v. 2.0 (or GPL-2.0-or-later).
IT Operations & System Automation
These specialized platforms address the need for reliable, event-driven automation for back-office processes, infrastructure management, and security response. Their primary function is to react to system-level events—such as alerts, failures, or deployments—and execute automated remediation, CI/CD pipelines, or security playbooks.
13. StackStorm
- Overview: StackStorm is an open-source, event-driven automation platform built specifically for IT operations, DevOps, and security automation. It operates on a powerful “if-then” model to connect various services and workflows.
- Key Features:
- Event-Driven Automation: Uses sensors to detect events, triggers to capture them, and rules to execute automated responses or complex workflows.
- Modular and Powerful Engine: Features a robust orchestration engine (Orquesta) for handling advanced logic and organizes integrations into modular
packs. - ChatOps Integration: Connects directly with chat platforms like Slack, allowing teams to trigger workflows and execute commands from their chat client for collaborative operations.
- Ideal Use Cases & Target Persona: Its common applications include automated remediation of system failures, continuous deployment pipelines, and automated security response. It targets DevOps, SRE, and security teams.
- Licensing and Deployment: StackStorm is an open-source platform licensed under Apache 2.0.
14. Wexflow
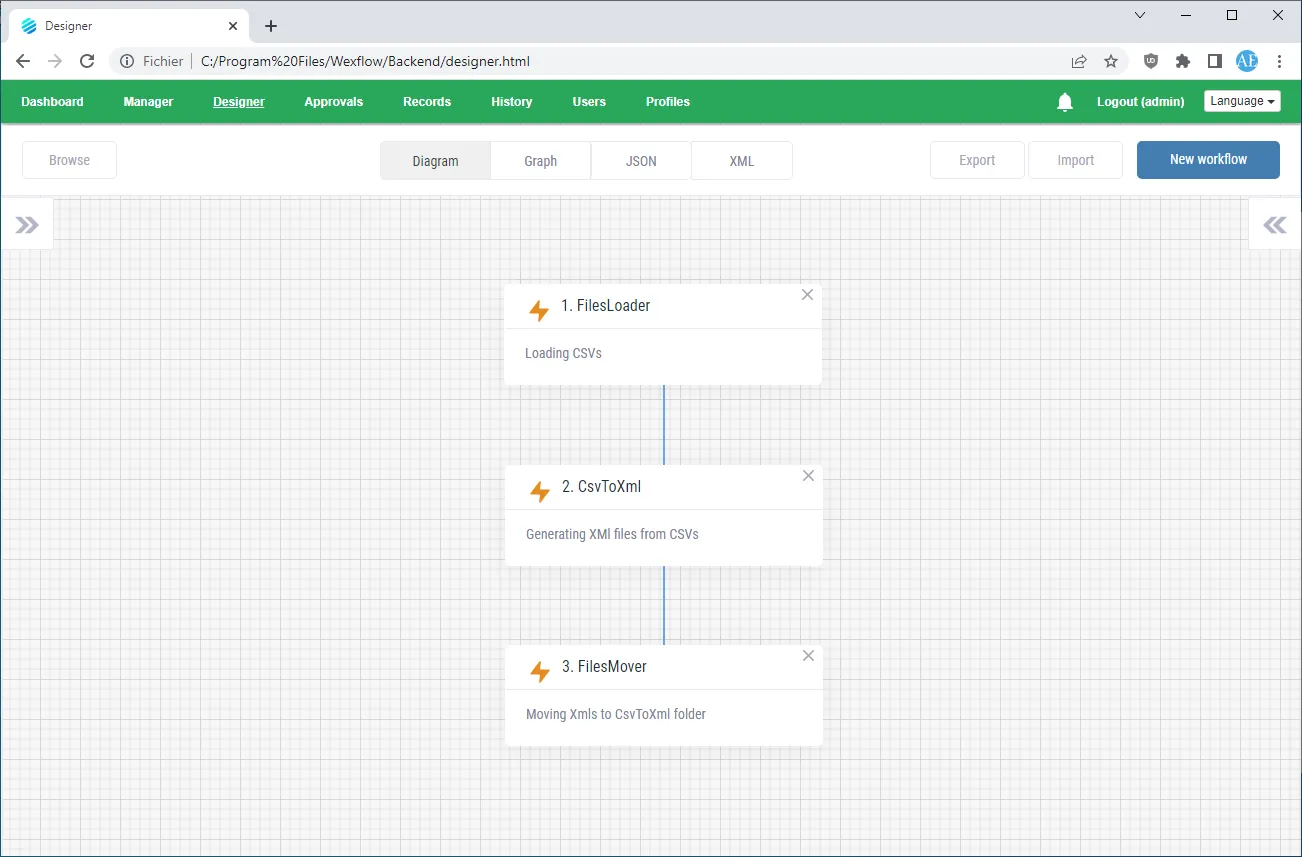
- Overview: Wexflow is an open-source workflow engine designed for automating and scheduling technical workflows and back-office batch processes.
- Key Features:
- Visual Workflow Designer: Provides a drag-and-drop experience for configuring workflow logic without extensive coding.
- Scripting Support: Offers capabilities for creating custom logic via scripts in languages such as PowerShell, Bash, and Python.
- Multi-Platform Support: Includes a web interface for management and a native Android app.
- Ideal Use Cases & Target Persona: Its primary use cases are back-office and system workflows, including file sharing, reporting, ETL pipelines, ITOps, and DevOps tasks. The source text notes that it may be a less mature offering compared to other tools on this list.
- Licensing and Deployment: Wexflow is an open-source workflow engine licensed under the MIT License.
Comparative Summary and Decision Framework
To help IT decision-makers select the best-fit tool at a glance, the following table summarizes the key attributes of each platform discussed in this analysis. It consolidates the primary user, core use case, interface style, and licensing model for a direct comparison.
| Tool | Primary User Persona | Core Use Case | Primary Interface | Licensing Model |
| n8n | Technical User, Developer | App Integration, AI Workflows | Visual Low-Code | Fair-Code |
| Activepieces | Non-Technical User | App Integration | Visual No-Code | MIT |
| Automatisch | Non-Technical User | App Integration | Visual No-Code | Not specified in source |
| Node-RED | Hobbyist, Industrial Operator | IoT, Event-Driven Automation | Visual Low-Code | Apache 2.0 |
| Apache Airflow | Data Engineer, Developer | Data Pipelines, ETL | Code-First (Python) | Apache 2.0 |
| Prefect | Data Engineer, ML/AI Team | Data Pipelines, ML Workflows | Code-First (Python) | Apache 2.0 |
| Windmill | Developer, Technical Team | Internal Tools, Script Orchestration | Code-First with Visual Flow Builder | AGPLv3 |
| Kubeflow Pipelines | Data Scientist, MLOps Team | Machine Learning Pipelines | Code-First (Python) | Apache 2.0 |
| Budibase | IT Team | Internal Tools, Approval Apps | Visual Low-Code | GPLv3 |
| Camunda | Developer, Architect, Business | Business Process Management | Visual (BPMN) & Code | Commercial (Free Non-Prod) |
| Bonita | Business Analyst, Developer | Business Process Management | Visual (BPMN) & Code | GPLv2 |
| Imixs-Workflow | Developer, Business Analyst | Human-Centric BPM | Visual (BPMN) & Code | EPL 2.0 / GPLv2+ |
| StackStorm | DevOps, SRE, Security Team | IT/Security Automation | Code-First (YAML) | Apache 2.0 |
| Wexflow | IT Team | Back-Office System Tasks | Visual Low-Code | MIT |
To use this framework effectively, align your team’s skills, primary automation needs, and security requirements with the tool characteristics outlined above. For instance, a data engineering team focused on ETL would gravitate toward Airflow or Prefect, while a marketing team needing to connect cloud apps would be better served by Activepieces or n8n.
Conclusion
Open-source workflow tools offer strong choices. However, this analysis clarifies one fact: the best platform fits your specific context. No single platform is “best.” The right tool must match your team’s skills. It must also suit your company’s security needs. Finally, it must handle the processes you aim to automate.
The key trade-offs exist between simplicity and control. For instance, no-code visual builders are simple. Conversely, pro-code, developer-centric platforms offer ultimate flexibility. A marketing team achieves rapid results with a tool like Activepieces. But, a data science team demands programmatic control. They need platforms like Prefect or Kubeflow Pipelines to manage complex ML models. Moreover, structured processes with human approvals (BPM) differ greatly. These contrast with the real-time, event-driven needs of IT operations.
Adopting an open-source automation plan yields more than just efficiency. Furthermore, organizations gain full control over their data. They foster innovation by empowering teams with the correct tools. Consequently, they build a resilient operational backbone. This structure adapts easily to the evolving technology landscape.
FAQs
Which is the best workflow automation tool?
The best tool depends on your team’s exact needs. n8n excels at extendable automation. Its flexible node-based design drives this capability. Apache Airflow is the industry leader for complicated data workflows.
Conversely, Activepieces offers no-code, AI-first automation. For enterprise-level orchestration, choose Camunda. This platform uses global visual standards. Finally, Windmill stands out for developers. It is the fastest self-hostable engine, prioritizing high performance.
What are the 4 primary types of automation applications used to streamline business processes?
Businesses streamline processes using four core automation types.
1. Automated Remediation: This acts as a first-tier support. It instantly troubleshoots and fixes known issues.
2. Continuous Deployment: Furthermore, it manages complex deployment pipelines. This goes beyond typical CI/CD tools.
3. ChatOps Optimization: It merges automation with collaboration tools. Consequently, this improves team workflows.
4. Automated Security Response: Crucially, it provides consistent, rapid reactions to security threats.
Can Chatgpt create workflows?
ChatGPT cannot run workflows alone. Instead, it serves as a component within existing automation tools.
Notably, many platforms now feature native “AI Copilots.” These tools use similar generative tech. For example, Camunda Copilot instantly creates BPMN diagrams from text. ProcessMaker also uses generative AI. It quickly builds entire workflows and scripts. Furthermore, n8n offers an AI Workflow Builder. This feature converts prompts into working automation.
Consequently, these integrations offer a ChatGPT-like interface. They streamline designing and troubleshooting complex workflows efficiently.
Why handle workflows with open-source tools?
Open-source tools ensure flexibility and vast customization. Teams easily tailor code to match specific business needs. Also, they offer massive cost savings. You eliminate expensive licensing fees.
Furthermore, security presents a core benefit. Open code permits comprehensive auditing. Therefore, self-hosting keeps critical data in your local environment.
Crucially, these platforms prevent vendor lock-in. This mitigates procurement risks, such as sudden price hikes. Finally, open-source scales well. Moreover, continuous community innovation drives platform improvements.
How does open source workflow management software differ from proprietary software?
The key difference is code access. Open-source software provides the code for users to modify features and conduct security reviews. Conversely, proprietary software restricts code access. It typically charges license fees.
Furthermore, open-source tools support self-hosting. This option keeps sensitive data local and prevents vendor dependence. Proprietary platforms usually rely on a vendor’s cloud. They offer less flexibility for unique needs. To summarize, open source champions openness and freedom. However, proprietary software remains a closed, paid system.