Augmented reality (AR) is a technology that superimposes digital information, such as images, sounds, or text, onto the real world. Unlike virtual reality (VR), which creates a fully immersive and simulated environment, AR enhances the existing reality with additional layers of information. AR has many applications in various fields and industries, such as entertainment, gaming, tourism, healthcare, and manufacturing.
One of the most promising and exciting applications of AR is education. AR can transform the way students learn and interact with the world, by providing them with immersive and engaging experiences that enhance their understanding and retention of knowledge. AR can also increase students’ motivation, curiosity, and collaboration, by making learning more fun and interactive.
In this blog post, we will explore how AR can be used for education, what are the benefits and challenges of using Augmented reality for education, and how to assess and improve the impact of AR for education on students’ learning.
Table of Contents
What is Augmented Reality for Education?
Augmented reality for education is the use of AR technology to create educational content and experiences that augment the real world with relevant and contextual information.
Augmented reality for education can be used to provide students with visual, auditory, or haptic feedback that helps them learn new concepts, skills, or facts. AR for education can also be used to create interactive simulations, games, or scenarios that allow students to explore and experiment with different phenomena, situations, or problems.
There are different types of AR for education, depending on how the digital information is triggered and displayed. Some of the common types are:
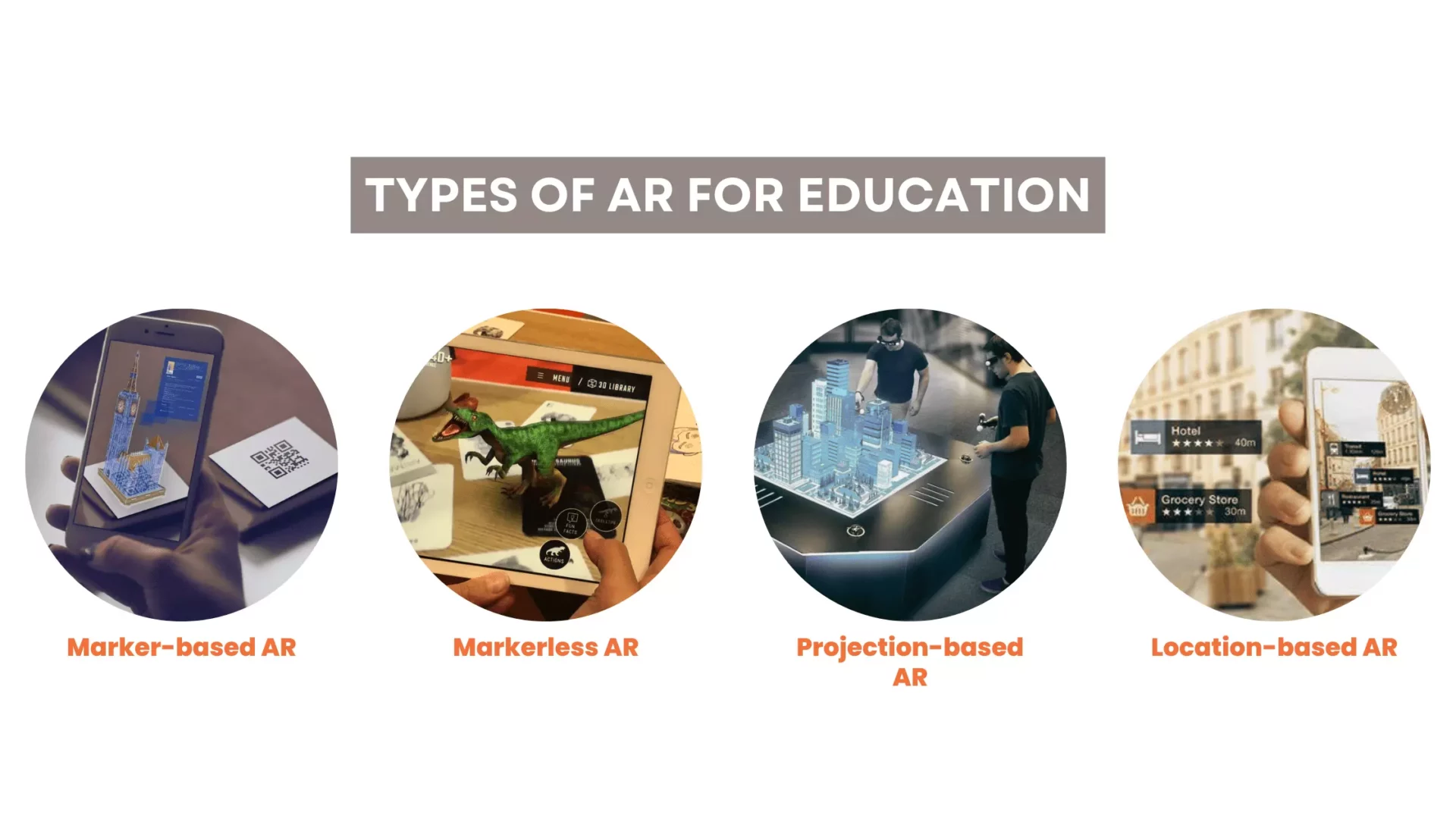
- Marker-based AR: This type of AR uses a physical object, such as a QR code, a barcode, or an image, as a marker that triggers the digital information when scanned by a camera. For example, a student can scan QR code (the marker) on a textbook page to see a 3D model of an animal or a plant. dditionally, students can use a dynamic QR code generator tool like QR now to access interactive content linked to different learning modules.
- Markerless AR: This type of AR does not require any specific marker to trigger the digital information. Instead, it uses sensors, such as GPS, accelerometer, or gyroscope, to detect the location and orientation of the device and display the digital information accordingly. For example, a student can use a smartphone to see historical landmarks or monuments overlaid on the real world.
- Projection-based AR: This type of AR uses a projector to display digital information on a surface or an object. For example, a teacher can use a projector to show an interactive map or a diagram on a wall or a table.
- Location-based AR: This type of AR uses geolocation data to display digital information based on the user’s location. For example, a student can use an app to see information about nearby places of interest or cultural events.
Each type of Augmented reality for education has its own advantages and challenges. For instance, marker-based AR is easy to use and control, but it requires printed markers that can be lost or damaged. Markerless AR is more flexible and versatile, but it requires more processing power and accuracy from the device.
Projection-based AR is more immersive and collaborative, but it requires a suitable surface and lighting condition. Location-based AR is more contextual and personalized, but it requires an internet connection and GPS signal.
There are many tools and platforms that can be used to create and access an Augmented reality for education content. Some of the popular ones are:
- Google Expeditions: This is an app that allows teachers and students to go on virtual trips to various places around the world using VR or AR. The app provides over 900 VR tours and over 100 AR tours that cover topics such as history, geography, science, art, and culture.
- Microsoft HoloLens: This is a mixed-reality headset that allows users to see holograms that blend with the real world. The headset can be used for various educational purposes, such as visualizing complex concepts, creating immersive simulations, or collaborating with remote peers.
How to Use Augmented Reality for Education on Different Subjects and Levels?

Augmented reality for education can be used in different subjects and levels to enhance the learning experience and outcomes of students. Here are some tips and best practices for using AR for education in different subjects and levels:
- Choose the right type of AR for your learning objectives: Depending on what you want your students to learn and how you want them to learn it, you should choose the type of AR that best suits your learning objectives. For example, if you want your students to learn about anatomy, you might use marker-based AR to show them 3D models of organs or systems. If you want your students to learn about geography, you might use location-based AR to show them information about different places or regions.
- Provide guidance and feedback: AR for education can be a powerful tool for engaging students, but it can also be overwhelming or distracting if not used properly. Therefore, you should provide your students with clear instructions, expectations, and feedback when using AR for education. For example, you should explain to your students how to use the AR device or app, what they should focus on, and what they should do after the AR experience. You should also monitor their progress and performance, and provide them with constructive feedback and support.
- Integrate AR with other learning activities: AR for education should not be used in isolation, but rather as a complement to other learning activities. For example, you should use AR to introduce, reinforce, or extend the concepts or skills that you teach in your lessons. You should also use AR to create connections between the real world and the curriculum and to encourage students to apply their learning to different contexts and situations.
- Encourage collaboration and reflection: AR for education can be a great way to foster collaboration and reflection among students. For example, you can use AR to create group projects or assignments that require students to work together, share their ideas, and solve problems. You can also use AR to prompt students to reflect on their learning process and outcomes, and to discuss their thoughts and feelings with their peers or teachers.
There are many examples of how Augmented reality for education can be used in various disciplines, such as science, math, history, art, and language. Here are some of them:w
- Science: AR can be used to visualize abstract or complex concepts, such as atoms, molecules, cells, or forces. AR can also be used to create realistic simulations of natural phenomena, such as volcanoes, earthquakes, or weather. For example, a student can use an app to see the structure and function of a DNA molecule or to experience the effects of a tornado.
- Math: AR can be used to illustrate mathematical concepts, such as shapes, numbers, or functions. AR can also be used to create interactive games or puzzles that challenge students’ logical thinking and problem-solving skills. For example, a student can use an app to see how different shapes fit together or to solve a Sudoku puzzle using AR markers.
- History: AR can be used to bring historical events or figures to life, such as wars, revolutions, or leaders. AR can also be used to create immersive tours or stories that transport students to different times and places. For example, a student can use an app to see how the Eiffel Tower was built or to hear a speech by Martin Luther King Jr.
- Art: AR can be used to enhance artistic expression and appreciation, such as painting, drawing, or photography. AR can also be used to create virtual galleries or museums that showcase different artworks or styles. For example, a student can use an app to add digital effects or filters to their photos or to explore the works of Vincent van Gogh.
- Language: AR can be used to improve language skills, such as reading, writing, speaking, or listening. AR can also be used to create engaging scenarios or dialogues that expose students to different cultures or contexts. For example, a student can use an app to scan a text and see its translation, or to practice a conversation with a native speaker.
There are many resources and references for finding and creating AR for educational content. Some of them are:
- Augmented Classroom: This tool from CleverBooks is browser-based; it lets students learn about plants and animals and explore the world.
- ARKit: This is a framework that allows developers to create AR apps for iOS devices using Swift or Objective-C.
- ARCore: This is a platform that allows developers to create AR apps for Android devices using Java or C++.
- Unity: This is a game engine that allows developers to create 3D games and applications for various platforms, including AR.
How to Assess the Impact of Augmented Reality for Education on Students’ Learning?

Assessing the impact of AR education on students’ learning is important for understanding its effectiveness and improving its quality. There are different methods and tools for measuring the impact of AR on education on students’ learning, such as surveys, quizzes, interviews, observations, and analytics.
Surveys are questionnaires that ask students about their opinions, attitudes, or perceptions regarding the Augmented reality for education experience. Surveys can be used to measure students’ satisfaction, engagement, or motivation when using AR for education.
Quizzes are tests that ask students about their knowledge, understanding, or skills regarding the content or topic covered by the AR for education experience. Quizzes can be used to measure students’ learning outcomes, achievement, or progress when using AR for education.
Interviews are conversations that ask students about their thoughts, feelings, or experiences regarding the AR for education experience. Interviews can be used to collect qualitative data, insights, or feedback.
Observations are records that capture students’ behaviors, actions, or interactions regarding the AR for education experience. Observations can be used to measure students’ engagement, collaboration, or problem-solving skills when using AR for education.
Analytics are data that track students’ usage, performance, or outcomes regarding the AR for education experience. Analytics can be used to measure students’ progress, achievement, or improvement when using AR for education.
There are many studies and research that have investigated the impact of AR for education on students’ learning. Here are some of the results and findings:
- AR can improve students’ learning outcomes: A meta-analysis of 28 studies found that AR had a positive effect on students’ learning outcomes, such as knowledge acquisition, retention, and transfer. Another study found that AR improved students’ conceptual understanding and spatial ability in geometry.
- AR can increase students’ motivation and engagement: A study found that AR increased students’ motivation and engagement in learning science. Another study found that AR increased students’ interest and curiosity in learning history.
- AR can foster collaboration and communication: A study found that AR fostered collaboration and communication among students in learning chemistry. Another study found that AR fostered social interaction and peer feedback among students in learning English.
There are some recommendations and suggestions for improving the impact of Augmented reality on education on students’ learning. Some of them are:
- Align AR with the curriculum and learning objectives: AR should be aligned with the curriculum and learning objectives of the subject and level. AR should not be used as a substitute or a distraction, but rather as a support or an enhancement for the learning process and outcomes.
- Design AR with pedagogical principles and practices: AR should be designed with pedagogical principles and practices, such as scaffolding, feedback, differentiation, and assessment. AR should not be used as a gimmick or a novelty, but rather as a tool or a resource for effective teaching and learning.
- Evaluate AR with appropriate methods and tools: AR should be evaluated with appropriate methods and tools, such as surveys, quizzes, interviews, observations, and analytics. AR should not be used without evidence or evaluation, but rather with data and feedback for continuous improvement and quality assurance.
How to Overcome the Barriers and Challenges of Implementing Augmented Reality for Education?

Implementing Augmented reality for education can face various barriers and challenges, such as technical issues, cost, accessibility, privacy, and ethical concerns. Here are some solutions and strategies for overcoming the barriers and challenges of implementing AR for education:
- Choose the right devices, platforms, and content: Depending on your budget, resources, and needs, you should choose the devices, platforms, and content that best suit your AR for education goals. For example, you should consider the compatibility, functionality, and usability of the devices, platforms, and content that you use for AR for education.
- Provide training and support: You should provide training and support to your teachers, students, and other stakeholders who are involved in AR for education. For example, you should train your teachers on how to use AR for education effectively and efficiently in their lessons. You should also support your students on how to use AR for education safely and responsibly in their learning.
- Ensure security and safety: You should ensure security and safety when using AR for education. For example, you should protect the personal data and privacy of your teachers and students who use AR for education. You should also prevent any physical or psychological harm that might occur from using AR for education.
- Involve stakeholders: You should involve stakeholders in the planning and implementation of AR for education. For example, you should consult your administrators, parents, or community members who might have an interest or influence on AR for education. You should also collaborate with other educators, researchers, or developers who might have expertise or experience in AR for education.
There are many examples and stories of successful implementation of AR for education in different settings and contexts. Here are some of them:
- The Smithsonian Institution: The Smithsonian Institution is a group of museums and research centers that use AR to enhance their exhibits and collections. The Smithsonian Institution uses an app called Skin & Bones to show visitors what animals look like under their skin. The Smithsonian Institution also uses an app called Beyond Spacesuit to show visitors how astronauts live and work in space.
- The British Museum: The British Museum is a museum of human history and culture that uses AR to enrich its artifacts and galleries. The British Museum uses an app called Museum of the World to show visitors how different objects are connected across time and space. The British Museum also uses an app called Ancient Egypt to show visitors how ancient Egyptians lived and died.
- The University of Rochester: The University of Rochester is a research university that uses AR to improve its teaching and learning. The University of Rochester uses an app called ARChemistry to teach students about chemical reactions and structures. The University of Rochester also uses an app called ARPhysics to teach students about physics concepts and phenomena.
There are some tips and advice for planning and managing the implementation of Augmented reality for education. Some of them are:
- Start small and scale up: You should start small and scale up when implementing AR for education. For example, you should pilot AR for education with a few teachers, students, or classes before expanding it to the whole school or district. You should also evaluate AR for education with a few methods, tools, or indicators before using more comprehensive or complex ones.
- Adapt and customize: You should adapt and customize AR for education to your context and needs. For example, you should modify AR for education to fit your curriculum, learning objectives, and pedagogical approaches. You should also personalize AR for education to suit your students’ preferences, abilities, and interests.
- Innovate and experiment: You should innovate and experiment with AR for education to explore its possibilities and potential. For example, you should create your own AR for education content, experiences, or activities that are relevant and meaningful to your subject or topic. You should also try out different types of AR for education that are suitable and appropriate for your level or mode.
Conclusion
Augmented reality for education is a powerful tool for engaging students in learning. AR for education can improve students’ learning outcomes, increase their motivation and engagement, and foster their collaboration and communication. AR for education can also be used in different subjects and levels, such as science, math, history, art, and language.
However, AR for education also faces some barriers and challenges, such as technical issues, cost, accessibility, privacy, and ethical concerns. Therefore, AR for education should be aligned with the curriculum and learning objectives, designed with pedagogical principles and practices, evaluated with appropriate methods and tools, and implemented with solutions and strategies that overcome barriers and challenges.
If you are interested in using AR for education in your classroom or school, you might want to check out HyScaler, a platform that helps you create and access high-quality AR solutions.
We hope you enjoyed reading this blog post about Augmented reality for education. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to leave them below.